零、学习目标
1、掌握application.properties配置文件
2、掌握application.yaml配置文件
3、掌握使用@ConfigurationProperties注入属性
4、掌握使用@Value注入属性
一、全局配置文件概述
- 全局配置文件能够对一些默认配置值进行修改。
Spring Boot使用一个application.properties或者application.yaml的文件作为全局配置文件,该文件存放在src/main/resource目录或者类路径的/config,一般会选择resource目录。
二、Application.properties配置文件
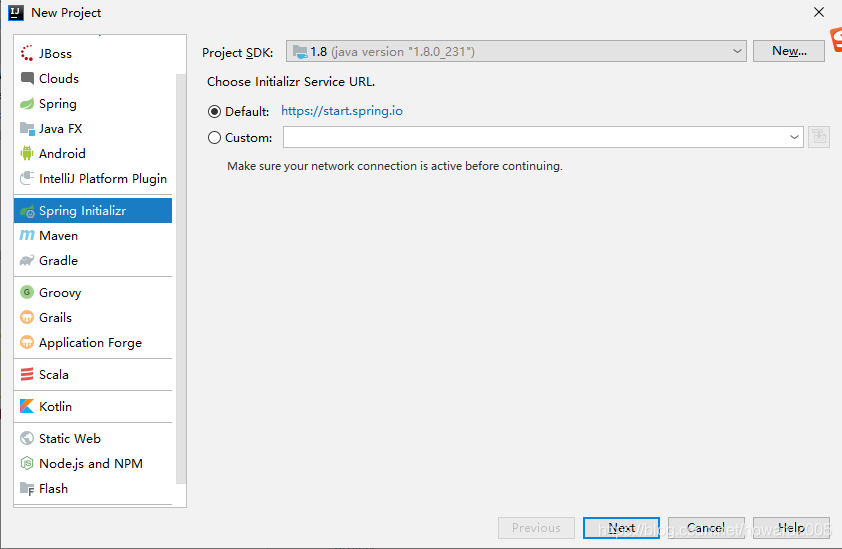
(一)创建Spring Boot的Web项目PropertiesDemo
- 利用Spring Initializr方式创建项目
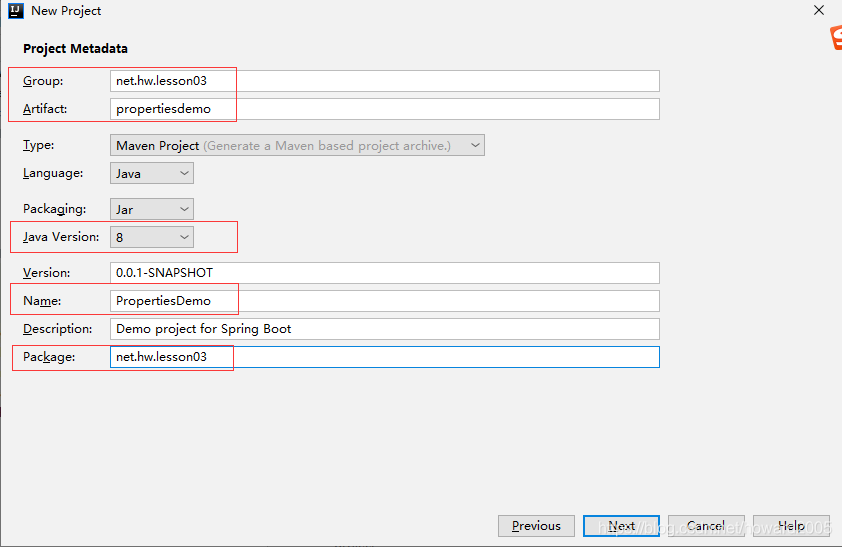
- 设置项目元数据
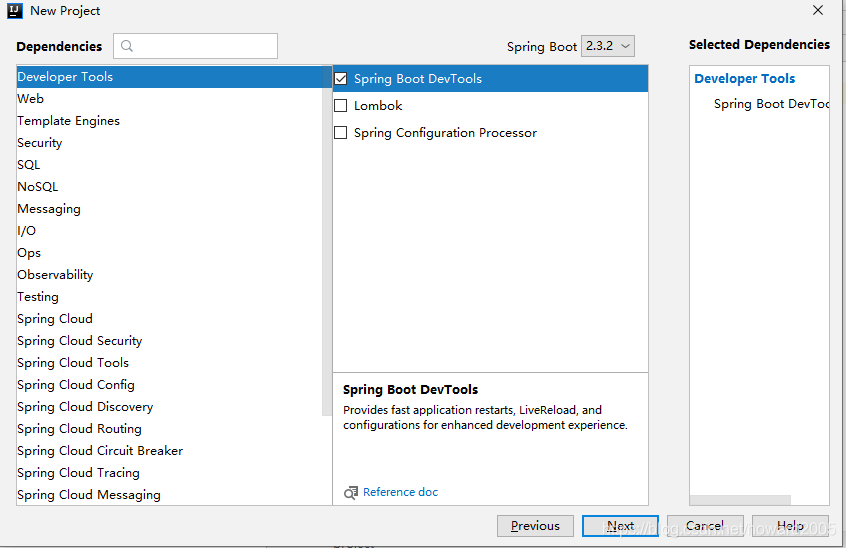
- 添加依赖
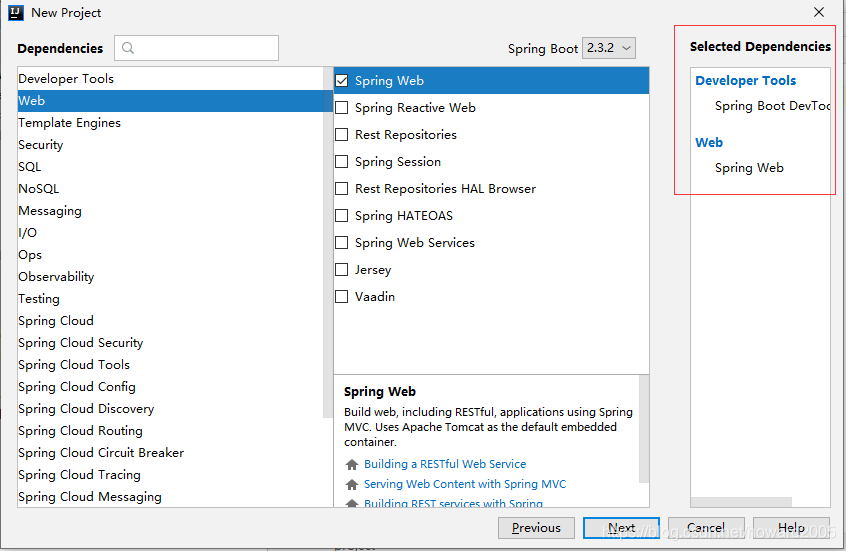
- 设置项目名称及保存位置
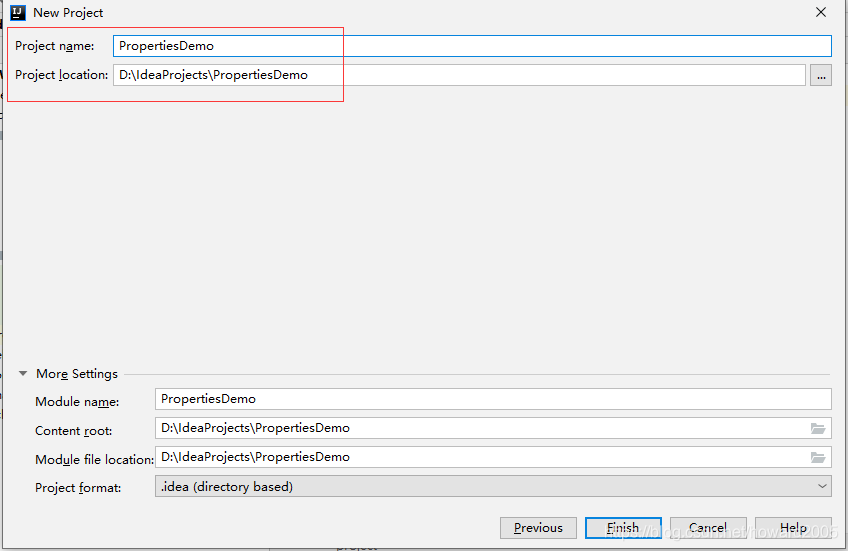
- 单击【Finish】按钮,完成项目初始化工作
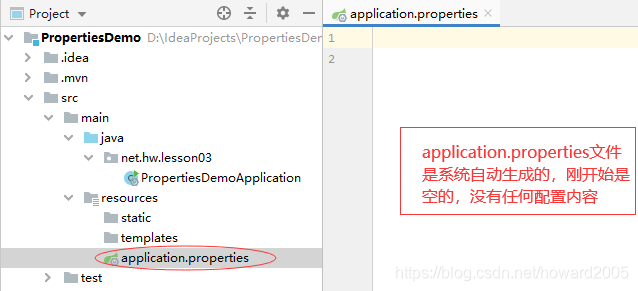
(二)在application.properties里添加相关配置
- 点开resource目录,查看应用程序属性配置文件
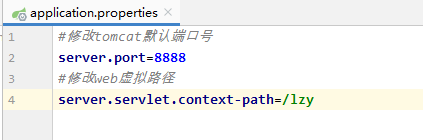
1、配置tomcat端口号和web虚拟路径
#修改tomcat默认端口号
server.port=8888
#修改web虚拟路径
server.servlet.context-path=/lzy
2、对象类型的配置与使用
(1)创建Pet类
package net.hw.lesson03;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
public class Pet {
private String type;
private String name;
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Pet{" +
"type='" + type + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
(2)创建Person类
package net.hw.lesson03;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class Person {
private int id;
private String name;
private List hobby;
private Map family;
private Pet pet;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public List getHobby() {
return hobby;
}
public void setHobby(List hobby) {
this.hobby = hobby;
}
public Map getFamily() {
return family;
}
public void setFamily(Map family) {
this.family = family;
}
public Pet getPet() {
return pet;
}
public void setPet(Pet pet) {
this.pet = pet;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", hobby=" + hobby +
", family=" + family +
", pet=" + pet +
'}';
}
}
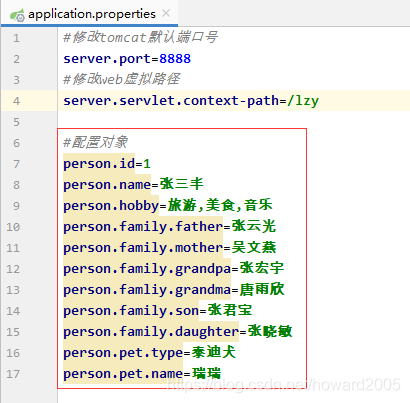
(3)在application.properties里配置对象
#配置对象
person.id=1
person.name=张三丰
person.hobby=旅游,美食,音乐
person.family.father=张云光
person.family.mother=吴文燕
person.family.grandpa=张宏宇
person.famliy.grandma=唐雨欣
person.family.son=张君宝
person.family.daughter=张晓敏
person.pet.type=泰迪犬
person.pet.name=瑞瑞
(4)给Person类添加注解
- 添加注解@Component,交给Spring去管理
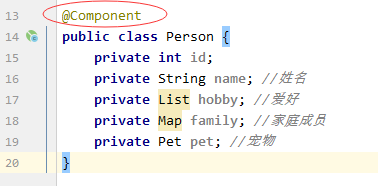
- 添加注解@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “person”)
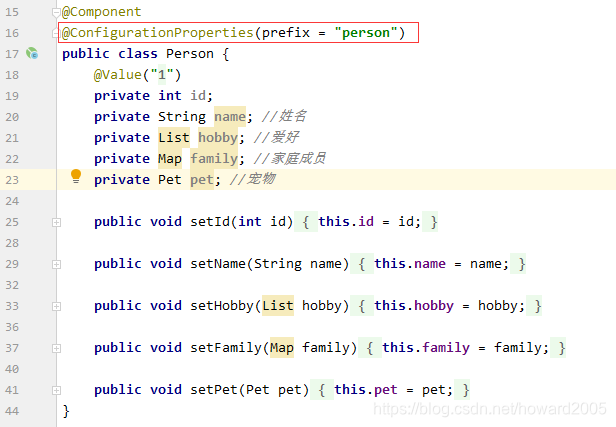
- 注意:采用
@ConfigurationProperties注解方式,必须要有set方法,才会自动为Person类所有属性注入相应的值,包括简单类型和复杂类型
(5)给Pet类添加注解
- 添加注解@Component,交给Spring去管理
- 添加注解@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “person.pet”) - 可以不用添加
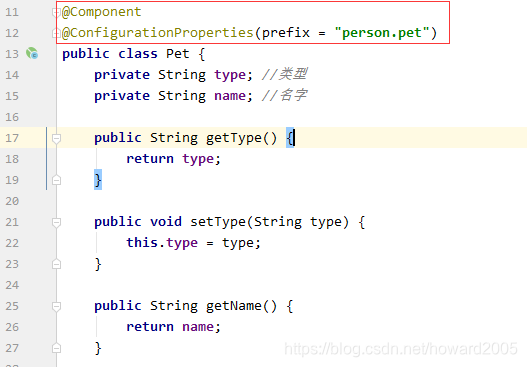
(6)从Spring容器里获取Person类的实例并输出
- 实现接口ApplicationContextAware,实现其抽象方法setApplicationContext

- 声明ApplicationContext对象,并在setApplicationContext里初始化
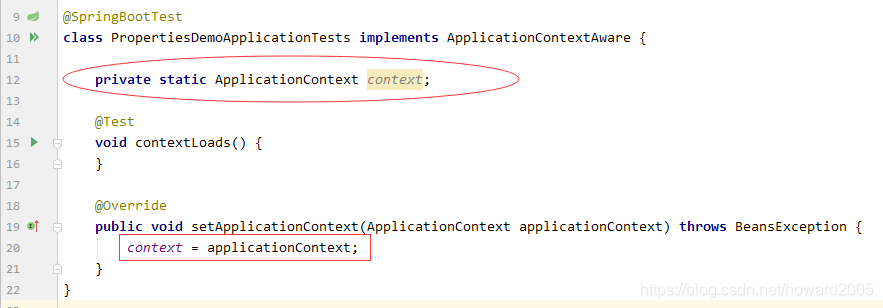
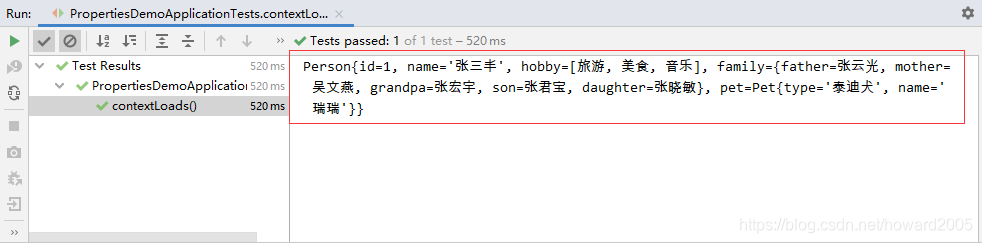
- 从Spring容器中获取Person类的实例并输出
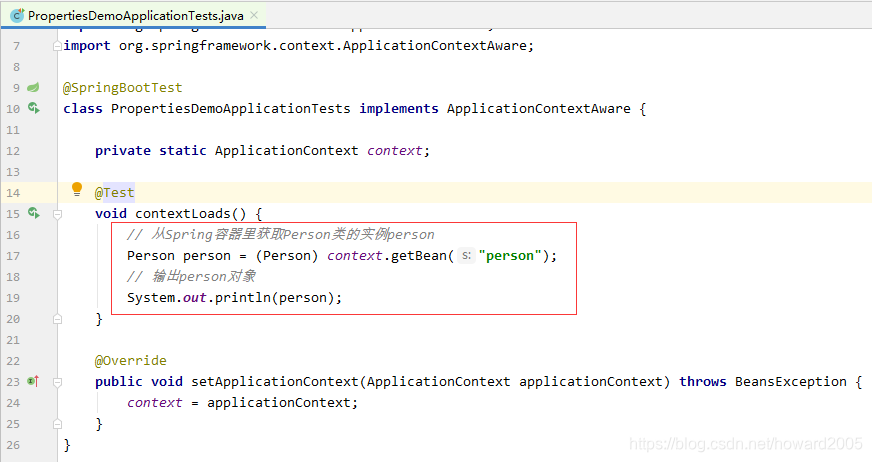
- 运行测试类,查看结果
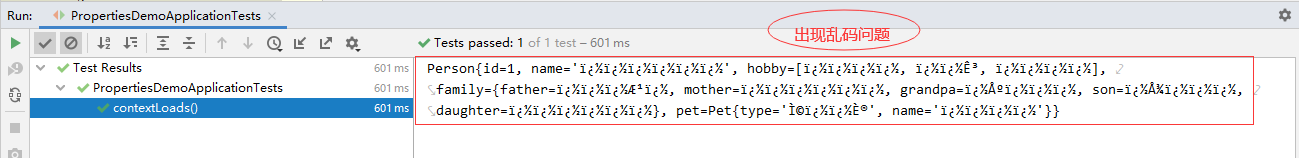
(7)解决输出结果的汉字乱码问题
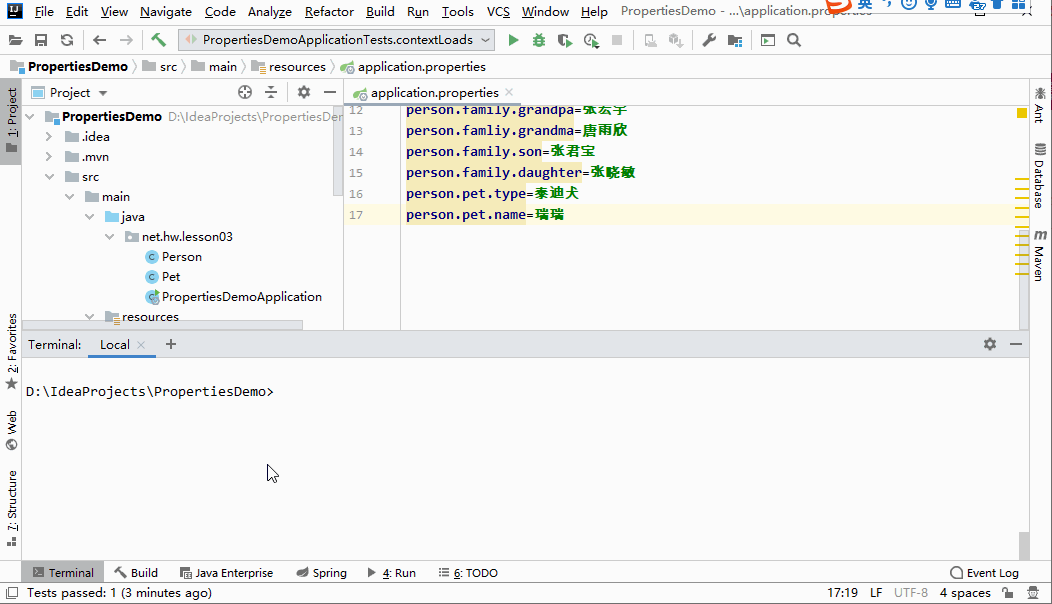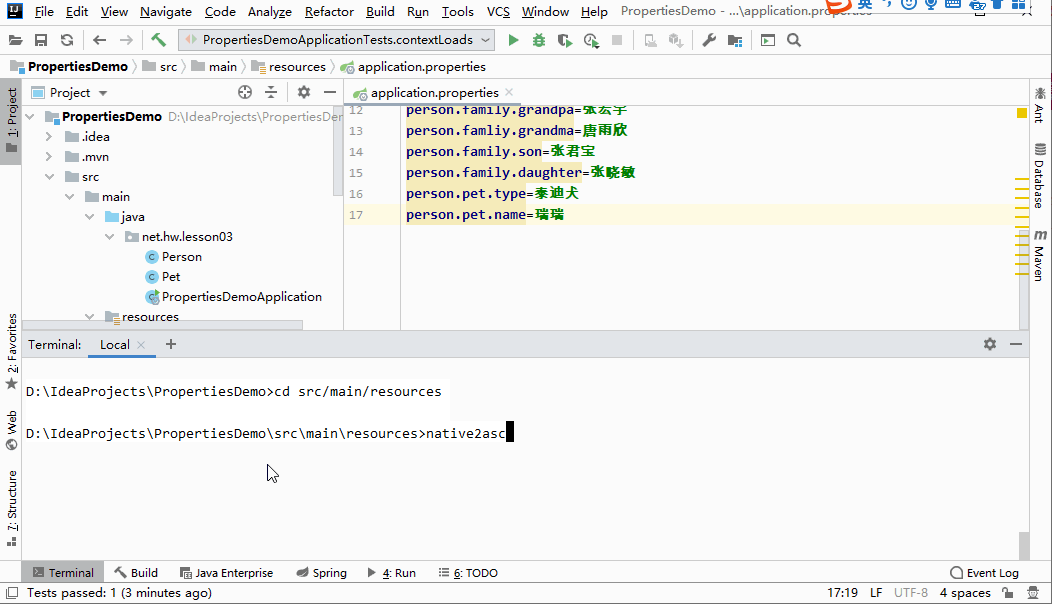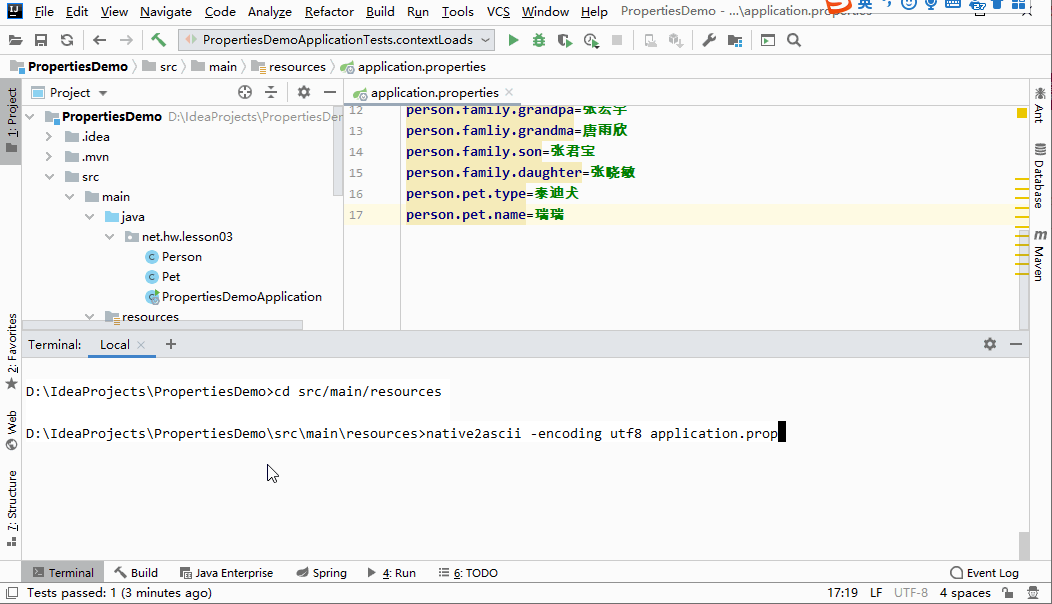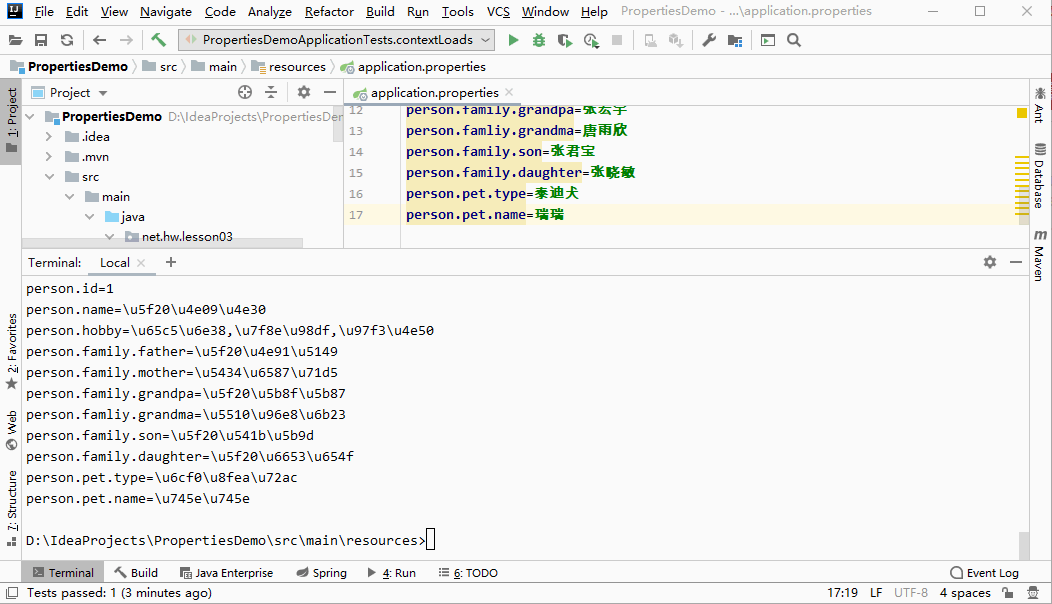
- 使用JDK工具
native2ascii.exe将汉字处理成uncode编码
D:\IdeaProjects\PropertiesDemo>cd src/main/resources
D:\IdeaProjects\PropertiesDemo\src\main\resources>native2ascii -encoding utf8 application.properties
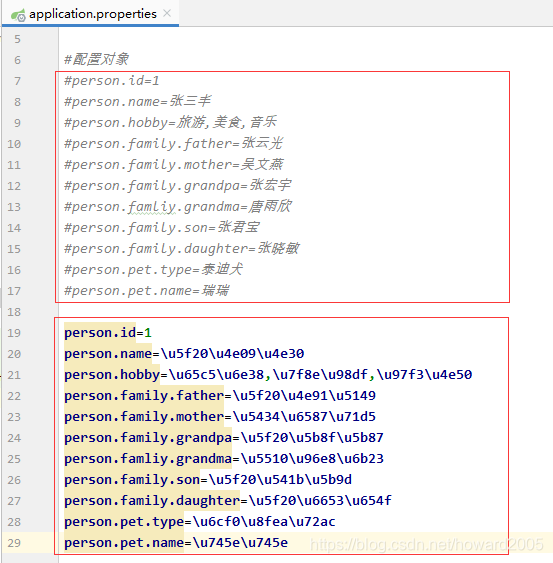
#\u4fee\u6539tomcat\u9ed8\u8ba4\u7aef\u53e3\u53f7
server.port=8888
#\u4fee\u6539web\u865a\u62df\u8def\u5f84
server.servlet.context-path=/lzy
#\u914d\u7f6e\u5bf9\u8c61
person.id=1
person.name=\u5f20\u4e09\u4e30
person.hobby=\u65c5\u6e38,\u7f8e\u98df,\u97f3\u4e50
person.family.father=\u5f20\u4e91\u5149
person.family.mother=\u5434\u6587\u71d5
person.family.grandpa=\u5f20\u5b8f\u5b87
person.famliy.grandma=\u5510\u96e8\u6b23
person.family.son=\u5f20\u541b\u5b9d
person.family.daughter=\u5f20\u6653\u654f
person.pet.type=\u6cf0\u8fea\u72ac
person.pet.name=\u745e\u745e
D:\IdeaProjects\PropertiesDemo\src\main\resources>
- 修改application.properties文件,汉字采用unicode编码形式
- 运行测试类PropertiesDemoApplicationTests,查看结果
(8)从Spring容器里获取Pet类的实例并输出
- 查看Pet类的注解,有配置属性的注解
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person.pet")
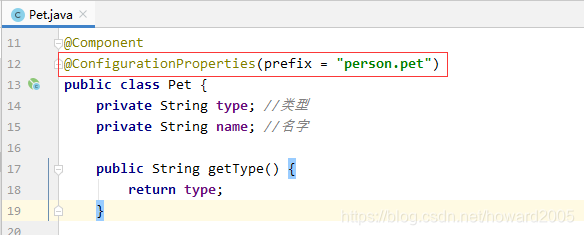
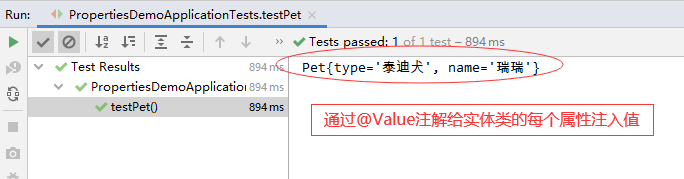
- 在测试类里添加测试方法testPet()
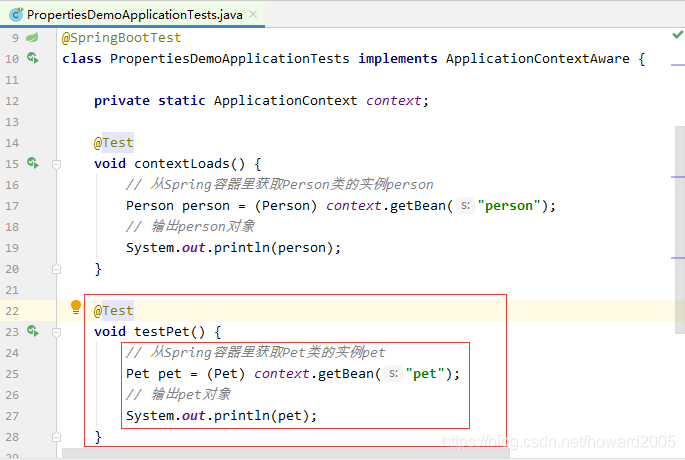
- 运行测试方法testPet(),查看结果
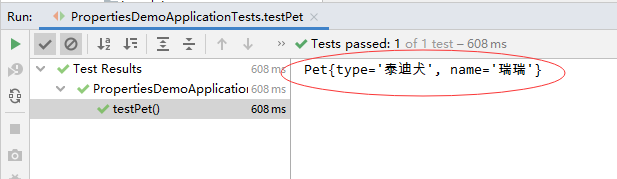
- 去掉Pet类的配置属性的注解
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person.pet")
- 运行测试方法testPet(),查看结果
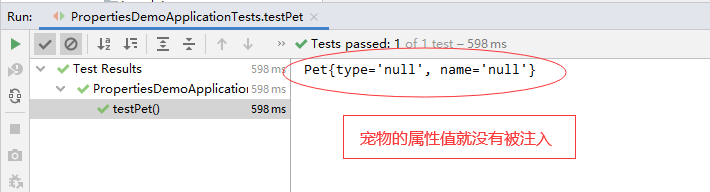
- 修改application.properties,配置宠物对象
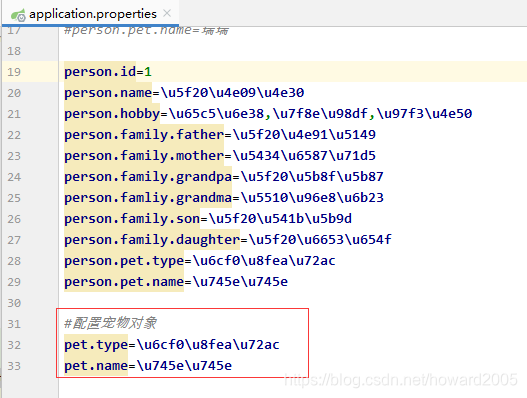
- 再次运行测试方法testPet(),查看结果
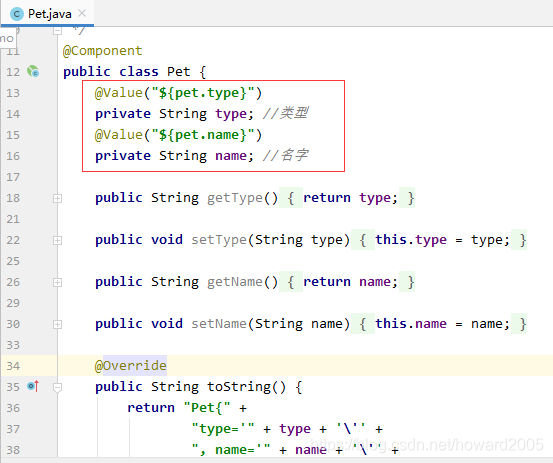
- 大家可以看到,宠物对象的属性依然没有被注入,下面我们换一种属性注解的方式,采用@Value注解方式。
- 给Pet类的属性添加值注解@Value
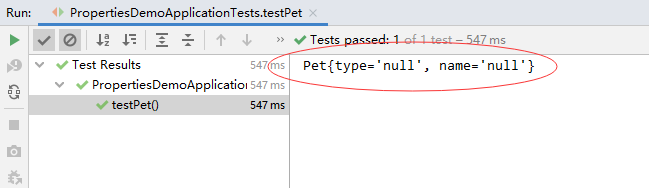
- 再次运行测试方法testPet(),查看结果
3、两种属性注解方式的对比
- 采用
@ConfigurationProperties注解方式,必须要有set方法,才会自动为所注解的类的全部属性注入相应的值,包括简单类型和复杂类型(List、Map、Pet……)。
- 采用
@Value注解方式,优点在于可以不要set方法,但是有两点不足:其一、需要一个一个地注入,显得麻烦;其二、对于复杂类型不能注入,比如Map、List、Pet等。
三、Application.yaml配置文件
1、备份application.properties文件
- 文件更名为
application.back,即让此文件不起作用
2、在resoures目录里创建application.yaml文件
- 创建application.yaml文件
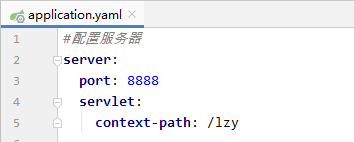
- 配置服务器属性
- 配置person对象属性

- 配置pet对象属性
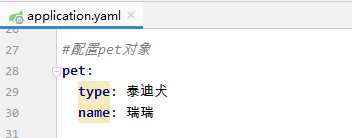
- 查看application.yaml文件内容
server:
port: 8888
servlet:
context-path: /lzy
person:
id: 1
name: 张三丰
hobby:
旅游
美食
音乐
family: {
father: 张云光,
mother: 吴文燕,
grandpa: 张宏宇,
grandma: 唐雨欣,
son: 张君宝,
daughter: 张晓敏
}
pet:
type: 泰迪犬
name: 瑞瑞
pet:
type: 泰迪犬
name: 瑞瑞
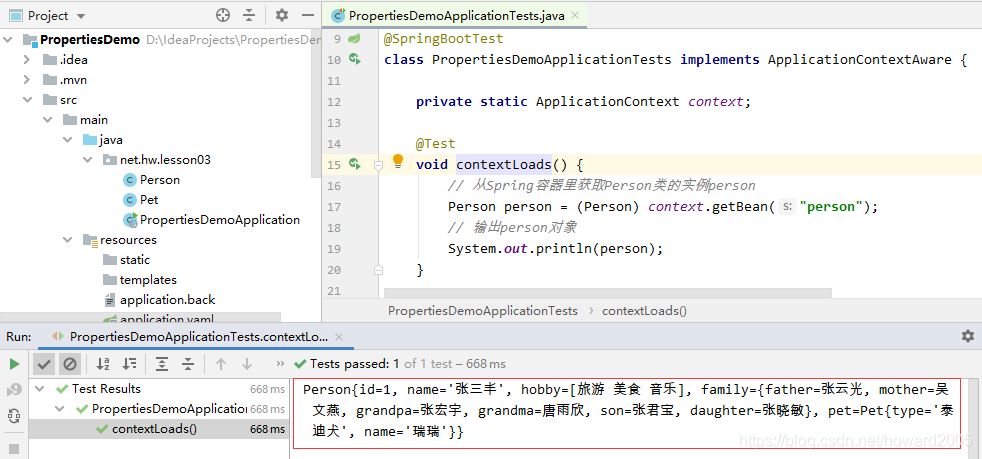
3、运行测试方法contextLoads(),查看结果
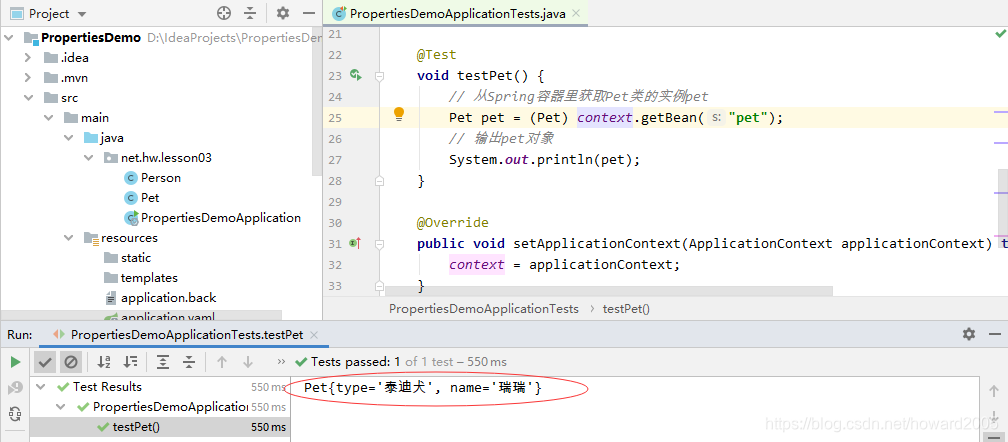
4、运行测试方法testPet(),查看结果
四、两种配置文件的比较
1、application.properties配置文件
- 采用XML语法,键值对:键=值,没有层次结构
- 如果值里有汉字,必须得转成unicode,否则会出现乱码问题
2、application.yaml配置文件
- 采用YAML语法,键值对:键: 值(冒号与值之间有空格),具有层次结构
- 允许值里有汉字,不必转成unicode,也不会出现乱码问题
五、课后作业
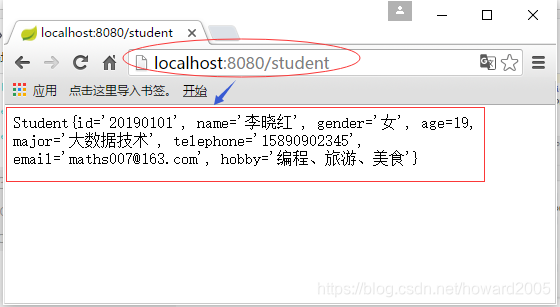
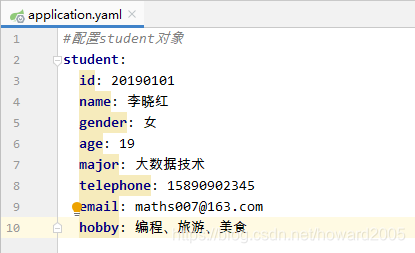
任务:修改StudentInfo项目输出学生信息

- 创建学生实体类Student

- 添加属性
private String id;
private String name;
private String gender;
private int age;
private String major;
private String telephone;
private String email;
private String hobby;
- 添加getter和setter
- 添加toString()方法
- 添加注解@Component
- 添加注解@ConfigureProperties
- 将application.properties更名为application.yaml
- 配置student对象属性
- 修改控制器StudentInfoController,student()方法里返回student的值
- 运行启动类

- 在浏览器里访问http://localhost:8080/student