在Spring的自动注入的源码中,我遇到了内省(Introspector),Spring会先找到全部的set和is方法,然后执行这些set和is方法注入属性。
如何找到这些set,is方法,JDK提供了内省(Introspector)API。
先看一个案例:
public class Bean { int age; String name; public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "Bean{" + "age=" + age + ", name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } }
import java.beans.BeanInfo; import java.beans.Introspector; import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class MyIntrospector { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Bean bean = new Bean(); BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Bean.class); PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors(); for (int i = 0; i < propertyDescriptors.length; i++) { Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptors[i].getWriteMethod(); if (propertyDescriptors[i].getName().equals("age")) { writeMethod.invoke(bean, 11); } if (propertyDescriptors[i].getName().equals("name")) { writeMethod.invoke(bean, "丽丽"); } } System.out.println(bean); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
运行结果:
从运行结果我们可以看到我们注入了属性。
分析:
代码中第一句:Introspector.getBeanInfo(Bean.class) 部分将你的对象变成一个BeanInfo。
BeanInfo 中存在几个比较重要的方法。
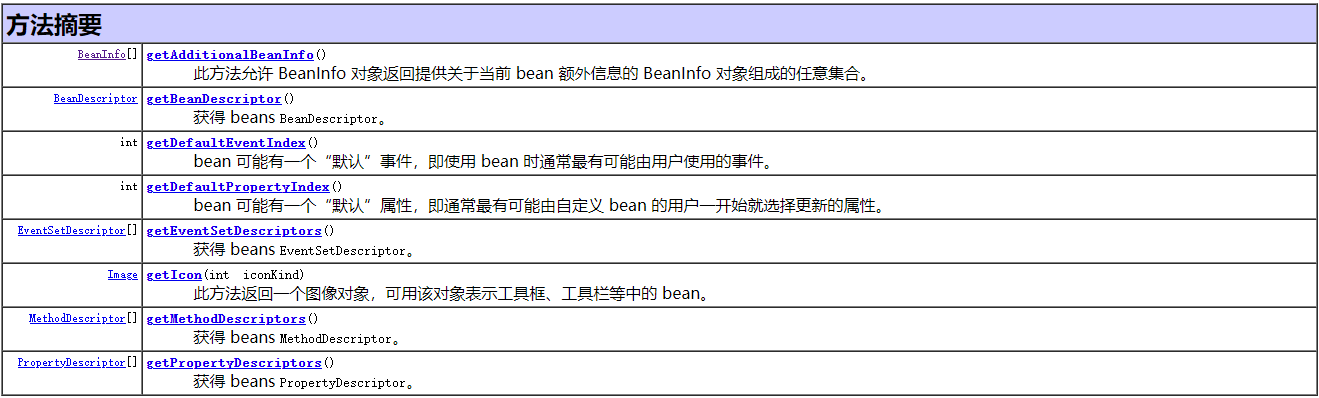
案例中使用了获取属性描述器的 getPropertyDescriptors(),该方法就是获取get/set/is 等描述属性的方法。
下面我的目的是为了注入属性,所以我需要的set方法,故通过getWriteMethod() 方法获取了set 和 is 方法。
然后通过 writeMethod.invoke(bean, 11); 方法将属性注入。
我修改一下代码:
public class Bean { int age; String name; public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAgedddd(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "Bean{" + "age=" + age + ", name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } }
import java.beans.BeanInfo; import java.beans.Introspector; import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class MyIntrospector { public static void main(String[] args) { try { Bean bean = new Bean(); BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Bean.class); PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors(); for (int i = 0; i < propertyDescriptors.length; i++) { Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptors[i].getWriteMethod(); if(writeMethod != null){ if (propertyDescriptors[i].getName().equals("age")) { writeMethod.invoke(bean, 11); } if (propertyDescriptors[i].getName().equals("name")) { writeMethod.invoke(bean, "丽丽"); } } } System.out.println(bean); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
修改点为:bean 里面的setAge 方法改成了 setAgedddd.
运行结果:

age 并没有注入,说明 propertyDescriptors[i].getName() 是获取了set方法去掉set部分的名字。
当然一般我们现在不会这样写代码。 我想这也是Java 为什么有set,get 这个约定。
我们在来看看属性描述器的API
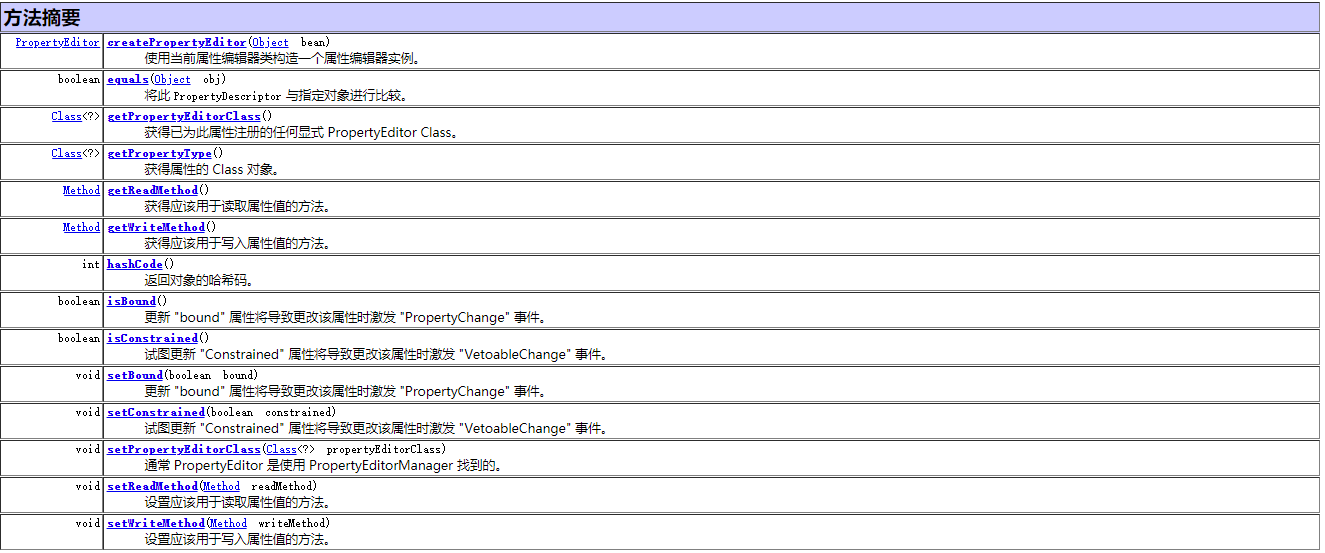
案例里面的getName 在其父类的ApI中。上述代码运行过程中,还会发现一个name "class" 的一个属性描述器,原因是因为该內省机制会将父类的属性描述也一并获取下来。
顶级父类Object 正好有一个getClass 方法。
这里我们主要说明了属性描述器,还是方法描述器,原理一致,不再多讲。
结束语:內省需要我们遵守Java的约定,但是这个又仅仅只是约定,可以不遵守的,所以这个內省机制个人觉得还是需要jdk出一个强制规则。不然总觉得漏洞比较大。