前言
四则运算经常提到, 之前我们可能用中缀转后缀的方法。再学习了自顶向下的文法规则之后,文法规则自顶向下分析
现在可以试试将文法规则写出来。(优先级和结合性体现在文法规则中了)
exp -> term {
addop term}
addop -> + | -
term -> factor {
mulop factor}
mulop -> * | /
factor -> (exp) | n
文法规则实现四则运算
//
// Created by Andy Dennis on 2020/12/9.
// 文法规则:
/*exp -> term {addop term}
* addop -> + | -
* term -> factor {mulop factor}
* mulop -> * | /
* factor -> (exp) | n
* */
# include <iostream>
# include <cmath>
using namespace std;
// 全局变量token
char token;
// 待处理的字符串
string str;
// 字符串读取到的地方
int strIndex = 0;
// 存放数字
double num;
// 用到的函数, 先提前声明
double string2float(string s);
void getToken();
void match(char expectToken, int errorId);
void Error(int errorId, char expectToken);
double exp();
double term();
double factor();
int main() {
string examples[] = {
"3.2-5+8", "3+8/2-6", "(5*(9-2)+1)/9",
"3+8-*7"}; // 第四个故意出错
for (int i = 0; i < examples->length(); i++) {
str = examples[i];
strIndex = 0;
cout << "task " << i + 1 << ": " << str << endl;
getToken();
cout << "result: " << exp() << endl;
}
// 测试一下getToken函数
// while (token != '$') {
// getToken();
// if (token == '0')
// cout << num << endl;
// else
// cout << token << endl;
// }
}
double exp() {
int errorId = 0;
double temp = 0;
temp = term();
while ((token == '+') || (token == '-')) {
if (token == '+') {
match('+', errorId);
temp = temp + term();
} else if (token == '-') {
match('-', errorId);
temp = temp - term();
}
}
return temp;
}
double term() {
int errorId = 1;
double temp = 0;
temp = factor();
while ((token == '*') || (token == '/')) {
if (token == '*') {
match('*', errorId);
temp = temp * factor();
} else if (token == '/') {
match('/', errorId);
temp = temp / factor();
}
}
return temp;
}
double factor() {
int errorId = 2;
double temp = 0;
if (token == '(') {
match('(', errorId);
temp = exp();
match(')', errorId);
} else if (token == '0') {
// 0 代表这是个数字,真正的值存储在全局变量num
match('0', errorId);
temp = num;
} else {
cout << "---> col " << strIndex << ",at the character " << str[strIndex - 1] << endl;
cout << "error at factor -> (exp) | n, expected token is ( or num, but not found!" << endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); // 非正常退出
}
return temp;
}
// 字符串转数字
double string2float(string s) {
double n = 0;
bool isXiaoShu = false; // 判断当前的数字是不是小数部分
int xiaoShuLength = 0; // 记录小数部分的长度
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9') {
n = n * 10 + float(s[i] - '0');
if (isXiaoShu)
xiaoShuLength++;
} else if (s[i] == '.') {
isXiaoShu = true; //开始进入小数部分
}
}
return n * 1.0 / pow(10, xiaoShuLength);
}
void getToken() {
if (strIndex < str.length()) {
if (str[strIndex] >= '0' && str[strIndex] <= '9') {
string tempNumStr;
while (strIndex < str.length() && (str[strIndex] >= '0' && str[strIndex] <= '9' || str[strIndex] == '.')) {
tempNumStr += str[strIndex];
strIndex++;
}
num = string2float(tempNumStr);
token = '0'; // token == 0 代表这个token的内容是 num
} else {
// + - * / ()
token = str[strIndex];
strIndex++;
}
} else {
token = '$'; // 结束符
}
}
void Error(int errorId, char expectToken) {
string grammar[3] = {
"exp -> term {addop term}", "term -> factor {mulop factor}",
"factor -> (exp) | n"};
cout << "---> col " << strIndex << ",at the character " << str[strIndex - 1] << endl;
cout << "error at " << grammar[errorId] << ", expected token is "
<< expectToken << " but not found!" << endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); // 表示当前操作系统下未能成功退出的终止代码
}
void match(char expectToken, int errorId) {
if (token == expectToken) {
getToken();
} else {
Error(errorId, expectToken); // Error函数
}
};
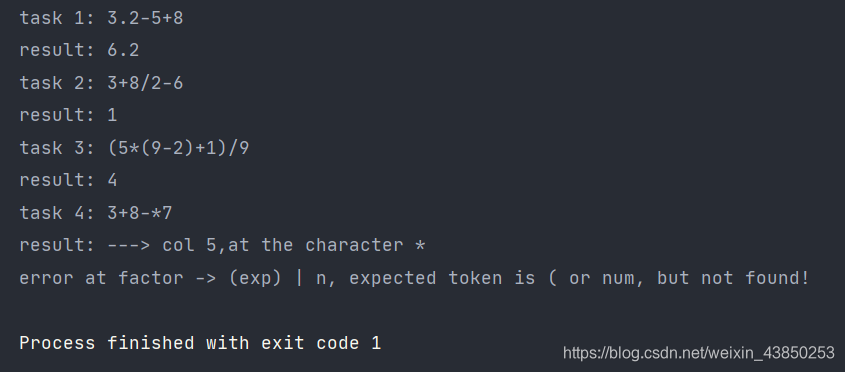
最后一个例子我故意让它出错看看我们的程序错误提示能力怎么样。
结语
后续有想法再补充。
大伙也可以看看我顺手写完这篇后写的另一篇博客: 自顶向下生成语法树和汇编代码。