java中常用的时间代码如下:
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { long request_time = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取当前时间,精确到毫秒 SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); System.out.println("当前时间为-----"+sf.format(new Date())); //将字符串转为时间 String date = "2020-07-23"; SimpleDateFormat sf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"); try { Date res = sf1.parse(date); System.out.println("字符串转为时间-----"+res); } catch (ParseException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } //将时间戳转化为字符串 long nowtime=Long.parseLong("1593575171000"); //13位时间戳; Date date1=new Date(nowtime); String res1=sf1.format(date1); System.out.println("时间戳转为字符串-----"+res1); //将时间转为时间戳 try { Date date2 = sf.parse("2020-07-23 16:34:19"); long ts = date2.getTime(); System.out.println("时间转为时间戳-----"+String.valueOf(ts)); } catch (ParseException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();//获取计算机的当前时间 System.out.println("整个过程所需时间-----"+(currentTime- request_time)+"毫秒");//计算整个过程所需时间 } }
运行后,控制台打印结果如图:
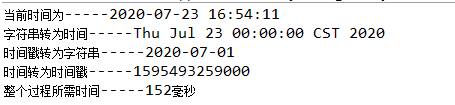
在开发过程中,时间这个字段一般都是需要往数据库中存值的,所以我们就需要上面那样对时间进行处理从而得到我们想要的数据。一般来说,数据库中对于时间的字段类型常用的是date跟datetime,区别就是一个精确到当日,一个精确到毫秒。但是我们在代码中构建实体类的时候,date的包都是util下的。还有就是既然我们在建立新表的时候给定时间的字段类型是date或者datetime,那么我们在java代码中存的时间类型也必须是date类型,所以我们要对拿到的时间进行处理,不然就会出现类型不一致导致无法插入到数据表中。