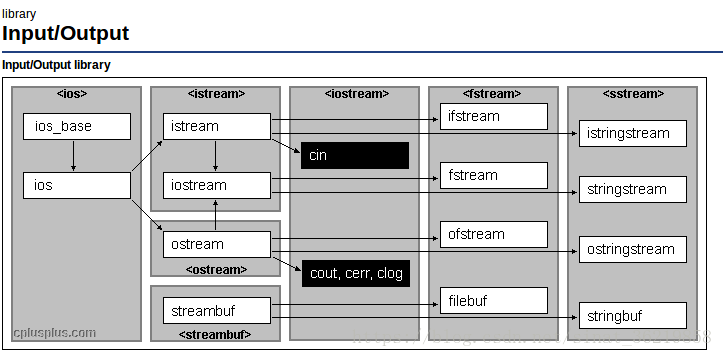
C++ 使用标准库类来处理面向流的输入和输出:
- iostream 处理控制台 IO
- fstream 处理命名文件 IO
- stringstream 完成内存 string 的IO
每个IO 对象都维护一组条件状态 flags (eofbit, failbit and badbit),用来指出此对象上是否可以进行 IO 操作。如果遇到错误—例如输入流遇到了文件末尾,则对象的状态变为是失效,所有的后续输入操作都不能执行,直到错误纠正。
头文件 <fstream>包含的多个文件流类,这里列出常用的4个:
ifstreamInput file stream class (class )链接ofstreamOutput file stream (class )链接fstreamInput/output file stream class (class )链接filebufFile stream buffer (class )链接
一. 输入流 ifstream 用法
输入流的继承关系:
ios_base <- ios <- istream <- ifstream
Public member functions (1-6)
1, (constructor)
第一种不绑定文件,后续用open() 绑定。
第二种绑定文件 filename ,读取模式默认参数为 ios_base::in可以省略。
default (1) ifstream();
initialization (2)
explicit ifstream (const char* filename, ios_base::openmode mode = ios_base::in);
explicit ifstream (const string& filename, ios_base::openmode mode = ios_base::in);2,ifstream::open
打开文件filename,模式默认 ios_base::in
void open (const char* filename, ios_base::openmode mode = ios_base::in);
void open (const string& filename, ios_base::openmode mode = ios_base::in);函数参数:
- filename 要打开文件的文件名
- mode 打开文件的方式
| member constant | stands for | access |
|---|---|---|
| in | input File | 读的方式打开文件 |
| out | output | 写的方式打开文件 |
| binary | binary | 二进制方式打开 |
| ate | at end | 打开的时候定位到文件末尾 |
| app | append | 所有操作都定位到文件末尾 |
| trunc | truncate | 丢弃打开前文件存在的内容 |
3,ifstream:: is_open
bool is_open() const;文件流对象与文件绑定,返回 true ,否则 false 。
4,ifstream:: close
void close(); //关闭文件流5,ifstream:: rdbuf
filebuf* rdbuf() const; 返回一个 filebuf 对象指针,(The pointer to the internal filebuf object.)
6,ifstream:: operator =
copy(1) ifstream& operator= (const ifstream&) = delete;
move(2) ifstream& operator= (ifstream&& rhs); 等号运算符禁止使用左值引用,可以使用右值引用。(即右边的值必须是一个即将销毁的临时对象)
Public member functions inherited from istream (7-17)
7,std::istream::operator>>
输入终端 cin 和 ifstream 都是 istream 的子类,所以输入操作符 >> 用法相同。对变量进入输入的时候重载了常用的数据类型。
arithmetic types (1)
istream& operator>> (bool& val);
istream& operator>> (short& val);
istream& operator>> (unsigned short& val);
istream& operator>> (int& val);
istream& operator>> (unsigned int& val);
istream& operator>> (long& val);
istream& operator>> (unsigned long& val);
istream& operator>> (long long& val);
istream& operator>> (unsigned long long& val);
istream& operator>> (float& val);
istream& operator>> (double& val);
istream& operator>> (long double& val);
istream& operator>> (void*& val);
stream buffers (2)
istream& operator>> (streambuf* sb );
manipulators (3)
istream& operator>> (istream& (*pf)(istream&));
istream& operator>> (ios& (*pf)(ios&));
istream& operator>> (ios_base& (*pf)(ios_base&));8,istream::gcount
streamsize gcount() const;返回最后一个输入操作读取的字符数目。
可以修改这个返回值的函数有:get,getline,ignore,peek,read, readsome,putback and unget. 其中函数peek, putback and unget 被调用后gcount()返回值为0。
9,istream::get
single character (1): //读取一个字符,遇到'\n',也从流中取出。
int get(); //字符按 int 返回
istream& get (char& c); // 读到c中
//读取n个 c 风格字符串到数组s中,遇到'\n'(或delim)停止读取,并把'\n'留在输入流中,若要读取多行,就要需要int get() 来取出'\n',才能读下一行。
c-string (2):
istream& get (char* s, streamsize n);//默认delim是换行字符'\n'
istream& get (char* s, streamsize n, char delim) //指定读取停止字符 delim
stream buffer (3): //内容读取到 streambuf 对象中。
istream& get (streambuf& sb);//默认delim是换行字符'\n'
istream& get (streambuf& sb, char delim);//指定读取停止字符 delim下面的程序演示get()读取到streambuf 的用法。
#include <iostream> // std::cout, std::streambuf, std::streamsize
#include <fstream> // std::ifstream
using namespace std;
int main () {
std::ifstream ifs ("test.txt");
std::ofstream ofs ("out.txt");
std::streambuf *pbuf = ofs.rdbuf();
ifs.get(*pbuf);//默认读取截止字符是'\n', 所以读取一行停止,且没有读取'\n'。
pbuf->sputc(ifs.get()); // '\n'并没有被读取到pbuf,所以需要get()来读取'\n',然后用函数sputc()加到 pbuf 中。
ifs.get(*pbuf); // 从流中取出了'\n' ,才能读取第二行
pbuf->sputc(ifs.get());
/*
上面使用了函数 istream& get (streambuf& sb);
之后不能使用 istream& get (char* s, streamsize n);
*/
char s[20];
ifs.get(s,20);//虽然输入流有第三行,但是没法读取。
cout<<"get:"<<s<<endl; //内容为空
ofs.close();
ifs.close();
return 0;
}
10,istream::getline
读取一行到字符数组。
istream& getline (char* s, streamsize n );//默认delim是换行字符'\n',遇到后丢弃,第二次读取从delim后开始读。
istream& getline (char* s, streamsize n, char delim );//自己定义停止符delim<string> 头文件对getline()进行了重载,读取一行到字符串
std::getline (string)
(1)
istream& getline (istream& is, string& str, char delim);
istream& getline (istream&& is, string& str, char delim);
(2)
istream& getline (istream& is, string& str);
istream& getline (istream&& is, string& str);11,istream::ignore
istream& ignore (streamsize n = 1, int delim = EOF);从输入流中读取n个字符并且丢弃,或者读到delim字符再停止读取。
12,istream::peek
int peek();返回输入流下一个字符,并把它留在输入流中,作为下一次读取的起点。返回值是整形ascll码值,可以用 char(c) 转化为字符。
13,istream::read
istream& read (char* s, streamsize n);从输入流中提取n个字符,并把他们存数组s中,不检测内容,也不加字符串结尾符号‘\0’,实例:
// read a file into memory
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <fstream> // std::ifstream
int main () {
std::ifstream is ("test.txt", std::ifstream::binary);
if (is) {
// get length of file:
is.seekg (0, is.end);
int length = is.tellg();
is.seekg (0, is.beg);
char * buffer = new char [length];
std::cout << "Reading " << length << " characters... ";
// read data as a block:
is.read (buffer,length);
if (is)
std::cout << "all characters read successfully.";
else
std::cout << "error: only " << is.gcount() << " could be read";
is.close();
// ...buffer contains the entire file...
delete[] buffer;
}
return 0;
}14,istream::putback
istream& putback (char c);
// 用法,从输入流读取一个字符,再把它返回。
char c = std::cin.get();
std::cin.putback (c);15,istream::unget
istream& unget();
// 返回最后一次读取的字符到输入流,类似putback()
char c = std::cin.get();
std::cin.unget();16,istream::tellg
读取输入流中文件指针的位置,返回值可转化为 int。
streampos tellg();
// get length of file:
is.seekg (0, is.end);
int length = is.tellg();
is.seekg (0, is.beg);17,istream::seekg
设定输入流中文件指针的位置。(1) 绝对位置 (2) 相对位置
(1)istream& seekg (streampos pos);
(2)istream& seekg (streamoff off, ios_base::seekdir way);参数 pos 是流中的绝对位置可以转化为 int
参数 off 是偏移量,与way相关,类型是 int
参数 way 可以选下表中的任意一个常量。
| value | offset is relative to… |
|---|---|
| ios_base::beg | beginning of the stream |
| ios_base::cur | current position in the stream |
| ios_base::end | end of the stream |
Public member functions inherited from ios (18-21)
18,ios::good
bool good() const;
bool eof() const;
bool fail() const;
bool bad() const;检测流的状态是否正常。当错误的状态flags (eofbit, failbit and badbit) 都没被设置的时候返回true
特定的错误状态可以用下面的函数(eof, fail, and bad)来检测。
| iostate value (member constant) | indicates | good() | eof() | fail() | bad() | rdstate() |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| goodbit | No errors (zero value iostate) | true | false | false | false | goodbit |
| eofbit | End-of-File reached on input operation | false | true | false | false | eofbit |
| failbit | Logical error on i/o operation | false | false | true | false | failbit |
| badbit | Read/writing error on i/o operation | false | false | true | true | badbit |
19,ios::operator!
bool operator!() const;
//Returns true if either failbit or badbit is set, and false otherwise.
// 有错误状态返回 true
int main () {
std::ifstream is;
is.open ("test.txt");
if (!is)
std::cerr << "Error opening 'test.txt'\n";
return 0;
}20,ios::operator bool
explicit operator bool() const;
C++11: Return true if none of failbit or badbit is set. false otherwise.
// 在条件语句中,无错误返回真,有错返回假。
int main () {
std::ifstream is;
is.open ("test.txt");
if (is) {
// read file
}
else {
std::cerr << "Error opening 'test.txt'\n";
}
return 0;
}21,ios::rdstate
iostate rdstate() const;
// Returns the current internal error state flags of the stream.
// 返回当前流中的内部错误状态,iostate二进制数,需要做位运算来获取其相应位置上的值。
//这个函数的功能可以被 good(),eof(),fail(),bad() 替换。
int main () {
std::ifstream is;
is.open ("test.txt");
if ( (is.rdstate() & std::ifstream::failbit ) != 0 )
std::cerr << "Error opening 'test.txt'\n";
return 0;
}