Spring Boot读取配置的 5 种方式
读取application文件
在application.yml或者properties文件中添加:
-
user.address=china user.company=demo user.name=让我康康
1、使用@Value注解读取
直接 代码如下:
package im.homeapi.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.omg.CORBA.PUBLIC_MEMBER;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value="/api")
public class HomeController {
@Value("${user.address}")
private String address;
@Value("${user.company}")
private String company;
@Value("${user.name}")
private String name;
//value 指定访问地址,method 指定请求类型
@RequestMapping(value = "/home",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String Home()
{
return "Hello Word";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/getConfig")
public String getConfig() {
return "获取的配置信息 :" +
" name=" + name +
" address=" + address +
" , company=" + company;
}
}
放到单独的配置类中读取:
package im.homeapi.entity;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class UserConfig {
@Value("${user.address}")
private String address;
@Value("${user.company}")
private String company;
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getCompany() {
return company;
}
public void setCompany(String company) {
this.company = company;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Value("${user.name}")
private String name;
}
调用如下:
@Autowired
private UserConfig userConfig;
//读取配置类
@RequestMapping(value = "/getConfigEntity")
public String getConfigEntity() {
return "获取的配置信息 :" +
" name=" + userConfig.getName() +
" address=" + userConfig.getAddress() +
" , company=" + userConfig.getCompany();
}运行结果如下:

2、使用@ConfigurationProperties注解读取方式
代码如下:
package im.homeapi.entity;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user")
public class UserConfig1 {
private String address;
private String company;
private String name;
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getCompany() {
return company;
}
public void setCompany(String company) {
this.company = company;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
调用:
package im.homeapi.controller;
import im.homeapi.entity.UserConfig;
import im.homeapi.entity.UserConfig1;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.omg.CORBA.PUBLIC_MEMBER;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value="/api")
public class ConfigController {
@Autowired
private UserConfig1 userConfig;
//读取配置类 ConfigurationProperties注解读取方式
@RequestMapping(value = "/getConfigEntity1")
public String getConfigEntity() {
return "获取的配置信息 :" +
" name=" + userConfig.getName() +
" address=" + userConfig.getAddress() +
" , company=" + userConfig.getCompany();
}
}
运行结果:

3、读取指定文件
3.1、@PropertySource+@Value注解读取方式
在resources下新建配置config/db-config.properties
注意:@PropertySource不支持yml文件读取。
db.username=root
db.password=123456如图:

代码:
package im.homeapi.entity;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@PropertySource(value = { "config/db-config.properties" })
public class DBConfig {
@Value("${db.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${db.password}")
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
调用代码:
package im.homeapi.controller;
import im.homeapi.entity.DBConfig;
import im.homeapi.entity.UserConfig;
import im.homeapi.entity.UserConfig1;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.omg.CORBA.PUBLIC_MEMBER;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value="/api")
public class DbController {
@Autowired
private DBConfig dbConfig;
//读取配置类 PropertySource+@Value注解读取方式
@RequestMapping(value = "/getConfigdb")
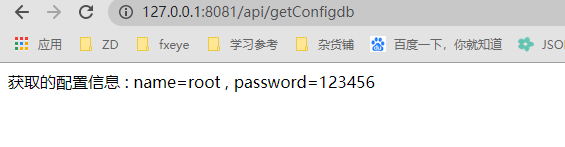
public String getConfigdb() {
return "获取的配置信息 :" +
" name=" + dbConfig.getUsername() +
" , password=" + dbConfig.getPassword();
}
}
运行结果:
3.2、@PropertySource+@ConfigurationProperties注解读取方式
代码:
package im.homeapi.entity;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "db")
@PropertySource(value = { "config/db-config.properties" })
public class DBconfig1 {
private String username;
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
调用代码:
@Autowired
private DBconfig1 dbConfig1;
//读取配置类 @PropertySource+@ConfigurationProperties注解读取方式
@RequestMapping(value = "/getConfigdb1")
public String getConfigdb1() {
return "获取的配置信息 :" +
" name=" + dbConfig1.getUsername() +
" , password=" + dbConfig1.getPassword();
}运行结果:

@Component 表示将该类标识为Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "db")用于绑定属性,其中prefix表示所绑定的属性的前缀。
@PropertySource(value = "config/db-config.properties")表示配置文件路径。
4、使用Environment读取
代码:
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
//读取配置类 CEnvironment读取方式
@RequestMapping(value = "/getConfigenv")
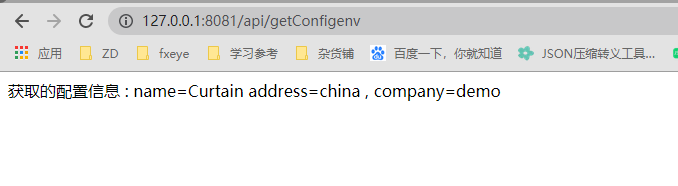
public String getConfigenv() {
return "获取的配置信息 :" +
" name=" + environment.getProperty("user.name") +
" address=" + environment.getProperty("user.address") +
" , company=" + environment.getProperty("user.company");
}运行结果:
总结
从以上示例来看,Spring Boot可以通过@PropertySource,@Value,@Environment,@ConfigurationProperties来绑定变量。