异常处理是一种处理运行时错误的技术,而 异步编程 允许我们在处理资源密集型的业务逻辑时不需要在 Main 方法或者在 执行线程 中被阻塞,值得注意的是,异步方法和同步方法的异常处理机制是不一样的,本篇我们就来讨论下如何在异步方法中处理异常。
异步方法 VS 同步方法 的异常处理
在同步代码中抛出异常,它会一直以冒泡的方式往上抛,直到遇到可以处理这个异常的 catch 块为止,可以想象,异步方法中的异常抛出肯定要比这个复杂。
大家都知道 异步方法 可以有三种返回类型,如:void, Task, Task<TResult>,当异常方法的返回值是 Task ,Task<TResult> 的方法中抛出异常的话,这个异常对象会被塞到 AggregateException 对象中,然后包裹在 Task 中进行返回,有些朋友可能要问,如果异步方法中抛出了几个异常怎么办?其实也是一样的道理,这些异常对象都会被塞到 AggregateException 中通过 Task 去返回。
最后,如果异常出现在返回值为 void 的异步方法中,异常是在调用这个异步方法的 SynchronizationContext 同步上下文上触发。
返回 void 异步方法中的异常
下面的程序展示了返回 void 的异步方法中抛出了异常。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ThisIsATestMethod();
Console.ReadLine();
}
public static void ThisIsATestMethod()
{
try
{
AsyncMethodReturningVoid();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
private static async void AsyncMethodReturningVoid()
{
await Task.Delay(1000);
throw new Exception("This is an error message...");
}
}
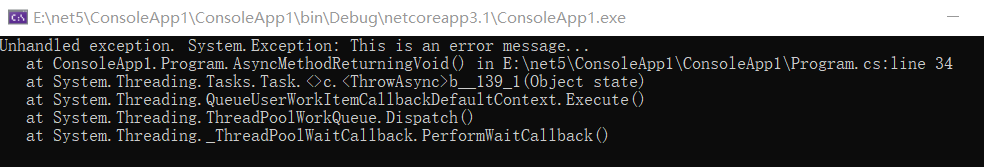
从图中可以看到,AsyncMethodReturningVoid 方法抛出的异常会被包裹此方法的 try catch 捕捉到。
返回 Task 的异步方法异常
当异常从返回值为 Task 的异步方法中抛出,这个异常对象会被包裹在 Task 中并且返回给方法调用方,当你用 await 等待此方法时,只会得到一组异常中的第一个被触发的异常,如果有点懵的话,如下代码所示:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ExceptionInAsyncCodeDemo();
Console.ReadLine();
}
public static async Task ExceptionInAsyncCodeDemo()
{
try
{
var task1 = Task.Run(() => throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("IndexOutOfRangeException is thrown."));
var task2 = Task.Run(() => throw new ArithmeticException("ArithmeticException is thrown."));
await Task.WhenAll(task1, task2);
}
catch (AggregateException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
}
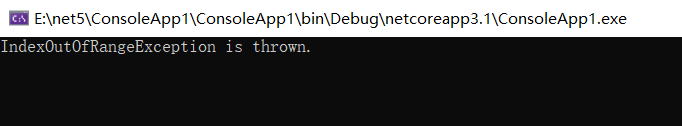
从上面代码中可以看出 task1 和 task2 都会抛出异常,但在 catch 块中只捕获了 task1 中的异常,这就说明返回值为 Task 的多个异常的方法中,调用方只能截获第一次发生异常的异常对象。
使用 Exceptions 属性 获取所有异常
要想获取已抛出的所有异常,可以利用 Task.Exceptions 属性来获取,下面的代码清单展示了如何在返回 Task 的方法中获取所有的异常信息。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ExceptionInAsyncCodeDemo();
Console.ReadLine();
}
public static async Task ExceptionInAsyncCodeDemo()
{
Task tasks = null;
try
{
var task1 = Task.Run(() => throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("IndexOutOfRangeException is thrown."));
var task2 = Task.Run(() => throw new ArithmeticException("ArithmeticException is thrown."));
tasks = Task.WhenAll(task1, task2);
await tasks;
}
catch
{
AggregateException aggregateException = tasks.Exception;
foreach (var e in aggregateException.InnerExceptions)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.GetType().ToString());
}
}
}
}
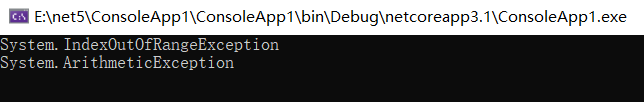
使用 AggregateException.Handle 处理所有异常
你可以利用 AggregateException.Handle 属性去处理一组异常中的某一个,同时忽略其他你不关心的异常,下面的代码片段展示了如何去实现。
class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
await ExceptionInAsyncCodeDemo();
Console.Read();
}
public static async Task ExceptionInAsyncCodeDemo()
{
Task tasks = null;
try
{
var task1 = Task.Run(() => throw new IndexOutOfRangeException("IndexOutOfRangeException is thrown."));
var task2 = Task.Run(() => throw new ArithmeticException("ArithmeticException is thrown."));
tasks = Task.WhenAll(task1, task2);
await tasks;
}
catch(AggregateException ex)
{
AggregateException aggregateException = tasks.Exception;
foreach (var e in aggregateException.InnerExceptions)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.GetType().ToString());
}
}
}
}
上面的代码片段表示:IndexOutOfRangeException 会被处理, InvalidOperationException 会被忽略。
最后想说的是,你可以利用 异步编程 来提高程序的扩展性和吞吐率,当你在使用异步方法时,请注意在异步方法中的异常处理语义和同步方法中的异常处理是不一样的。
译文链接:https://www.infoworld.com/article/3453659/how-to-handle-exceptions-in-asynchronous-code-in-c.html