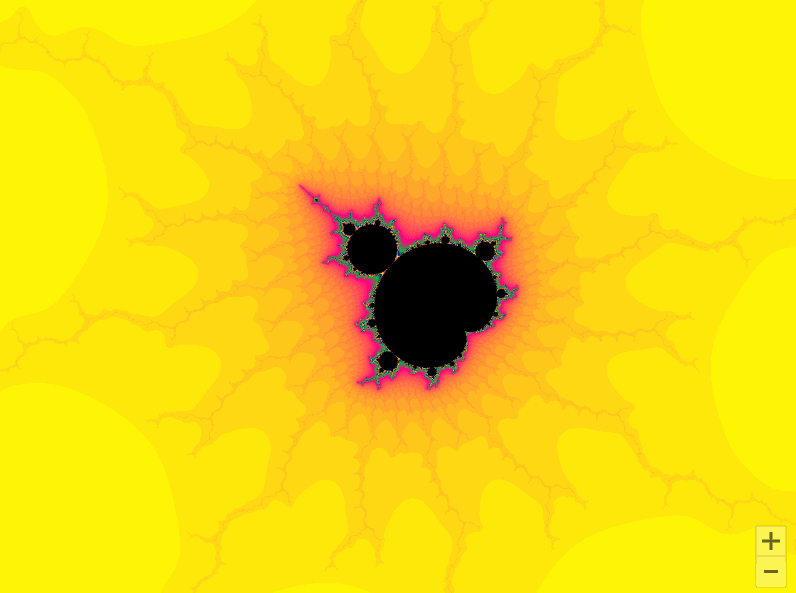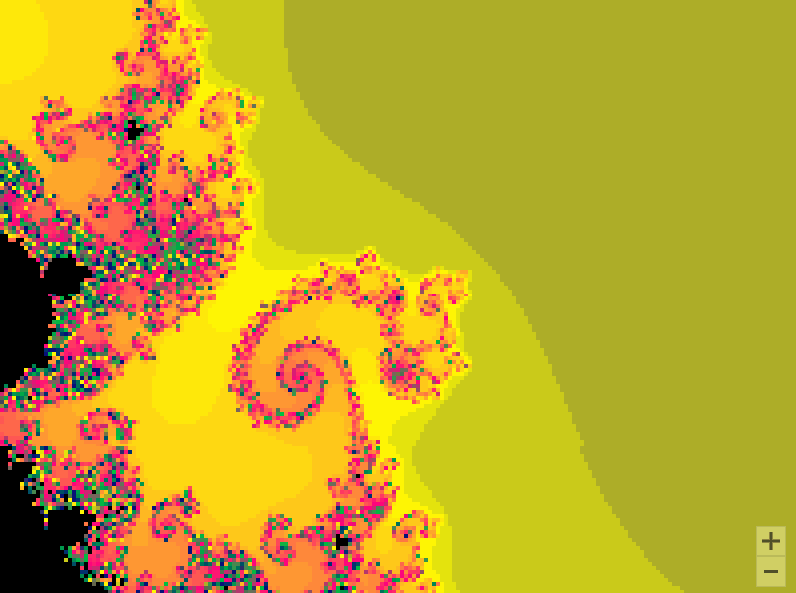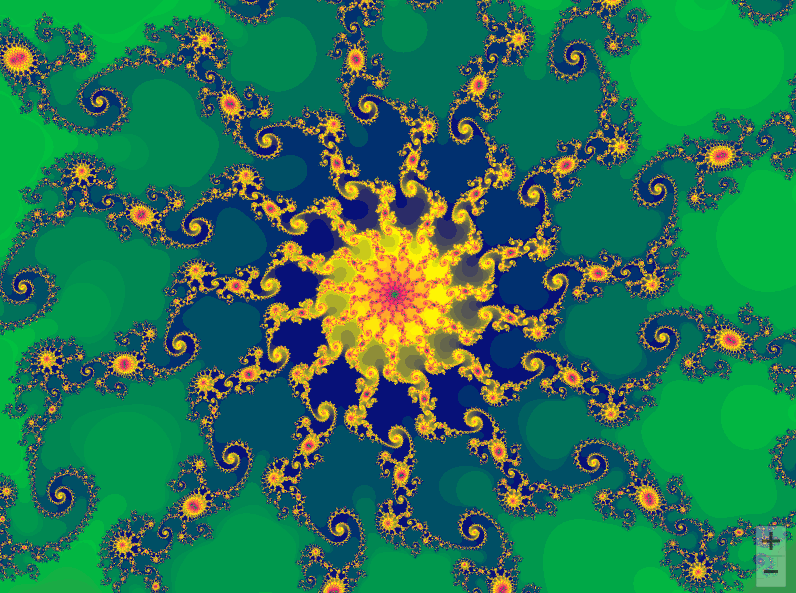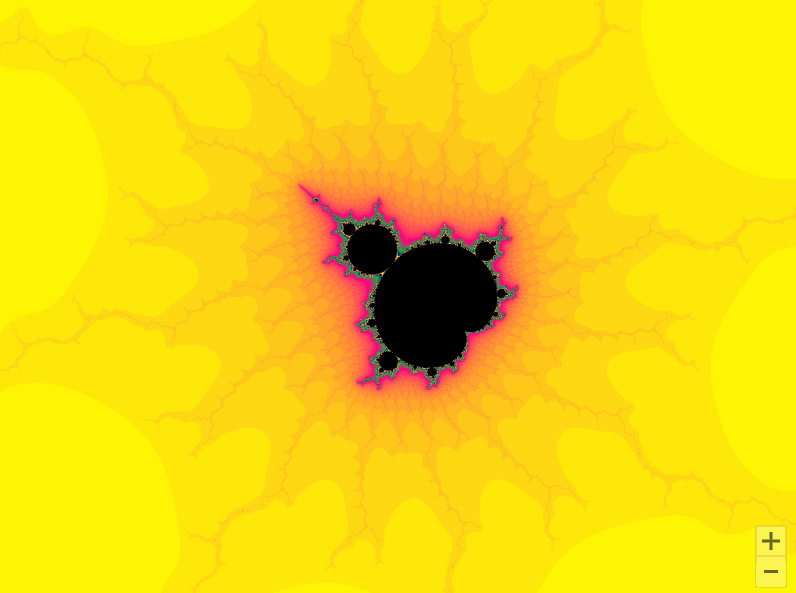
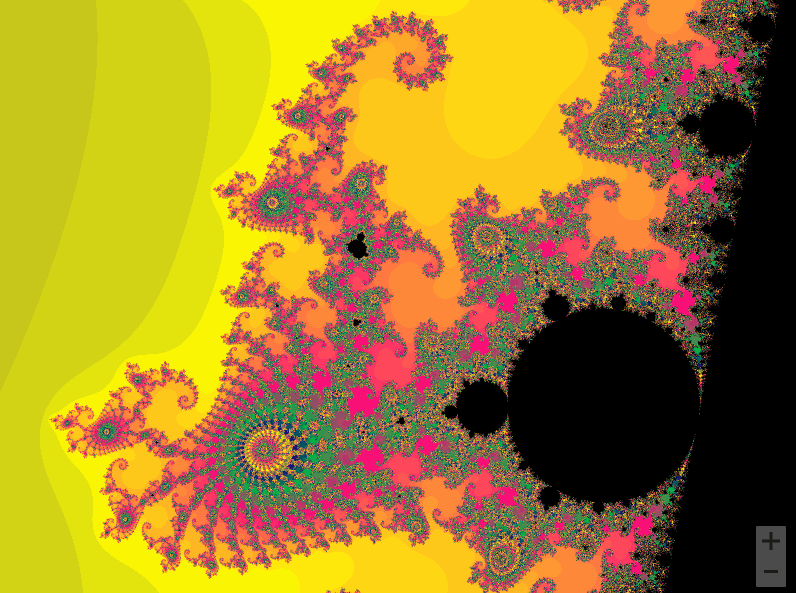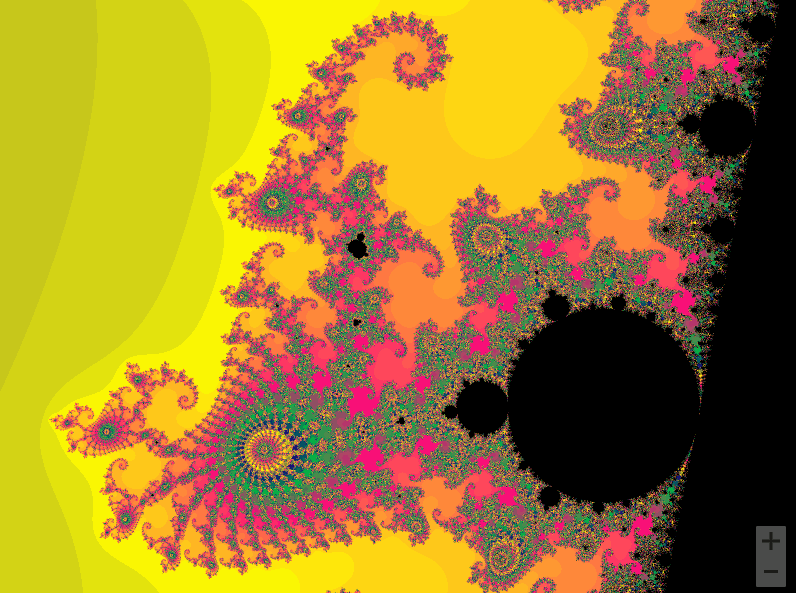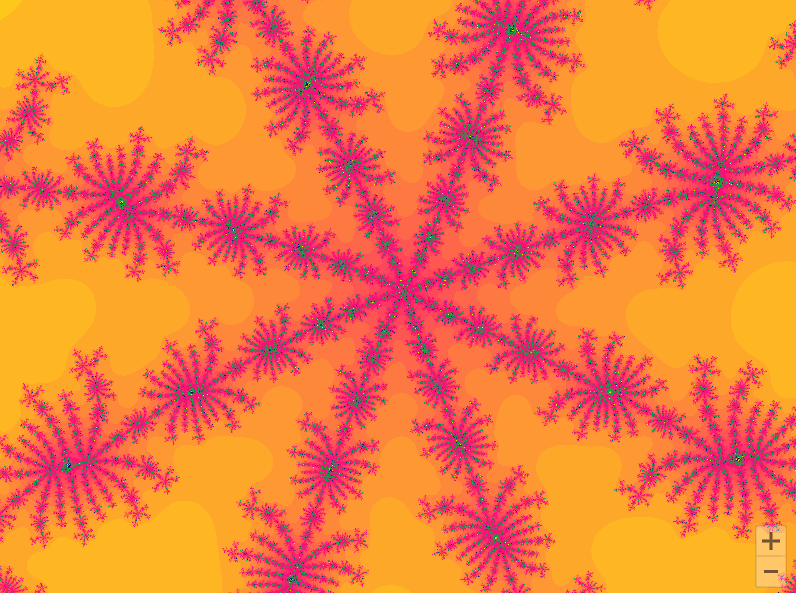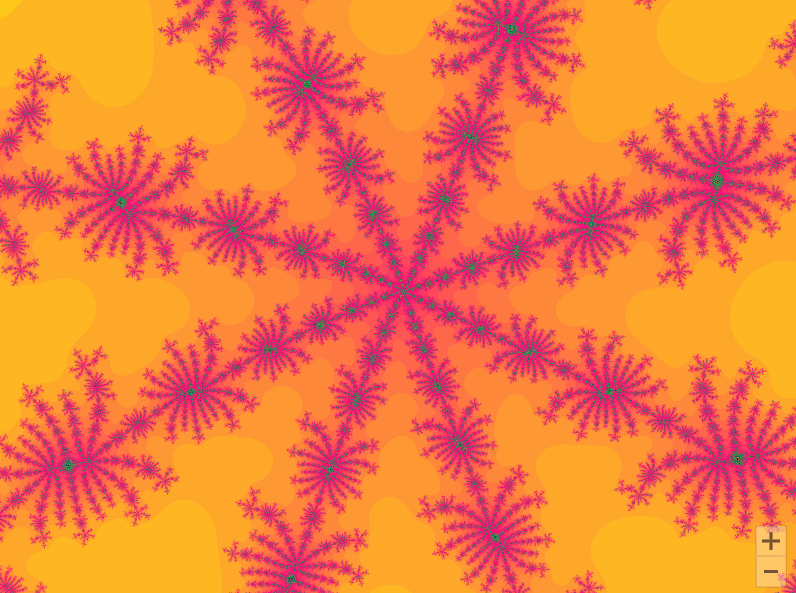
01曼德勃罗集合
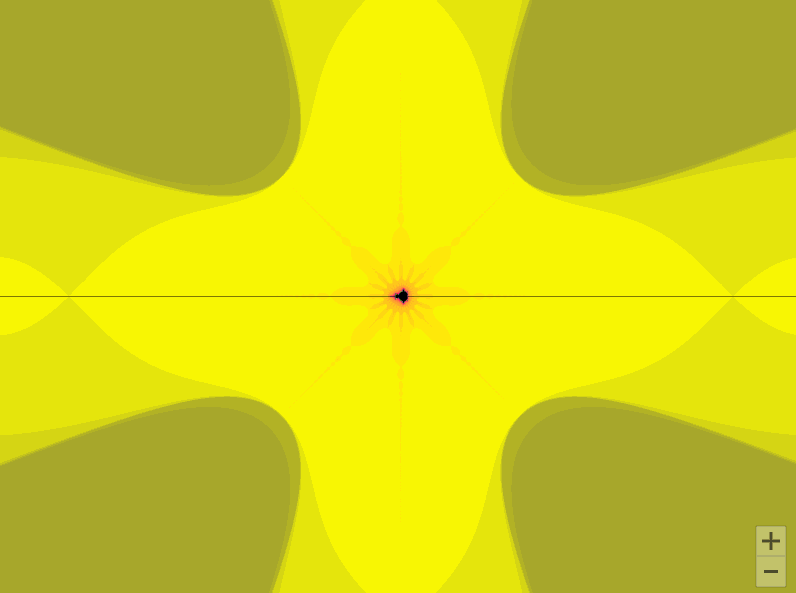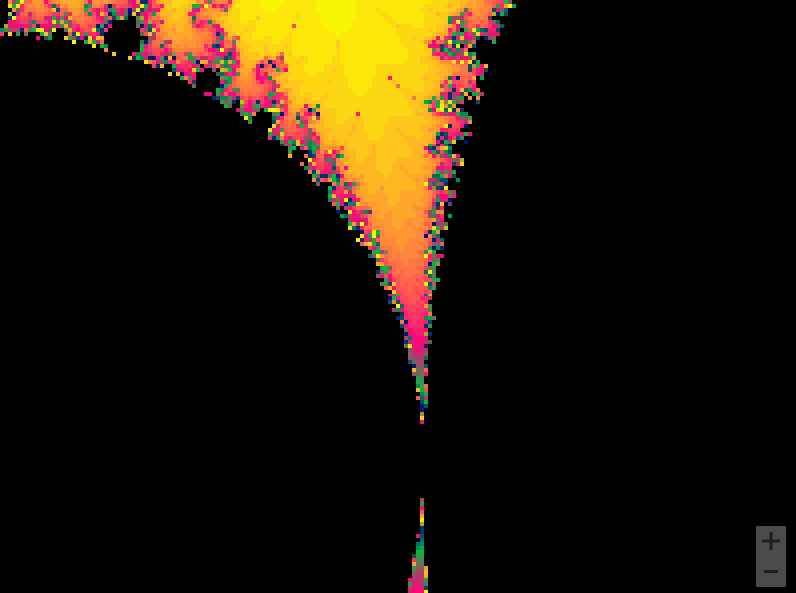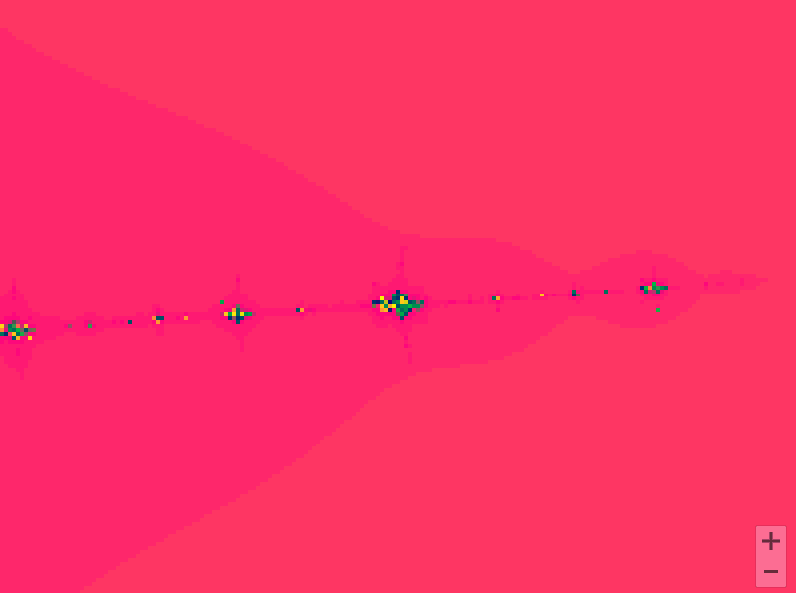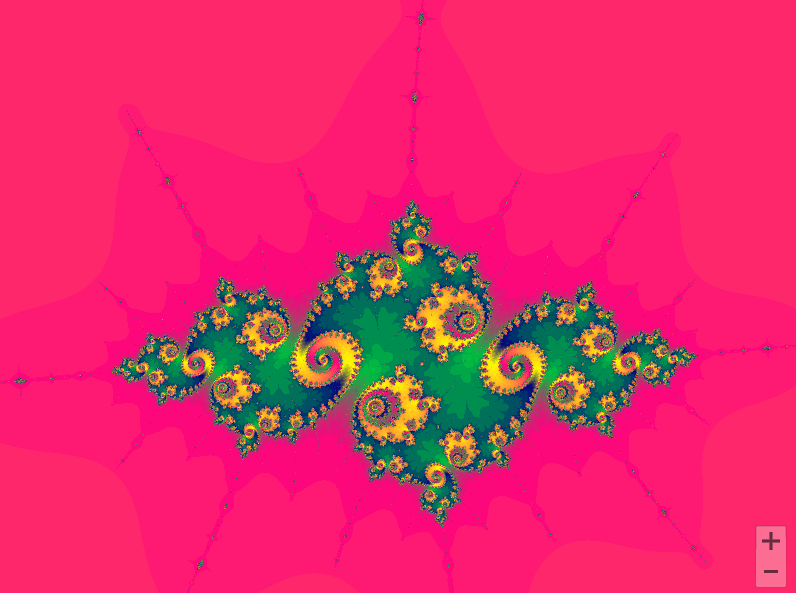
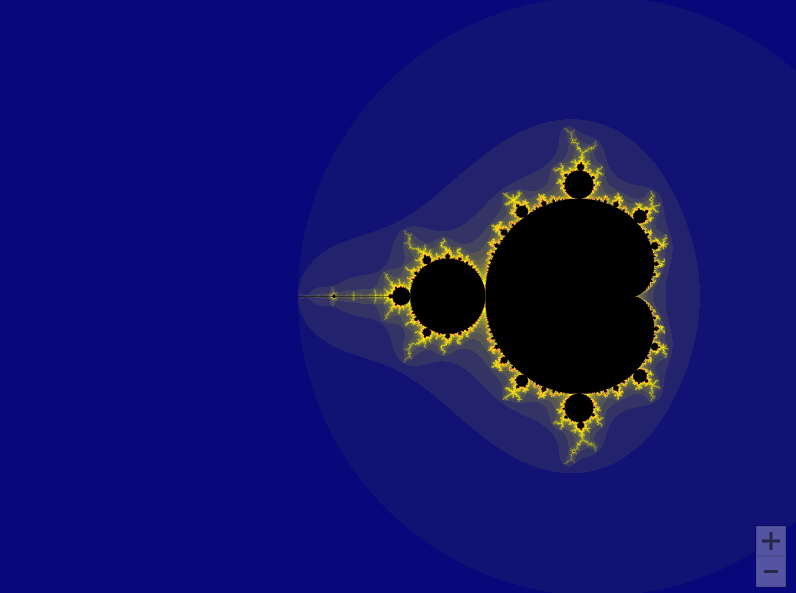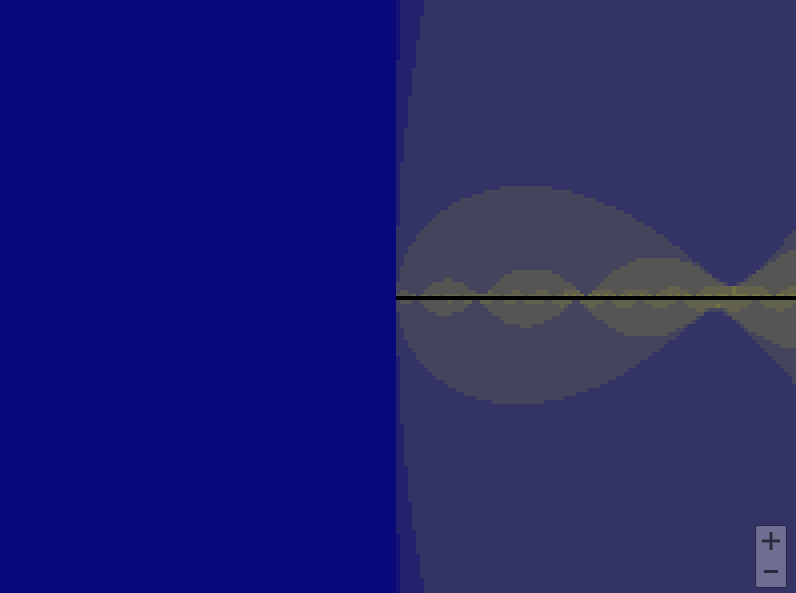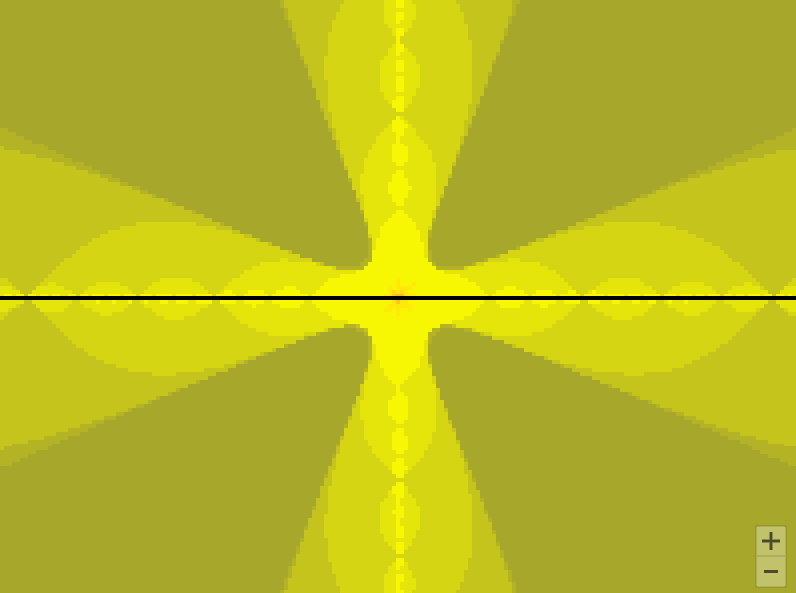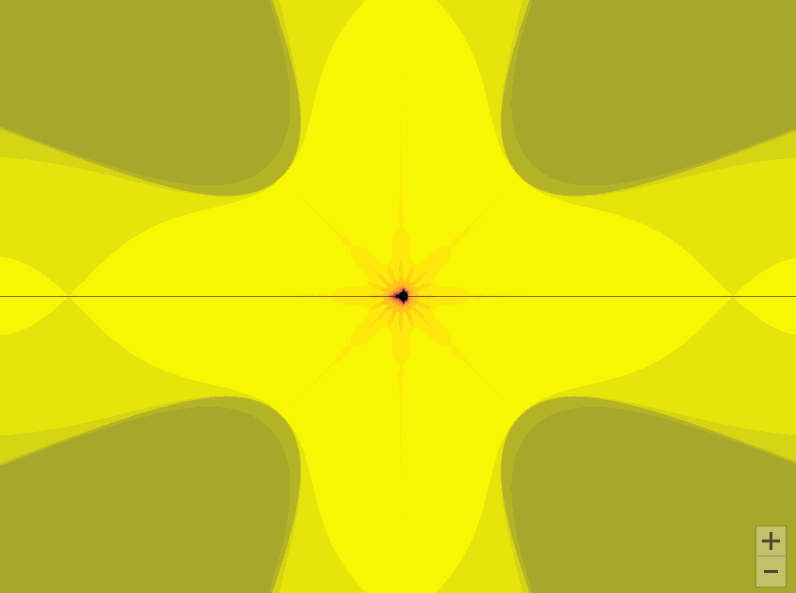
曼德勃罗集合就是复平面上的点 ,对于下面二次迭代方程收敛。


#!/usr/local/bin/python
# -*- coding: gbk -*-
#============================================================
# TEST1.PY -- by Dr. ZhuoQing 2020-06-10
#
# Note:
#============================================================
from headm import *
import pylab as pl
from matplotlib import cm
def iter_point(c):
z = c
for i in range(1, 100):
if abs(z) > 2: break
z = z*z+c
return i
def draw_mandelbrot(cx, cy, d):
x0, x1, y0, y1 = cx-d, cx+d, cy-d, cy+d
y, x = ogrid[y0:y1:200j, x0:x1:200j]
c = x + y*1j
start = time.process_time()
mandelbrot = frompyfunc(iter_point, 1, 1)(c).astype(float)
printf('Time=%f'%(time.process_time() - start))
pl.imshow(mandelbrot, cmap=cm.jet, extent=[x0, x1, y0, y1])
pl.gca().set_axis_off()
x,y = 0.27322626, 0.595153338
plt.subplot(231)
draw_mandelbrot(-0.5, 0, 1.5)
for i in range(2, 7):
pl.subplot(230+i)
draw_mandelbrot(x, y, 0.2**(i - 1))
pl.subplots_adjust(0.0, 0, 1, 1, 0.0, 0)
pl.show()
#------------------------------------------------------------
# END OF FILE : TEST1.PY
#============================================================



02分形树叶

#!/usr/local/bin/python
# -*- coding: gbk -*-
#============================================================
# TEST2.PY -- by Dr. ZhuoQing 2020-06-10
#
# Note:
#============================================================
from headm import *
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pl
import time
# 蕨类植物叶子的迭代函数和其概率值
eq1 = np.array([[0,0,0],[0,0.16,0]])
p1 = 0.01
eq2 = np.array([[0.2,-0.26,0],[0.23,0.22,1.6]])
p2 = 0.07
eq3 = np.array([[-0.15, 0.28, 0],[0.26,0.24,0.44]])
p3 = 0.07
eq4 = np.array([[0.85, 0.04, 0],[-0.04, 0.85, 1.6]])
p4 = 0.85
def ifs(p, eq, init, n):
"""
进行函数迭代
p: 每个函数的选择概率列表
eq: 迭代函数列表
init: 迭代初始点
n: 迭代次数
返回值: 每次迭代所得的X坐标数组, Y坐标数组, 计算所用的函数下标
"""
# 迭代向量的初始化
pos = np.ones(3, dtype=np.float)
pos[:2] = init
# 通过函数概率,计算函数的选择序列
p = np.add.accumulate(p)
rands = np.random.rand(n)
select = np.ones(n, dtype=np.int)*(n-1)
for i, x in enumerate(p[::-1]):
select[rands<x] = len(p)-i-1
# 结果的初始化
result = np.zeros((n,2), dtype=np.float)
c = np.zeros(n, dtype=np.float)
for i in range(n):
eqidx = select[i] # 所选的函数下标
tmp = np.dot(eq[eqidx], pos) # 进行迭代
pos[:2] = tmp # 更新迭代向量
# 保存结果
result[i] = tmp
c[i] = eqidx
return result[:,0], result[:, 1], c
start = time.clock()
x, y, c = ifs([p1,p2,p3,p4],[eq1,eq2,eq3,eq4], [0,0], 100000)
time.clock() - start
pl.figure(figsize=(6,6))
pl.subplot(121)
pl.scatter(x, y, s=1, c="g", marker="s", linewidths=0)
pl.axis("equal")
pl.axis("off")
pl.subplot(122)
pl.scatter(x, y, s=1,c = c, marker="s", linewidths=0)
pl.axis("equal")
pl.axis("off")
pl.subplots_adjust(left=0,right=1,bottom=0,top=1,wspace=0,hspace=0)
pl.gcf().patch.set_facecolor("#D3D3D3")
pl.show()
#------------------------------------------------------------
# END OF FILE : TEST2.PY
#============================================================