1、
就画一个
2、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(){
int num = 0;//计算运行次数的,自己添加的
int sign;
double pi = 0.0, n = 1.0, term = 1.0;
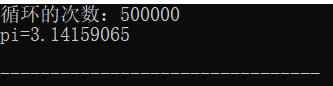
while(fabs(term) >= pow(10,-6)){
pi = pi + term;
n = n + 2;
sign = -sign;
term = sign / n;
num++;
}
printf("循环的次数:%d\n",num);
pi = pi * 4;
printf("pi=%10.8f\n", pi);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(){
int num = 0;//计算运行次数的,自己添加的
int sign;
double pi = 0.0, n = 1.0, term = 1.0;
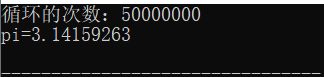
while(fabs(term) >= pow(10,-8)){
pi = pi + term;
n = n + 2;
sign = -sign;
term = sign / n;
num++;
}
printf("循环的次数:%d\n",num);
pi = pi * 4;
printf("pi=%10.8f\n", pi);
return 0;
}
3、
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int a,b,c,m;
printf("请输入两个数:\n");
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
if(a < b){
a = a + b;
b = a - b;
a = a - b;
}
m = a * b;
c = a % b;
while(c != 0)
{
a = b;
b = c;
c = a % b;
}
printf("最大公约数是:\n%d\n",b);
printf("最小公倍数是:\n%d\n",m/b);
}
4、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(){
int mathSum = 0;
int alphabet = 0;
int another = 0;
int blank = 0;
char input;
int count = 0;
scanf("%c", &input);
while((input = getchar()) != '\n'){
if(input == ' '){
blank++;
}else if(input >= 'a' && input <= 'z' ){
alphabet++;
}else if(input >= 'A' && input <= 'Z'){
alphabet++;
}else if(input >= 48 && input <= 57){
mathSum = mathSum + 1;
}else {
another++;
}
count++;
if(count == 10){
break;
}
}
printf("空格字符为%d个,英文字母为%d个,其他字符为%d个,数字为%d个\n",blank ,alphabet, another, mathSum);
return 0;
}
5、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(){
int n;
int a;
int sum = 0;
int num = 10;
printf("输入数字以及这个数字的位数:\n");
scanf("%d %d",&a, &n);
while(n != 0){
sum = (a % num);
num = num * 10;
--n;
if(n == 0){
printf("%d",sum);
}else{
printf("%d + ",sum);
}
}
return 0;
}
6、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(){
int count;
int num;
int temp;
int sum;
printf("输入要阶乘的数字:\n");
scanf("%d", &count);
while(count >= 1){
num = count;
temp = 1;
while(num >= 1){
temp = num * temp;
num--;
}
sum = sum + temp;
count--;
}
printf("总和为:%d", sum);
return 0;
}
7、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(){
double sum = 0;
int count = 100;
while(count >= 1){
sum = sum + count;
count--;
}
count = 50;
while(count >= 1){
sum = sum + (count * count);
count--;
}
count = 10;
while(count >= 1){
sum = sum + (1 / count);
count--;
}
printf("总和为:%lf",sum);
return 0;
}
8、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(){
int i,j,k,n;
for(i=100;i<1000;i++) {
j = i % 10;
k = i/10 % 10;
n = i / 100;
if(j * j * j + k * k * k + n * n * n == i){
printf("%5d\n",i);
}
}
return 0;
}
9、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(){
int s, i, j, m;
for(i = 1; i <= 1000; i++){
s = 0;
for(j = 1; j < i; j++){
if(i % j == 0){
s = s + j; //求这个数的因子的和
}
}
if(s == i){ //如果这个数的因子等于这个数
printf("%d its factors are ", s); //输出这个数
for(m = 1; m < s; m++){
if(s % m == 0){
printf("%d ", m); //循环输出这个数的因子
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
10、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(){
int count = 20;
double M = 1; //分母
double S = 2; //分子
double sum = 0;
double temp = 0;
while(count >= 1){
sum = sum + S / M;
temp = S;
S = S + M; //后面分子等于前面分子分母之和
M = temp; //后面分母等于前面的分子
count--;
}
printf("总和为:%lf", sum);
return 0;
}
11、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(){
float hight = 100;
float halfHight = hight / 2;
float tenHight = 0;
float sum;
int count = 10;
while(count >= 1){
sum = hight + halfHight + sum;
hight = halfHight;
halfHight = hight / 2;
count--;
}
printf("第10次落地时经过了:%f米\n第10次反弹:%f米",sum, hight);
return 0;
}
12、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(){
//第一天摘了若干桃子,吃了一半,又多吃了一个;
//第二天吃了一半,又多吃了一个
//....
//第10天只剩一个
int n = 0;
int a = 1;
int count = 10;
int b = 0;
while(count >= 1){
if(count == 10){
n = 1; //第10天的桃子
}else{
b = 2 * (n + 1);
n = b;
}
count--;
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(){
double X1;
double X2 = 1; //为啥初始化为1呢,因为啊,0它不允许啊 ,当然初始化为其它数也行的哇
double a;
scanf("%lf", &a);
while(1){
X1 = X2;
X2 = (X1 + a / X1) / 2.0;
if(fabs(X1 - X2) < 0.00006) {
printf("%lf", X2);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
牛顿迭代法,没书哇,算了,不写了