
Pre
MyBatis源码-深入理解MyBatis Executor的设计思想
工程部分见
MyBatis源码- SqlSession门面模式 & selectList 源码解析
实际中,我们都是面向SqlSession编程的,不会直接调用Executor来执行业务逻辑,这里我们仅仅是为了深入了解下Executor体系架构才这么搞的,切记。
Executor 执行器
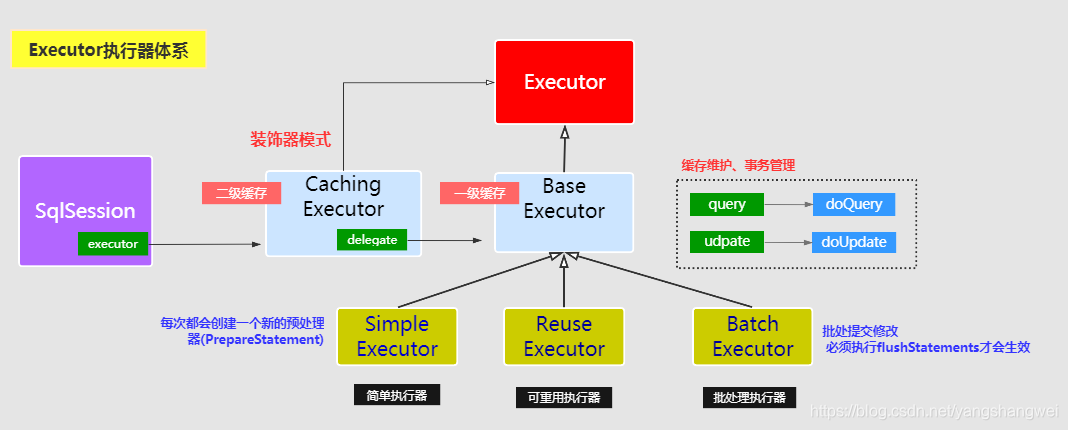
接口继承关系
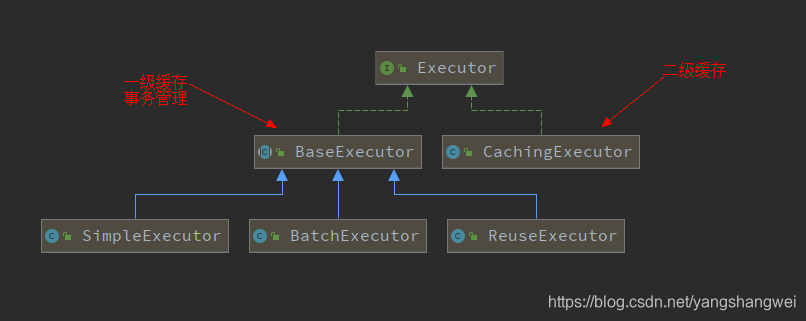
这里我们重点看下Executor的 三个实现子类。
分别是:SimpleExecutor(简单执行器)、ReuseExecutor(重用执行器)、BatchExecutor(批处理执行器)。
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
11482972 查看本文章


ReuseExecutor(重用执行器)
回归下JDBC中的 Statement , 再和MyBatis 所封装的 对比一下
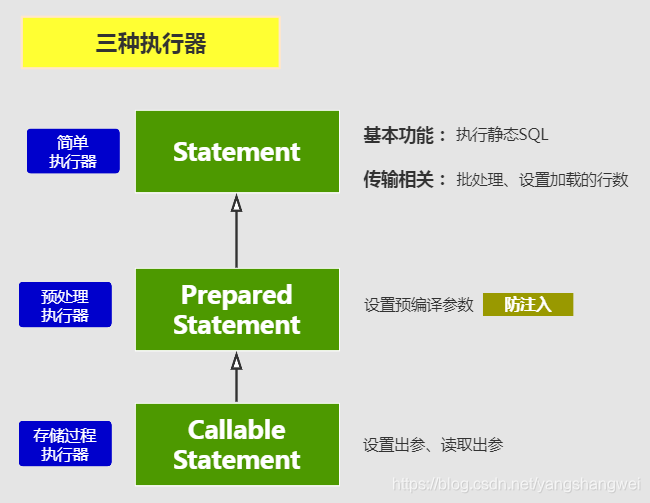
PreparedStatement 支持预编译参数
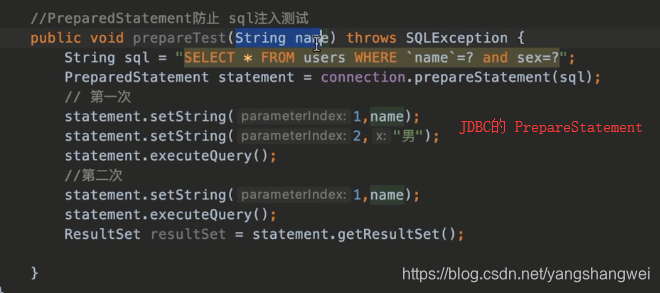
MyBatis的ReuseExecutor就是利用了JDBC Statement的这个特点 来处理的。
入门小demo
@Test
public void testReuseExecutor() throws SQLException {
// 通过factory.openSession().getConnection()实例化JdbcTransaction ,用于构建ReuseExecutor
jdbcTransaction = new JdbcTransaction(factory.openSession().getConnection());
// 映射SQL
ms = configuration.getMappedStatement("com.artisan.UserMapper.selectByid");
// 实例化ReuseExecutor
ReuseExecutor executor = new ReuseExecutor(configuration, jdbcTransaction);
// 调用doQuery执行查询
List<User> userList = executor.doQuery(ms, 1, RowBounds.DEFAULT, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER, ms.getBoundSql(1));
System.out.println(userList.get(0));
List<User> userList2 = executor.doQuery(ms, 1, RowBounds.DEFAULT, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER, ms.getBoundSql(1));
System.out.println(userList2.get(0));
}
执行结果
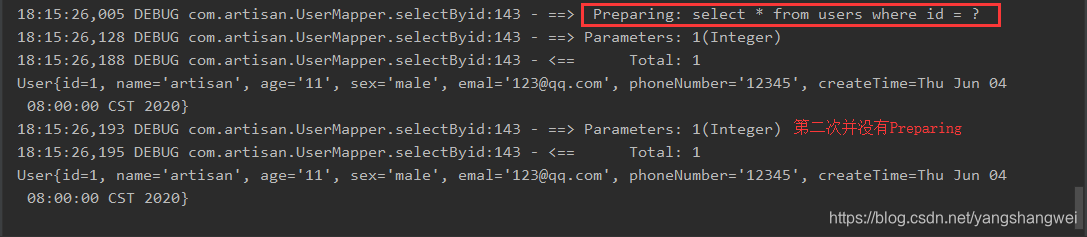
可以看到 相同的SQL语句 会缓存对应的PrepareStatement , 缓存的生命周期: 会话有效期
源码实现
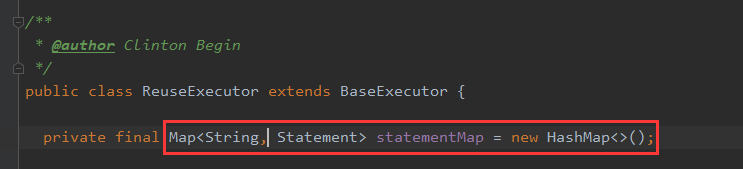
Key 是 sql , Value 是 Statement
执行过程:
executor.doQuery ----> prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog())
---------> 见下方源码
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql();
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
if (hasStatementFor(sql)) {
stmt = getStatement(sql);
applyTransactionTimeout(stmt);
} else {
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
putStatement(sql, stmt);
}
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
先判断本地缓存statementMap是否有数据,有的话从statementMap获取,没有的话建立Statement,并存入本地缓存statementMap 。
注意这个缓存的声明周期 是仅限于本次会话。 会话结束后,这些缓存都会被销毁掉。
区别于SimpleExecutor的实现,多了个本地缓存。 推荐使用ReuseExecutor 。