本文主要讲解List接口的三个实现类ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector的使用方法以及三者之间的区别。
注意:本文中代码使用的JDK版本为1.8.0_191
1. ArrayList使用
ArrayList是List接口最常用的实现类,内部通过数组来实现,因此它的优点是适合随机查找和遍历,缺点是不适合插入和删除。
ArrayList类的代码声明如下所示:
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
}
1.1 添加元素
使用ArrayList添加元素有以下两个重载:
boolean add(E e);
void add(int index, E element);
boolean add(E e);是将元素添加到集合的末尾,
void add(int index, E element);是将元素添加到指定的索引位置(索引是从0开始的)。
使用方法如下所示:
List<String> platformList = new ArrayList<>();
// 添加元素
platformList.add("博客园");
platformList.add("掘金");
platformList.add("微信公众号");
// 添加重复元素,会添加成功,因为List支持添加重复元素
platformList.add("博客园");
platformList.add("掘金");
platformList.add(3, "个人博客");
1.2 获取元素
获取ArrayList中指定索引处的元素的使用方法如下所示:
System.out.println("索引为3的元素为:" + platformList.get(3));
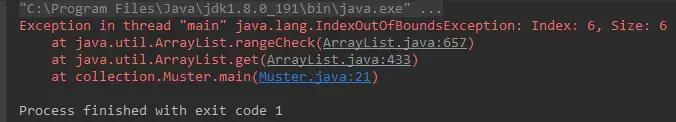
如果指定的索引超出了集合的最大索引,比如platformList.get(6)就会抛出异常java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException:
1.3 获取集合元素个数
获取ArrayList元素个数的使用方法如下所示:
System.out.println("platformList的元素个数为:" + platformList.size());
1.4 删除元素
使用ArrayList删除元素有以下两个重载:
E remove(int index);
boolean remove(Object o);
E remove(int index);是删除集合中指定索引处的元素,boolean remove(Object o);是删除集合中的指定元素。
使用方法如下所示:
// 指定索引删除重复的元素 "博客园" "掘金"
platformList.remove(4);
platformList.remove(4);
// 删除指定元素 "个人博客"
platformList.remove("个人博客");
1.5 修改元素
修改ArrayList中指定索引处的元素值的使用方法如下所示:
platformList.set(0, "博客园:https://www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/");
platformList.set(1, "掘金:https://juejin.im/user/5c7ce730f265da2dca388167");
platformList.set(2, "微信公众号:大型网站架构");
1.6 判断集合是否为空
判断ArrayList是否为空的使用方法如下所示:
System.out.println("isEmpty:" + platformList.isEmpty());
1.7 遍历元素(面试常问)
遍历ArrayList的元素主要有以下3种方式:
- 迭代器遍历
- for循环
- foreach循环
使用方法如下所示:
System.out.println("使用Iterator遍历:");
Iterator<String> platformIterator = platformList.iterator();
while (platformIterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(platformIterator.next());
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("使用for循环遍历:");
for (int i = 0; i < platformList.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(platformList.get(i));
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("使用foreach遍历:");
for (String platform : platformList) {
System.out.println(platform);
}
1.8 清空集合
清空ArrayList中所有元素的使用方法如下所示:
platformList.clear();
1.9 完整示例代码
上面讲解的几点,完整代码如下所示:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> platformList = new ArrayList<>();
// 添加元素
platformList.add("博客园");
platformList.add("掘金");
platformList.add("微信公众号");
// 添加重复元素,会添加成功,因为List支持添加重复元素
platformList.add("博客园");
platformList.add("掘金");
platformList.add(3, "个人博客");
System.out.println("索引为3的元素为:" + platformList.get(3));
System.out.println("platformList的元素个数为:" + platformList.size());
// 指定索引删除重复的元素 "博客园" "掘金"
platformList.remove(4);
platformList.remove(4);
// 删除指定元素 "个人博客"
platformList.remove("个人博客");
System.out.println("platformList的元素个数为:" + platformList.size());
platformList.set(0, "博客园:https://www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/");
platformList.set(1, "掘金:https://juejin.im/user/5c7ce730f265da2dca388167");
platformList.set(2, "微信公众号:Java大型网站架构
");
System.out.println("isEmpty:" + platformList.isEmpty());
System.out.println("使用Iterator遍历:");
Iterator<String> platformIterator = platformList.iterator();
while (platformIterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(platformIterator.next());
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("使用for循环遍历:");
for (int i = 0; i < platformList.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(platformList.get(i));
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("使用foreach遍历:");
for (String platform : platformList) {
System.out.println(platform);
}
System.out.println();
// 清空集合
platformList.clear();
System.out.println("isEmpty:" + platformList.isEmpty());
}
输出结果为:
> 索引为3的元素为:个人博客
>
> platformList的元素个数为:6
>
> platformList的元素个数为:3
>
> isEmpty:false
>
> 使用Iterator遍历:
>
> 博客园:www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/
>
> 掘金:juejin.im/user/5c7ce7…
>
> 微信公众号:大型网站架构
>
> 使用for循环遍历:
>
> 博客园:www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/
>
> 掘金:juejin.im/user/5c7ce7…
>
> 微信公众号:大型网站架构
>
> 使用foreach遍历:
>
> 博客园:www.cnblogs.com/zwwhnly/
>
> 掘金:juejin.im/user/5c7ce7…
>
> 微信公众号:大型网站架构
>
> isEmpty:true
2. LinkedList使用
LinkedList也是List接口的实现类,内部使用链表结构存储数据,因此它的优点是适合动态插入和删除元素,缺点是随机查找和遍历速度比较慢。
LinkedList类的代码声明如下所示:
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
}
LinkedList类的使用方法和ArrayList基本一样,只需修改下声明处的代码即可:
List<String> platformList = new LinkedList<>();
3. Vector使用
Vector也是List接口的实现类,内部也是通过数组来实现。
Vector类的代码声明如下所示:
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
}
与ArrayList不同的是,Vector是线程安全的,即某一时刻只有一个线程能够写Vector,避免多线程同时写而引起的不一致性。不过这也造成Vector的缺点:实现线程的同步需要额外的花费,因此它的访问速度会比ArrayList慢一些。
可以认为Vector是ArrayList在多线程环境下的实现版本。
所以Vector类的使用方法和ArrayList基本一样,只需修改下声明处的代码即可:
List<String> platformList = new Vector<>();
由于要支持线程同步,因此Vector类的很多方法都有synchronized关键字,如下所示:
public synchronized boolean isEmpty() {
return elementCount == 0;
}
public synchronized int size() {
return elementCount;
}
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}
4. ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector的区别(面试常问)
4.1 相同点
ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector都实现了List接口,所以使用方式很类似,通过上面的示例也能发现这一点。
4.2 不同点
但是ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector的内部实现方式不同,也就导致了它们之间是有区别的。
4.2.1 存储结构
ArrayList和Vector是基于数组实现的,LinkedList是基于双向链表实现的。
这也就导致ArrayList适合随机查找和遍历,而LinkedList适合动态插入和删除元素。
关于数组和双向链表,这里不做详解,后续会单独写篇文章总结。
4.2.2 线程安全性
ArrayList和LinkedList是线程不安全的,Vector是线程安全的。
Vector可以看做是ArrayList在多线程环境下的另一种实现方式,这也导致了Vector的效率没有ArraykList和LinkedList高。
如果要在并发环境下使用ArrayList或者LinkedList,可以调用Collections类的synchronizedList()方法:
Collections.synchronizedList(platformList);
4.2.3 扩容机制
ArrayList和Vector都是使用Object类型的数组来存储数据的,ArrayList的默认容量是0,Vector的默认容量是10。
空说无凭,我们先看下ArrayList的使用示例:
List<String> strArrayList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
strArrayList.add(String.valueOf(i));
}
执行的ArrayList构造函数的源码为:
transient Object[] elementData;
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {
};
再看下Vector的使用示例:
List<String> strVector = new Vector<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
strVector.add(String.valueOf(i));
}
执行的Vector构造函数的源码为:
protected Object[] elementData;
protected int capacityIncrement;
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
当向这两种类型中添加元素时,若容量不够,就会进行扩容,扩容的本质是产生一个新数组,将原数组的数据复制到新数组,再将新的元素添加到新数组中,使用的方法是Arrays.copyOf(),其中ArrayList扩容后的容量是之前的1.5倍,Vector默认情况下扩容后的容量是之前的2倍。
仍然使用上面的ArrayList的例子:
List<String> strArrayList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
strArrayList.add(String.valueOf(i));
}
在执行完List strArrayList = new ArrayList<>();后,此时strArrayList的容量是0,
然后在添加第1个元素时,strArrayList的容量会扩容为容量10,
当添加第11个元素时,strArrayList的容量会扩容为容量15,
当添加第16个元素时,strArrayList的容量会扩容为容量22,
如果还需要扩容,依次会扩容到33–>49。
看下ArrayList的源码,就明白为什么会这样扩容:
p
rivate static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
最核心的代码就是int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);,所以ArrayList扩容后的容量是之前的1.5倍。
再看下上面的Vector例子:
List<String> strVector = new Vector<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
strVector.add(String.valueOf(i));
}
在执行完List strVector = new Vector<>();后,此时strVector的容量是10,
当添加第11个元素时,strVector的容量会扩容为容量20,
当添加第21个元素时,strVector的容量会扩容为容量40,
如果还需要扩容,依次会扩容到80–>160。
看下Vector的源码,就明白为什么会这样扩容:
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
最核心的代码就是int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);,所以Vector默认情况下扩容后的容量是之前的2倍。
4.2.4 效率
ArrayList随机查找和遍历的效率会高一些,但动态插入和删除元素的效率会低一些。
LinkedList动态插入和删除元素的效率会高一些,但随机查找和遍历的效率会低一些。
如果需要在多线程下操作集合元素,建议使用Vector,否则的话,建议使用ArrayList。
彩蛋:
本文到这里就结束了,喜欢的朋友可以帮忙转发和关注一下,感谢支持!
平时收集了很多面试的资料 也做了整理
还赠送Spring源码分析、Dubbo、Redis、Netty、zookeeper、Spring cloud、分布式资料
有需要的可以看我的主页。
记得点个赞再走哦~