Tomcat服务器顶层结构
先看一下Tomcat架构图
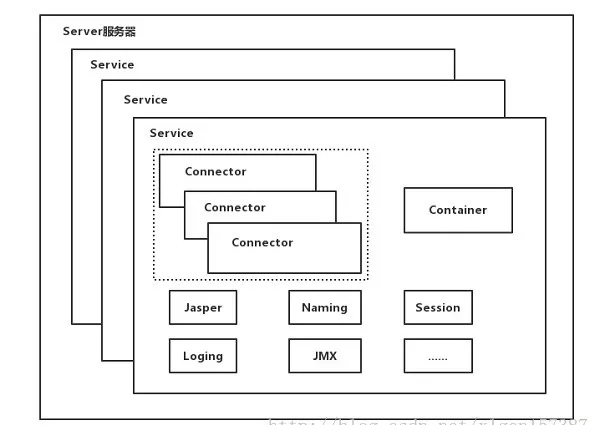
Tomcat中最顶层的容器是Server,代表着整个服务器,从上图中可以看出,一个Server可以包含至少一个Service,用于具体提供服务。 Service主要包含两个部分:Connector和Container。
Connector用于处理链接相关的事情,并提供Socket与Request和Response相关的转化;
Container用于封装和管理Servlet,以及具体处理Request请求;
一个Tomcat中只有一个Server,一个Server可以包含多个Service,一个Service只有一个Container,但是可以有多个Connectors,这是因为一个服务可以有多个连接,如同时提供http和https链接,也可以提供向相同协议不同端口的连接。
多个 Connector 和一个 Container 就形成了一个 Service,有了 Service 就可以对外提供服务了,但是 Service 还要一个生存的环境,必须要有人能够给她生命、掌握其生死大权,那就非 Server 莫属了。所以整个 Tomcat 的生命周期由 Server 控制。
server.xml内容
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--
Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
(the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
--><!-- Note: A "Server" is not itself a "Container", so you may not
define subcomponents such as "Valves" at this level.
Documentation at /docs/config/server.html
--><Server port="8005" shutdown="SHUTDOWN">
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.startup.VersionLoggerListener"/>
<!-- Security listener. Documentation at /docs/config/listeners.html
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.security.SecurityListener" />
-->
<!--APR library loader. Documentation at /docs/apr.html -->
<Listener SSLEngine="on" className="org.apache.catalina.core.AprLifecycleListener"/>
<!-- Prevent memory leaks due to use of particular java/javax APIs-->
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.JreMemoryLeakPreventionListener"/>
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.mbeans.GlobalResourcesLifecycleListener"/>
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.ThreadLocalLeakPreventionListener"/>
<!-- Global JNDI resources
Documentation at /docs/jndi-resources-howto.html
-->
<GlobalNamingResources>
<!-- Editable user database that can also be used by
UserDatabaseRealm to authenticate users
-->
<Resource auth="Container" description="User database that can be updated and saved" factory="org.apache.catalina.users.MemoryUserDatabaseFactory" name="UserDatabase" pathname="conf/tomcat-users.xml" type="org.apache.catalina.UserDatabase"/>
</GlobalNamingResources>
<!-- A "Service" is a collection of one or more "Connectors" that share
a single "Container" Note: A "Service" is not itself a "Container",
so you may not define subcomponents such as "Valves" at this level.
Documentation at /docs/config/service.html
-->
<Service name="Catalina">
<!--The connectors can use a shared executor, you can define one or more named thread pools-->
<!--
<Executor name="tomcatThreadPool" namePrefix="catalina-exec-"
maxThreads="150" minSpareThreads="4"/>
-->
<!-- A "Connector" represents an endpoint by which requests are received
and responses are returned. Documentation at :
Java HTTP Connector: /docs/config/http.html (blocking & non-blocking)
Java AJP Connector: /docs/config/ajp.html
APR (HTTP/AJP) Connector: /docs/apr.html
Define a non-SSL/TLS HTTP/1.1 Connector on port 8080
-->
<Connector connectionTimeout="20000" port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1" redirectPort="8443"/>
<!-- A "Connector" using the shared thread pool-->
<!--
<Connector executor="tomcatThreadPool"
port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443" />
-->
<!-- Define a SSL/TLS HTTP/1.1 Connector on port 8443
This connector uses the NIO implementation that requires the JSSE
style configuration. When using the APR/native implementation, the
OpenSSL style configuration is required as described in the APR/native
documentation -->
<!--
<Connector port="8443" protocol="org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol"
maxThreads="150" SSLEnabled="true" scheme="https" secure="true"
clientAuth="false" sslProtocol="TLS" />
-->
<!-- Define an AJP 1.3 Connector on port 8009 -->
<Connector port="8009" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectPort="8443"/>
<!-- An Engine represents the entry point (within Catalina) that processes
every request. The Engine implementation for Tomcat stand alone
analyzes the HTTP headers included with the request, and passes them
on to the appropriate Host (virtual host).
Documentation at /docs/config/engine.html -->
<!-- You should set jvmRoute to support load-balancing via AJP ie :
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost" jvmRoute="jvm1">
-->
<Engine defaultHost="localhost" name="Catalina">
<!--For clustering, please take a look at documentation at:
/docs/cluster-howto.html (simple how to)
/docs/config/cluster.html (reference documentation) -->
<!--
<Cluster className="org.apache.catalina.ha.tcp.SimpleTcpCluster"/>
-->
<!-- Use the LockOutRealm to prevent attempts to guess user passwords
via a brute-force attack -->
<Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.LockOutRealm">
<!-- This Realm uses the UserDatabase configured in the global JNDI
resources under the key "UserDatabase". Any edits
that are performed against this UserDatabase are immediately
available for use by the Realm. -->
<Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.UserDatabaseRealm" resourceName="UserDatabase"/>
</Realm>
<Host appBase="webapps" autoDeploy="true" name="localhost" unpackWARs="true">
<!-- SingleSignOn valve, share authentication between web applications
Documentation at: /docs/config/valve.html -->
<!--
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.authenticator.SingleSignOn" />
-->
<!-- Access log processes all example.
Documentation at: /docs/config/valve.html
Note: The pattern used is equivalent to using pattern="common" -->
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve" directory="logs" pattern="%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b" prefix="localhost_access_log" suffix=".txt"/>
<!-- 最后一次编辑的项目是BDQX-->
<Context docBase="BDQX" path="/BDQX" reloadable="true" source="org.eclipse.jst.jee.server:BDQX"/></Host>
</Engine>
</Service>
</Server>
Tomcat链接方式
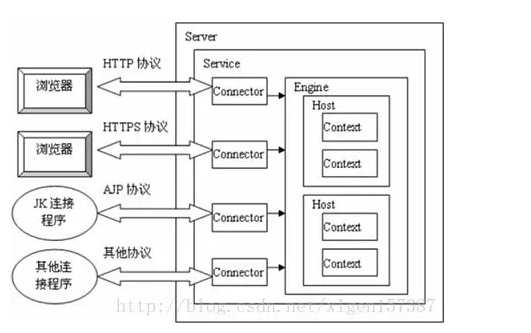
多个 Connector 和一个 Container 就形成了一个 Service,有了 Service 就可以对外提供服务了,但是 Service 还要一个生存的环境,必须要有人能够给她生命、掌握其生死大权,那就非 Server 莫属了!所以整个 Tomcat 的生命周期由 Server 控制。
Tomcat顶层架构小结
- Tomcat中只有一个Server,一个Server可以有多个Service,一个Service可以有多个Connector和一个Container;
- Server掌管着整个Tomcat的生死大权;
- Service 是对外提供服务的;
- Connector用于接受请求并将请求封装成Request和Response来具体处理;
- Container用于封装和管理Servlet,以及具体处理request请求; 由上述内容我们大致可以知道一个请求发送到Tomcat之后,首先经过Service然后会交给我们的Connector,Connector用于接收请求并将接收的请求封装为Request和Response来具体处理,Request和Response封装完之后再交由Container进行处理,Container处理完请求之后再返回给Connector,最后在由Connector通过Socket将处理的结果返回给客户端,这样整个请求的就处理完了!
Connector最底层使用的是Socket来进行连接的,Request和Response是按照HTTP协议来封装的,所以Connector同时需要实现TCP/IP协议和HTTP协议!
Container架构分析
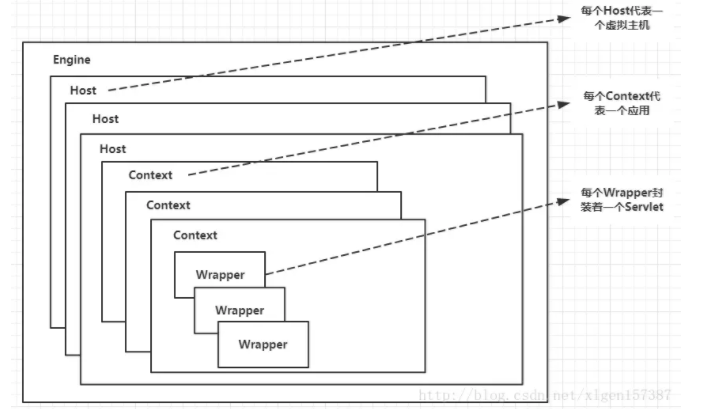
4个子容器的作用分别是:
- Engine:引擎,用来管理多个站点,一个Service最多只能有一个Engine;
- Host:代表一个站点,也可以叫虚拟主机,通过配置Host就可以添加站点;
- Context:代表一个应用程序,对应着平时开发的一套程序,或者一个WEB-INF目录以及下面的web.xml文件;
- Wrapper:每一Wrapper封装着一个Servlet;
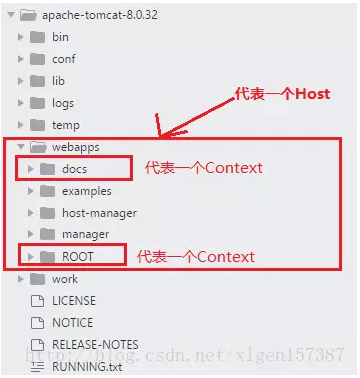
Context和Host的区别是Context表示一个应用,我们的Tomcat中默认的配置下webapps下的每一个文件夹目录都是一个Context,其中ROOT目录中存放着主应用,其他目录存放着子应用,而整个webapps就是一个Host站点。
我们访问应用Context的时候,如果是ROOT下的则直接使用域名就可以访问,例如:www.ledouit.com,如果是Host(webapps)下的其他应用,则可以使用www.ledouit.com/docs进行访问,当然默认指定的根应用(ROOT)是可以进行设定的,只不过Host站点下默认的主营用是ROOT目录下的。