1. String 和StringBuffer性能对比
生成10位长度的随机字符串,然后,先使用String的+,连接10000个随机字符串,计算消耗的时间,然后,再使用StringBuffer连接10000个随机字符串,计算消耗的时间
String使用字符串连接+的方式
StringBuffer的方式sb.append(s)
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int total = 10000;
String s = randomString(10);
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
String str1 = "";
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i <total; i++) {
str1+=s;
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf("使用字符串连接+的方式,连接%d次,耗时%d毫秒%n",total,end-start);
total *=100;
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i <total; i++) {
sb.append(s);
}
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf("使用StringBuffer的方式,连接%d次,耗时%d毫秒%n",total,end-start);
}
private static String randomString(int length) {
String pool = "";
for (short i = '0'; i <= '9'; i++) {
pool += (char) i;
}
for (short i = 'a'; i <= 'z'; i++) {
pool += (char) i;
}
for (short i = 'A'; i <= 'Z'; i++) {
pool += (char) i;
}
char cs[] = new char[length];
for (int i = 0; i < cs.length; i++) {
int index = (int) (Math.random() * pool.length());
cs[i] = pool.charAt(index);
}
String result = new String(cs);
return result;
}
}
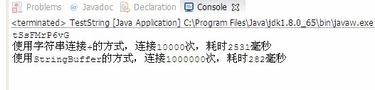
查看结果,分析看看,结果明显,StringBuffer比String快了进1000倍。为什么会这样呢?
StringBuffer中有capacity(容量)这个概念。StringBuffer在每次追加的时候,不需要每次创建新的对象。但是String每次追加都会创建一个创新的String对象。
下面我们开始写一个StringBuffer
2. IStringBuffer接口
public interface IStringBuffer {
public void append(String str); //追加字符串
public void append(char c); //追加字符
public void insert(int pos,char b); //指定位置插入字符
public void insert(int pos,String b); //指定位置插入字符串
public void delete(int start); //从开始位置删除剩下的
public void delete(int start,int end); //从开始位置删除结束位置-1
public void reverse(); //反转
public int length(); //返回长度
}
3. 接口实现MyStringBuffer
public class MyStringBuffer implements IStringBuffer{
int capacity = 16;//capacity: 容量
int length = 0;
char[] value;//value:用于存放字符数组
public MyStringBuffer(){//无参构造方法: 根据容量初始化value
value = new char[capacity];
}
//有参构造方法
public MyStringBuffer(String str){
this();
//为空直接返回
if(null==str)
return;
//大于容量,进行扩容,把容量增大一倍,初始化value容量
if(capacity<str.length()){
capacity = value.length*2;
value=new char[capacity];
}
//小于容量,将str数组复制到新的数组value中
if(capacity>=str.length())
System.arraycopy(str.toCharArray(), 0, value, 0, str.length());
//改变length的值
length = str.length();
}
//追加,就是在最后位置插入。 所以不需要单独开发方法,直接调用insert方法,就能达到最后位置插入的效果
@Override
public void append(String str) {
insert(length,str);
}
@Override
public void append(char c) {
append(String.valueOf(c));
}
@Override
public void insert(int pos, char b) {
insert(pos,String.valueOf(b));
}
@Override
public void delete(int start) {
delete(start,length);
}
@Override
public void delete(int start, int end) {
//边界条件判断
if(start<0)
return;
if(start>length)
return;
if(end<0)
return;
if(end>length)
return;
if(start>=end)
return;
System.arraycopy(value, end, value, start, length- end);
length-=end-start;
}
//反转 reverse
@Override
public void reverse() {
for (int i = 0; i < length/2; i++) {
char temp = value[i];
value[i] = value[length-i-1];
value[length-i-1] = temp;
}
}
@Override
public int length() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return length;
}
@Override
public void insert(int pos, String b) {
//边界条件判断1. 插入位置是否合法 2. 插入的字符串是否为空
if(pos<0)
return;
if(pos>length)
return;
if(null==b)
return;
//扩容1. 要判断是否需要扩容。 如果插入的字符串加上已经存在的内容的总长度超过了容量,那么就需要扩容。
//2. 数组的长度是固定的,不能改变的,数组本身不支持扩容。 我们使用变通的方式来解决这个问题。
//3. 根据需要插入的字符串的长度和已经存在的内容的长度,计算出一个新的容量。
// 然后根据这个容量,创建一个新的数组,接着把原来的数组的内容,
//复制到这个新的数组中来。并且让value这个引用,指向新的数组,从而达到扩容的效果。
while(length+b.length()>capacity){
capacity = (int) ((length+b.length())*1.5f);
char[] newValue = new char[capacity];
System.arraycopy(value, 0, newValue, 0, length);
value = newValue;
}
char[] cs = b.toCharArray();
// 插入字符串
//1. 找到要插入字符串的位置,从这个位置开始,把原数据看成两段,把后半段向后挪动一个距离,这个距离刚好是插入字符串的长度
//2. 然后把要插入的数据,插入这个挪出来的,刚刚好的位置里。
//先把已经存在的数据往后移
System.arraycopy(value, pos, value,pos+ cs.length, length-pos);
//把要插入的数据插入到指定位置
System.arraycopy(cs, 0, value, pos, cs.length);
//修改length的值,最后修改length的值,是原来的值加上插入字符串的长度
length = length+cs.length;
}
public String toString(){
char[] realValue = new char[length];
System.arraycopy(value, 0, realValue, 0, length);
return new String(realValue);
}
}
4. 使用自带的 StringBuffer和自己开发的MyStringBuffer性能比较
比较方案:
- 生成长度是10的随机字符串
- 使用StringBuffer追加1000000次统计时间
- 使用MyStringBuffer追加1000000次统计时间
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int total = 1000000;
String s = randomString(10);
MyStringBuffer msb = new MyStringBuffer();
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i <total; i++) {
sb.append(s); //使用 StringBuffer
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf("使用StringBuffer的方式,连接%d次,耗时%d毫秒%n",total,end-start);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i <total; i++) {
msb.append(s); //使用MyStringBuffer
}
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf("使用MyStringBuffer的方式,连接%d次,耗时%d毫秒%n",total,end-start);
}
private static String randomString(int length) {
String pool = "";
for (short i = '0'; i <= '9'; i++) {
pool += (char) i;
}
for (short i = 'a'; i <= 'z'; i++) {
pool += (char) i;
}
for (short i = 'A'; i <= 'Z'; i++) {
pool += (char) i;
}
char cs[] = new char[length];
for (int i = 0; i < cs.length; i++) {
int index = (int) (Math.random() * pool.length());
cs[i] = pool.charAt(index);
}
String result = new String(cs);
return result;
}
}
错误Error,指的是系统级别的异常,通常是内存用光了
在默认设置下,一般java程序启动的时候,最大可以使用16m的内存
如例不停的给StringBuffer追加字符,很快就把内存使用光了。抛出OutOfMemoryError
与运行时异常一样,错误也是不要求强制捕捉的
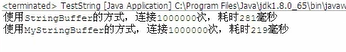
发现我们自己做的比java的还好一些
这是因为java自带的StringBuffer还考虑到一些线程安全的问题。