题目:用Huffman编码方法 实现对通信字符的编码和解码
效果图:
- 输入字符串原码来实现HuffmanTree
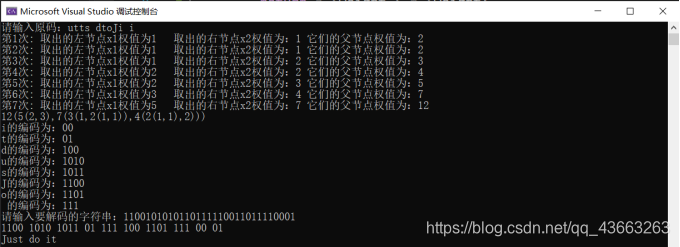
- 输入权值来实现HuffmanTree

- 可以同时输入数字、字符、空格、符号
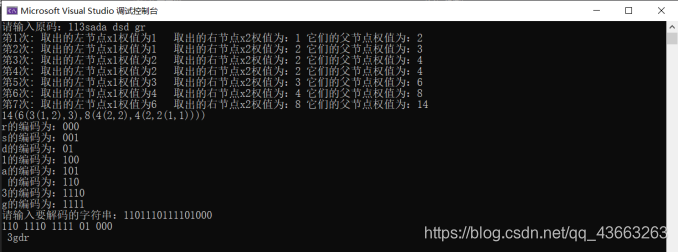
思路:
- ①:首先,要想构造出HuffmanTree,我们需要对输入的字符权值进行处理,这里由于主要的输入方式为输入字符串,通过相应的函数来计算每个字符的占比权值或者是直接输入每个字符的权值两种方式,相应的处理方式有略微的不同,但是大体是一致的,我定义了一个double类型的weight数组来存放字符的权值,然后再定义了一个code数组来存放每个不重复的字符,这样就能解决当用户输入字符串时,就算有大量重复字符也能计算出正确的权值,得到完整的权值后,我们就可以开始构建HuffmanTree。
- ②首先我们根据code数组的大小来建立相应数量的HuffmanTree结点,同时也要对这些结点进行初始化,然后我们建立一个HuffmanTree结点类型的优先队列q,根据结点的权值从小到大进行内部排序,这样就为我们下一步正式构建HuffmanTree做好准备,我们每次将q中最前面的两个元素拿出进行合并,这样实现了每次合并结点都是权值最小的结点进行合并,然后我们将两个结点合并后的结点再次放入q队列中,这样循环直到q中只剩一下一个元素根节点,这样一棵HuffmanTree就构造完毕了。
- ③HuffmanTree构造完毕后,我们可以利用递归函数来对HuffmanTree进行遍历,这样做的目的是可以将每个字符的编码进行打印,同时我们也可以模拟HuffmanTree树将每个结点的权值打印出来,这样可以更直观的看到HuffmanTree内部的构建情况。
- ④解码的过程只需要根据输入的密文对HuffmanTree树进行遍历,从根结点和密文的第一位,如果当前一位是‘0’则当前结点由根结点变成根结点的左节点,如果当前一位是‘1’则当前结点由根结点变成根结点的右节点,就这样直到根结点没有左右结点时,我们再将这个节点中保存的字符打印出来,就实现了一个字符的解码,要继续解码的话只需要当前结点更新回最原本的根结点即可。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include<windows.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
vector<char> code;
double weight[256];
int n;
typedef struct HuffTree
{
string code;
char symbol;
double weight;
HuffTree* lchild;
HuffTree* rchild;
} Node,*Nodeptr;
struct cmp
{
bool operator()(Nodeptr & a, Nodeptr & b)
{
return a->weight > b->weight;
}
};
priority_queue<Nodeptr, vector<Nodeptr>, cmp>q;
void codework()
{
cout << "----------欢迎使用霍夫曼树---------" << endl;
cout << "请选择输入字符串原码或者输入权值:" << endl;
cout << "1.输入原码 2.输入权值" << endl;
int x;
cin >> x;
char ch=getchar();
system("cls");
switch (x)
{
case 1:
{
string s;
cout << "请输入原码:";
getline(cin, s);
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
if (count(code.begin(), code.end(), s[i]) == 0)
code.push_back(s[i]);
weight[s[i]]++;
}
}
break;
case 2:
{
int num;
cout << "请输入要输入多少个字符:";
cin >> num;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
getchar();
char x;
double y;
cout << "请输入第" << i + 1 << "个字符" ;
x = getchar();
cout << "请输入第" << i + 1 << "个字符的权值";
cin >> y;
if (count(code.begin(), code.end(), x) == 0)
code.push_back(x);
weight[x]= y;
}
}
break;
}
}
void PrintHuffmanTree(Nodeptr root)
{
cout << root->weight;
if (root->lchild != NULL || root->rchild != NULL)
{
cout << "(";
PrintHuffmanTree(root->lchild);
cout << ",";
PrintHuffmanTree(root->rchild);
cout << ")";
}
}
Nodeptr CreatHuffmanTree()
{
codework();
n = code.size();
for (int i = 0; i <n; i++)
{
Nodeptr CurNode = new Node;
CurNode->symbol = code[i];
CurNode->weight = weight[code[i]];
CurNode->lchild = NULL;
CurNode->rchild = NULL;
q.push(CurNode);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; i++)
{
Nodeptr x1 = q.top();
q.pop();
Nodeptr x2 = q.top();
q.pop();
cout << "第" << i<< "次: 取出的左节点x1权值为" << (double)x1->weight << " 取出的右节点x2权值为:" << (double)x2->weight <<" 它们的父节点权值为:"<< (double)(x1->weight + x2->weight) << endl;
Nodeptr NewNode = new Node;
NewNode->symbol = 0;
NewNode->weight = x1->weight + x2->weight;
NewNode->lchild = x1;
NewNode->rchild = x2;
q.push(NewNode);
}
PrintHuffmanTree(q.top());
cout << endl;
return q.top();
}
void Coding(Nodeptr root,string code)
{
if (root->lchild == NULL && root->rchild == NULL)
{
root->code = code;
cout << root->symbol << "的编码为:" << root->code << endl;
return;
}
if (root->lchild != NULL)
{
code +='0';
Coding(root->lchild, code);
code = code.substr(0, code.size() - 1);
}
if (root->rchild != NULL)
{
code += '1';
Coding(root->rchild, code);
code = code.substr(0, code.size() - 1);
}
}
void Decodeing(Nodeptr root)
{
string s, Ciphertext, Plaintext;
cout << "请输入要解码的字符串:";
cin >> s;
Nodeptr temp = root;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
if (s[i] == '0')
{
if (temp->lchild != NULL)
{
Ciphertext += '0';
temp = temp->lchild;
}
}
else if (s[i] == '1')
{
Ciphertext += '1';
if (temp->rchild != NULL)
{
temp = temp->rchild;
}
}
if (temp->lchild == NULL && temp->rchild == NULL)
{
Ciphertext += ' ';
Plaintext += temp->symbol;
temp = root;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < Ciphertext.size(); i++)
cout << Ciphertext[i];
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < Plaintext.size(); i++)
cout << Plaintext[i];
cout << endl;
}
void DestroyHuffmanTree(Nodeptr root)
{
if (root->lchild != NULL)
DestroyHuffmanTree(root->lchild);
if (root->rchild != NULL)
DestroyHuffmanTree(root->rchild);
delete(root);
}
int main()
{
Node* root= CreatHuffmanTree();
Coding(root, "");
Decodeing(root);
DestroyHuffmanTree(root);
return 0;
}


