循环双向链表(带头节点)
这里我是为了解决王道书上的算法题写的,可能功能不是太多,大多是解题的算法。有的功能我注释了,测试的话去掉注释就行
list.h头文件
typedef struct node
{
DataType data;
struct node *next;
struct node *prior;
}SLNode;
//初始化
void ListInitiate(SLNode **head)
{
*head=(SLNode *)malloc(sizeof(SLNode));
(*head)->next=(*head);
(*head)->prior=(*head);
}
//插入函数
int ListInsert(SLNode *head,DataType x)
{
SLNode *s,*q,*p;
if(head->next==head)//刚开始只有头结点
{
s=(SLNode *)malloc(sizeof(SLNode));
s->data=x;
s->next=head;
head->next=s;
head->prior=s;
s->prior=head;
return 1;
}
else
{
p=(SLNode *)malloc(sizeof(SLNode));
p->data=x;
q=head->next;
while(q->next!=head)//找到表尾结点
{
q=q->next;
}
p->next=q->next;
q->next=p;
p->prior=q;
head->prior=p;
return 1;
}
}
//删除函数,指向那个结点删除哪个结点
int ListDelete(SLNode *head,SLNode *p)
{
SLNode *q=head;
while(q->next!=head)//最终让q指向表尾结点
{
q=q->next;
}
if(p!=q)//删除的不是表尾结点
{
p->prior->next=p->next;
p->next->prior=p->prior;
return 1;
}
else//删除表尾结点
{
q->prior->next=q->next;
q->next->prior=q->prior;
return 1;
}
}
//输出链表所有数据结点的值
int ListPrint(SLNode *head)
{
SLNode *p=head->next;
if(head->next==head)
{
printf("当前链表为空");
return 0;
}
else
{
while(p!=head)
{
printf("%d ",p->data);
p=p->next;
}
printf("\n");
return 1;
}
}
//判断链表是否对称
int Symmetry(SLNode *head)
{
//本算法从两头扫描循环双向链表,以判断链表是否对称
SLNode *p=head->next,*q=head->prior;
while(p!=q&&q->next!=p)
{
if(p->data==q->data)
{
p=p->next;
q=q->prior;
}
else
return 0; //否则,返回0
}
return 1; //比较结束后返回1
}
//将两个循环链表合并,第二个从头结点的下一个开始链在第一个后面
void ListMerge(SLNode *head1,SLNode *head2)
{
SLNode *p,*q;
p=head1->next;
q=head2->next;
while(p->next!=head1)//最终p指向head1表尾结点
{
p=p->next;
}
while(q->next!=head2)//最终q指向head2的表尾结点
{
q=q->next;
}
q->next=head1;
head1->prior=q;
p->next=head2->next;
head2->next->prior=p;
}
//遍历链表,每次删除值最小的元素,知道所有的元素都删除
int DeleteLeast(SLNode *head)
{
if(head->next==head)
{
printf("空链表");
return 0;
}
else
{
while(head->next!=head)
{
SLNode *p=head->next;
SLNode *min=p;
while(p->next!=head) //遍历链表,找到当前链表中值最小的结点
{
if(p->next->data<p->data)
{
min=p->next;
}
else
{
p=p->next;
}
}
printf("最小的值是%d\n",min->data);
ListDelete(head,min);
}
return 1;
}
}
源文件:test.cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
typedef int DataType;
#include"list.h"
int main()
{
// int x;
SLNode *head,*head1;
ListInitiate(&head);
ListInitiate(&head1);
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
ListInsert(head,i+1);
}
for(int j=5; j>0; j--)
{
ListInsert(head1, j);
}
/* ListInsert(head,4);
ListInsert(head,3);
ListInsert(head,2);
ListInsert(head,1);
*/
ListPrint(head);
ListPrint(head1);
/*
//合并两个链表
printf("\n");
ListMerge(head,head1);
printf("链表合并之后:");
ListPrint(head);
*/
/*
//判断链表是否对称
int number=Symmetry(head);
if(number)
{
printf("该链表是对称链表");
}
else
{
printf("该链表不是对称链表!!");
}
*/
//找到当前链表中值最下的元素结点的值
DeleteLeast(head);
ListPrint(head);
return 0;
}
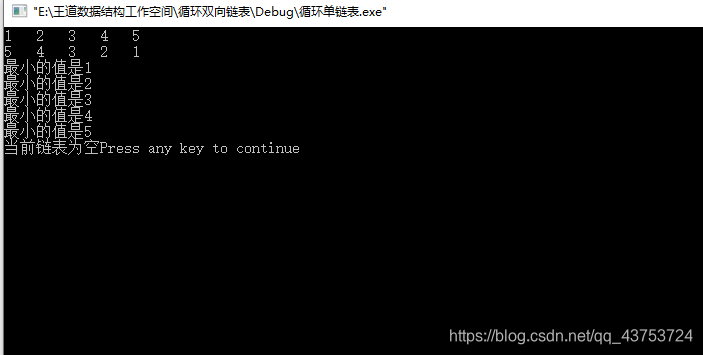
结果:(这里结果是将第一个链表的值遍历,每次删除最小的,知道链表为空)