1、在app下创建一个自己用户认证文件,文件名随意,记得为.py文件
2、编辑该userauth.py文件

1 #!/usr/bin/env python 2 #coding:utf-8 3 from django.db import models 4 from django.contrib.auth.models import ( 5 BaseUserManager, AbstractBaseUser 6 ) 7 import django 8 9 class UserManager(BaseUserManager): 10 def create_user(self, email, name, password=None): 11 """ 12 Creates and saves a User with the given email, date of 13 birth and password. 14 """ 15 if not email: 16 raise ValueError('Users must have an email address') 17 18 user = self.model( 19 email=self.normalize_email(email), 20 name=name, 21 #token=token, 22 #department=department, 23 #tel=tel, 24 #memo=memo, 25 26 ) 27 28 user.set_password(password) 29 user.save(using=self._db) 30 return user 31 32 def create_superuser(self, email, name ,password): 33 """ 34 Creates and saves a superuser with the given email, date of 35 birth and password. 36 """ 37 user = self.create_user(email, 38 password=password, 39 name=name, 40 #token=token, 41 #department=department, 42 #tel=tel, 43 #memo=memo, 44 ) 45 user.is_admin = True 46 user.save(using=self._db) 47 return user 48 49 50 class UserProfile(AbstractBaseUser): 51 email = models.EmailField( 52 verbose_name='email address', 53 max_length=255, 54 unique=True, 55 ) 56 57 is_active = models.BooleanField(default=True) 58 is_admin = models.BooleanField(default=False) 59 60 name = models.CharField(u'名字', max_length=32) 61 token = models.CharField(u'token', max_length=128,default=None,blank=True,null=True) 62 department = models.CharField(u'部门', max_length=32,default=None,blank=True,null=True) 63 64 65 mobile = models.CharField(u'手机', max_length=32,default=None,blank=True,null=True) 66 67 memo = models.TextField(u'备注', blank=True,null=True,default=None) 68 date_joined = models.DateTimeField(blank=True, auto_now_add=True) 69 valid_begin_time = models.DateTimeField(default=django.utils.timezone.now) 70 valid_end_time = models.DateTimeField(blank=True,null=True) 71 72 73 74 75 76 USERNAME_FIELD = 'email' #定义email为用户名 77 #REQUIRED_FIELDS = ['name','token','department','tel','mobile','memo'] 78 REQUIRED_FIELDS = ['name'] 79 80 def get_full_name(self): 81 # The user is identified by their email address 82 return self.email 83 84 def get_short_name(self): 85 # The user is identified by their email address 86 return self.email 87 88 def __str__(self): # __unicode__ on Python 2 89 return self.email 90 91 def has_perm(self, perm, obj=None): 92 "Does the user have a specific permission?" 93 # Simplest possible answer: Yes, always 94 return True 95 def has_perms(self, perm, obj=None): 96 "Does the user have a specific permission?" 97 # Simplest possible answer: Yes, always 98 return True 99 def has_module_perms(self, app_label): 100 "Does the user have permissions to view the app `app_label`?" 101 # Simplest possible answer: Yes, always 102 return True 103 104 @property 105 def is_staff(self): 106 "Is the user a member of staff?" 107 # Simplest possible answer: All admins are staff 108 return self.is_admin 109 110 class Meta: 111 verbose_name = u'用户信息' 112 verbose_name_plural = u"用户信息" 113 def __unicode__(self): 114 return self.name 115 116 objects = UserManager()
3、在models中导入该文件中的UserProfile类

4、admin中注册
编辑admin.py文件

1 #_*_coding:utf8_*_ 2 from django.contrib import admin 3 4 # Register your models here. 5 6 from django import forms 7 from django.contrib import admin 8 from django.contrib.auth.models import Group 9 from django.contrib.auth.admin import UserAdmin 10 from django.contrib.auth.forms import ReadOnlyPasswordHashField 11 import models 12 13 from userauth import UserProfile 14 from django.contrib.auth import forms as auth_form 15 16 class UserCreationForm(forms.ModelForm): 17 """A form for creating new users. Includes all the required 18 fields, plus a repeated password.""" 19 password1 = forms.CharField(label='Password', widget=forms.PasswordInput) 20 password2 = forms.CharField(label='Password confirmation', widget=forms.PasswordInput) 21 22 class Meta: 23 model = UserProfile 24 fields = ('email','token') 25 26 def clean_password2(self): 27 # Check that the two password entries match 28 password1 = self.cleaned_data.get("password1") 29 password2 = self.cleaned_data.get("password2") 30 if password1 and password2 and password1 != password2: 31 raise forms.ValidationError("Passwords don't match") 32 return password2 33 34 def save(self, commit=True): 35 # Save the provided password in hashed format 36 user = super(UserCreationForm, self).save(commit=False) 37 user.set_password(self.cleaned_data["password1"]) 38 if commit: 39 user.save() 40 return user 41 42 43 class UserChangeForm(forms.ModelForm): 44 """A form for updating users. Includes all the fields on 45 the user, but replaces the password field with admin's 46 password hash display field. 47 """ 48 password = ReadOnlyPasswordHashField(label="Password", 49 help_text=("Raw passwords are not stored, so there is no way to see " 50 "this user's password, but you can change the password " 51 "using <a href=\"password/\">this form</a>.")) 52 53 class Meta: 54 model = UserProfile 55 fields = ('email', 'password','is_active', 'is_admin') 56 57 def clean_password(self): 58 # Regardless of what the user provides, return the initial value. 59 # This is done here, rather than on the field, because the 60 # field does not have access to the initial value 61 return self.initial["password"] 62 class UserProfileAdmin(UserAdmin): 63 # The forms to add and change user instances 64 form = UserChangeForm 65 add_form = UserCreationForm 66 67 # The fields to be used in displaying the User model. 68 # These override the definitions on the base UserAdmin 69 # that reference specific fields on auth.User. 70 list_display = ('id','email','is_admin','is_active') 71 list_filter = ('is_admin',) 72 fieldsets = ( 73 (None, {'fields': ('email', 'password')}), 74 ('Personal info', {'fields': ('department','name','mobile','memo')}), 75 ('API TOKEN info', {'fields': ('token',)}), 76 ('Permissions', {'fields': ('is_active','is_admin')}), 77 ('账户有效期', {'fields': ('valid_begin_time','valid_end_time')}), 78 ) 79 # add_fieldsets is not a standard ModelAdmin attribute. UserAdmin 80 # overrides get_fieldsets to use this attribute when creating a user. 81 add_fieldsets = ( 82 (None, { 83 'classes': ('wide',), 84 'fields': ('email', 'password1', 'password2','is_active','is_admin')} 85 ), 86 ) 87 search_fields = ('email',) 88 ordering = ('email',) 89 filter_horizontal = () 90 91 # Now register the new UserAdmin... 92 admin.site.register(models.UserProfile,UserProfileAdmin) 93 admin.site.unregister(Group)
#这里需注意,第51行 "using <a href=\"password/\">this form</a>.")) #这是django1.8的写法,如果>1.8的话需要修改成 "using <a href=\"../password/\">this form</a>.")) 否则在admin后台点击修改密码的话会提示404找不到页面
5、在settings告诉django使用我们自己定义的用户认证系统
修改settings,结尾添加
AUTH_USER_MODEL = 'database.UserProfile'
#database为app名称 #UserProfile为我们刚才在userauth.py中创建的类名称
6、同步数据库
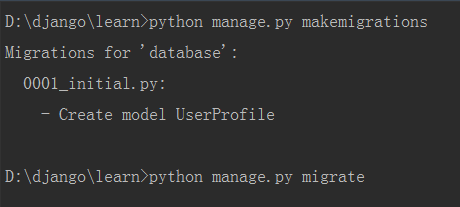
可以看到创建了UserProfile表,这样就可以直接使用django的用户认证功能
7、创建超级用户
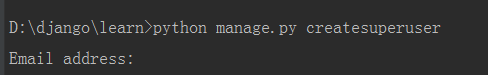
可以看到提示已经跟django默认的不一样了,以email地址作为用户名
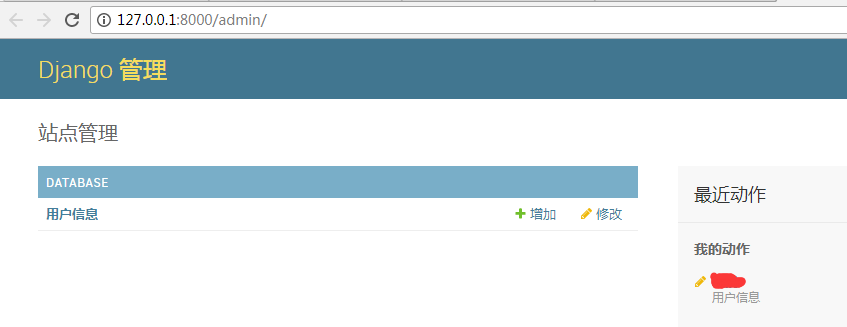
8、此时访问django admin