stack:栈
后进先出。
成员函数:
empty() 堆栈为空则返回真
pop() 移除栈顶元素
push() 在栈顶增加元素
size() 返回栈中元素数目
top() 返回栈顶元素
代码展示:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<math.h>
#include<set>
#include<list>
#include<string>
#include<random>
#define maxn 50
using namespace std;
struct Example{
//无法定义排序
int x,y;
};
void init(stack<int>& s)
{
default_random_engine e;
uniform_int_distribution<unsigned> u(0, 9);//产生随机数,0到9的闭区间。
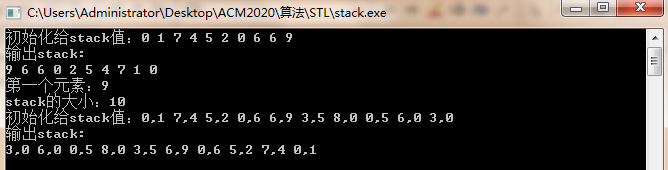
cout<<"初始化给stack值:";
for(int i=0; i<10; ++i)
{
int value=u(e);
cout<<value<<" ";
s.push(value);
}
cout<<endl;
}
void output(stack<int> s)
{
cout<<"输出stack:"<<endl;
while(!s.empty())
{
cout<<s.top()<<" ";
s.pop();
}
cout<<endl;
}
void init2( stack<Example>& s)
{
default_random_engine e;
uniform_int_distribution<unsigned> u(0, 9);//产生随机数,0到9的闭区间。
cout<<"初始化给stack值:";
for(int i=0; i<10; ++i)
{
int valueX=u(e);
int valueY=u(e);
cout<<valueX<<","<<valueY<<" ";
s.push({
valueX,valueY});
}
cout<<endl;
}
void output2(stack<Example> s)
{
cout<<"输出stack:"<<endl;
while(!s.empty())
{
cout<<s.top().x<<","<<s.top().y<<" ";
s.pop();
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
stack<int> s1;
init(s1);
output(s1);
cout<<"第一个元素:"<<s1.top()<<endl;
cout<<"stack的大小:"<<s1.size()<<endl;
stack<Example> s2;
init2(s2);
output2(s2);
return 0;
}
结果展示: