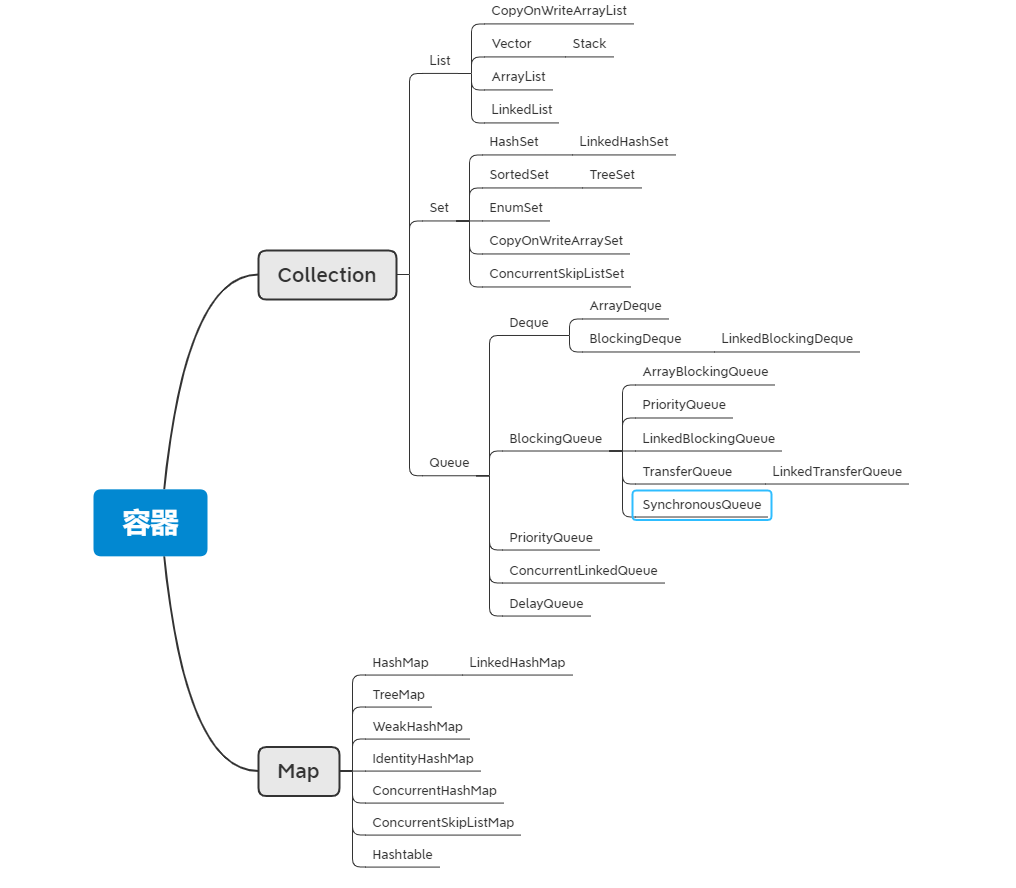
一,基础概念 什么是线程 进程里最小的执行单元,程序里不通的执行路径 线程实现 继承thread 实现runnable 实现callable 用过线程池创建 ExecutorServices=Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); s.execute(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());}); 常用方法 yield 指让出一下CPU sleep 指休眠固定时间 join 只让固定线程插队执行 线程状态 new runnable包含两个状态ready running timedWaiting t.sleep(500); o.wait(500); t.join(500); LockSupport.parkNanos(500); LockSupport.parkUntil(200); waiting o.wait(); o.notify(); o.notifyAll(); t.join(t1); LockSupport.park(); LockSupport.unpark(t1); blocked 线程同步 synchronized,保证数据一致性 方法 锁一个方法 public class T{ privateint count=10; public synchronized void m(){ count--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"count="+count); } } 对象加锁 synchronized(this)锁当前对象 public class T{ private int count=10; private Object o=new Object(); public void m(){ synchronized(o){ count--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"count="+count); } } } synchronized锁升级 偏向锁,对象为32位,前两位记录线程id,有线程进来的话进行判断,有过线程id相同,就继续执行 自旋锁,如果线程id不同就等待,自旋10圈 重量级锁,自旋10圈之后直接请求操作系统 执行时间短,线程数少用自旋锁 执行时间长,线程数多,用系统锁 synchronized同步方法与非同步方法 可以相互调用 synchronized锁重入 都是可重入的,sleep,yield,join 异常与锁 异常发生后释放锁,不影响其他线程 volatile 保证线程间可见,MESI缓存一致性协议 防止指令重排序 AtomicXXX 本身是线程安全的,针对加锁专门设计的 wait notify(面试高频) 等待,唤醒 可以替代为LockSupport的park和unpark 二,JUC同步工具 cas自旋原理 AtomicInteger底层是调用的UnSafe调用的是CompareAndSetI方法 ReentrantLock可重入锁 和syncronized一样的功能,只是在需要加锁的代码前写lock.lock()在finally里面释放锁lock.unlock() public class T01_ReentrantLock2 { Lock lock= new ReentrantLock(); void m1(){ try { lock.lock();//synchronized (this) for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { SleepUtil.sleepSecond(1); System.out.println(i); } }finally { lock.unlock(); } } void m2(){ try { lock.lock(); System.out.println("m2..."); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { T01_ReentrantLock2 r1= new T01_ReentrantLock2(); new Thread(r1::m1).start(); SleepUtil.sleepSecond(1); new Thread(r1::m2).start(); } } ReentrantLock有tryLock()方法进行尝试锁定,用返回值判断是否锁定,不管锁定与否,方法继续执行 public class T01_ReentrantLock3 { Lock lock= new ReentrantLock(); void m1(){ try { //加锁 lock.lock();//synchronized (this) for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { SleepUtil.sleepSecond(1); System.out.println(i); } }finally { //finally解锁 lock.unlock(); } } /** * ReentrantLock比较强大,可以使用tryLock进行尝试锁定,不管锁定与否,方法继续执行, * 可以根据ReentrantLock返回值来判断是否锁定 * 也可以指定truLock的时间 */ void m2(){ boolean locked =false; try { //尝试获取锁 locked = this.lock.tryLock(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS); System.out.println("m2..."+locked); //lock.lockInterruptibly();//可以对interrupt方法做出响应 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //finally解锁 if (locked)lock.unlock(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { T01_ReentrantLock3 r1= new T01_ReentrantLock3(); new Thread(r1::m1).start(); SleepUtil.sleepSecond(1); new Thread(r1::m2).start(); //t2.interrupt();//打断线程2的等待 } } condition条件等待与通知 一个condition等待与通知,与wait(),notify类似 private Lock lock=new ReentrantLock(); private Condition condition=lock.newCondition(); condition.await(); condition.signalAll(); 多个condition等待与通知和生产者消费者类似 /** * 写一个固定容量同步容器,拥有put()get()方法,以及getCount方法, * 能够支持两个生产者线程以及10个消费者线程阻塞调用 * @param <T> */ public class MyContainer2<T> { final private LinkedList<T> lists= new LinkedList<>(); //初始化容器 final private int MAX=10;//最大容量 private int count=0;//表示当前容量 private Lock lock= new ReentrantLock(); private Condition producer=lock.newCondition(); private Condition consumer=lock.newCondition(); /** * 生产者 * @param t */ public void put(T t){ try { lock.lock(); while (lists.size()==MAX){//用while的目的是要保证list的size不能为负数 producer.await();//生产者等待 } lists.add(t); ++count; consumer.signalAll();//通知消费者线程进行消费 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } /** * 消费者 * @return */ public T get(){ T t= null; try { lock.lock(); while (lists.size()==0) {//用while的目的是要保证list的size不能为负数 consumer.await(); } t=lists.removeFirst();//消费第一个 count--; producer.signalAll();//通知生产者线程进行生产 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } return t; } public static void main(String[] args) { MyContainer2<String> c= new MyContainer2(); //启动消费者线程 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { new Thread(()->{ for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) { System.out.println(c.get()); } },"c"+i).start(); } SleepUtil.sleepSecond(2); //启动生产者线程 for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { new Thread(()->{ for (int j = 0; j < 25; j++) { c.put(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+j); } },"p"+i).start(); } } } CountDownLatch门闩 latch.countDown();主要用于线程间倒数 public class T05_CountDownLatch { volatile List list = new ArrayList(); // volatile List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>()); public void add (Object o){ list.add(o); } public int size(){ return list.size(); } public static void main(String[] args) { T05_CountDownLatch c= new T05_CountDownLatch(); CountDownLatch latch= new CountDownLatch(1); new Thread(()->{ System.out.println("t2 启动"); if (c.size()!=5){ try { latch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("t2 结束"); },"t2").start(); SleepUtil.sleepSecond(1); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { c.add(new Object()); System.out.println("add "+i); if (c.size()==5){ latch.countDown(); //释放锁,让t2执行 try { latch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } SleepUtil.sleepMillis(100); } },"t1").start(); } } CyclicBarrier分批执行,每一批执行一次 /** * 一个栅栏,循环使用,什么时候人满了,栅栏打开,放大家过关 * CyclicBarrier循环栅栏,一直监听,到达指定容量,就放行 * barrier.await();监听是否到达设置的容量20,够20人就发一次车,不到就一直等着 */ public class T07_TestCyclicBarrier { public static void main(String[] args) { CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(20, () -> System.out.println("满人发车")); for (int i = 0; i < 105; i++) { new Thread(()->{ try { barrier.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (BrokenBarrierException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }).start(); } } } 三,同步容器 各个容器的特性 list可以按索引位置取数据 set去重 map键值对存取数据 让容器变得安全(加锁工具类) Collections.synchronizedList(list); Collections.synchronizedSet(set); Collections.synchronizedMap(map); Queue为高并发设计
四,线程池 线程池7个参数介绍 ThreadPoolExecutor tpe=new ThreadPoolExecutor( 2,//核心线程数 4,//最大线程数 60,//生存时间 TimeUnit.SECONDS,//生存时间的单位 new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(4),//任务队列,最多可以装4个任务 Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),//线程工厂,可以指定线程名称 new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy() /**拒绝策略,四种: *abort,抛异常 *discard,扔掉,不抛异常 *discardOldest,扔掉排队时间最久的 *callerRuns调用者处理服务 */ ); for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { tpe.execute(new Task(i)); } //缓存线程池,没有核心线程数,最大线程数可以有好多,60秒没有调用就回收线程,使用默认工厂和拒绝策略,来一个任务我给你启动一个线程, ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); Future<String> submit = service.submit(call); //单线程线程池,保证扔进去的任务按顺序执行 ExecutorService s = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); s.execute(()->{System.out.println(j+Thread.currentThread().getName());}) //固定大小线程池,可以并行计算,把计算任务分成多个小段执行 ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4); MyTask t1 = new MyTask(1, 80000); //MyTask实现了Callable Future<List<Integer>> f1 = service.submit(t1); //定时任务线程池 scheduleAtFixedRate间隔多长时间在一定的频率上来执行这个任务 第一个参数是delay 第二个参数是间隔多长时间period 第三个参数是时间单位timeunit ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(4); service.scheduleAtFixedRate(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());},0,500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); MyTask t1 = new MyTask(1, 80000); Future<List<Integer>> f1 = service.submit(t1); ExecutorService service = Executors.newWorkStealingPool(); service.execute(new R(1000)); ForkJoinPool public class T12_ForkJoinPool { static int[] nums = new int[1000000]; static final int MAX_NUM = 50000; static Random r = new Random(); static { for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++) { nums[i] = r.nextInt(100); } System.out.println("---" + Arrays.stream(nums).sum()); //stream api } static class AddTask extends RecursiveAction { int start, end; public AddTask(int start, int end) { this.start = start; this.end = end; } @Override protected void compute() { if (end-start<=MAX_NUM){ long sum=0L; for (int i = start ; i <end ; i++) { sum+=nums[i]; } System.out.println("from "+start+" to: "+end+" = "+sum); }else { int middle = start+(end-start)/2; AddTask addTask1= new AddTask(start, middle); AddTask addTask2= new AddTask(middle, end); addTask1.fork(); addTask2.fork(); } } } static class AddTaskRet extends RecursiveTask<Long> { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; int start, end; public AddTaskRet(int start, int end) { this.start = start; this.end = end; } @Override protected Long compute() { if (end-start<=MAX_NUM){ long sum=0L; for (int i = start ; i <end ; i++) { sum+=nums[i]; } return sum; } int middle = start+(end-start)/2; AddTaskRet addTask1= new AddTaskRet(start, middle); AddTaskRet addTask2= new AddTaskRet(middle, end); addTask1.fork(); addTask2.fork(); return addTask1.join()+addTask2.join(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { T12_ForkJoinPool temp = new T12_ForkJoinPool(); ForkJoinPool fjp = new ForkJoinPool(); AddTaskRet task= new AddTaskRet(0, nums.length); fjp.execute(task); Long result = task.join(); System.out.println(result); } } 线程池execute和submit用法 1.execute提交的是Runnable类型的任务,而submit提交的是Callable或者Runnable类型的任务 2.execute的提交没有返回值,而submit的提交会返回一个Future类型的对象 3.execute提交的时候,如果有异常,就会直接抛出异常,而submit在遇到异常的时候,通常不会立马抛出异常,而是会将异常暂时存储起来,等待你调用Future.get()方法的时候,才会抛出异常 五,JMH(Java Microbenchmark Harness) 创建JMH测试 新建maven项目,引入依赖 <dependencies> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.openjdk.jmh/jmh-core --> <dependency> <groupId>org.openjdk.jmh</groupId> <artifactId>jmh-core</artifactId> <version>1.21</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.openjdk.jmh/jmh-generator-annprocess --> <dependency> <groupId>org.openjdk.jmh</groupId> <artifactId>jmh-generator-annprocess</artifactId> <version>1.21</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> idea安装JMH插件 JMH plugin v1.0.3 由于用到了注解,打开运行程序注解配置:compiler -> Annotation Processors -> Enable Annotation Processing 定义需要测试类PS (ParallelStream) public class PS { static List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>(); static { Random r = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) nums.add(1000000 + r.nextInt(1000000)); } static void foreach() { nums.forEach(v->isPrime(v)); } static void parallel() { nums.parallelStream().forEach(PS::isPrime); } static boolean isPrime(int num) { for(int i=2; i<=num/2; i++) { if(num % i == 0) return false; } return true; } } 写单元测试(在test下,与ps类同路径) public class PSTest { @Benchmark public void testForEach() { PS.foreach(); } } 运行测试类,如果遇到下面的错误: Exception while trying to acquire the JMH lock (C:\WINDOWS\/jmh.lock): C:\WINDOWS\jmh.lock (拒绝访问。), exiting. Use -Djmh.ignoreLock=true to forcefully continue. 这个错误是因为JMH运行需要访问系统的TMP目录,解决办法是: 打开RunConfiguration -> Environment Variables -> include system environment viables 阅读测试报告 1. Warmup 预热,由于JVM中对于特定代码会存在优化(本地化),预热对于测试结果很重要 2. Mesurement 总共执行多少次测试 3. Timeout 4. Threads 线程数,由fork指定 5. Benchmark mode 基准测试的模式 6. Benchmark 测试哪一段代码 六,Disruptor Disruptor的特点 对比ConcurrentLinkedQueue : 链表实现 JDK中没有ConcurrentArrayQueue Disruptor是数组实现的 无锁,高并发,使用环形Buffer,直接覆盖(不用清除)旧的数据,降低GC频率 实现了基于事件的生产者消费者模式(观察者模式) RingBuffer 环形队列 RingBuffer的序号,指向下一个可用的元素 采用数组实现,没有首尾指针 对比ConcurrentLinkedQueue,用数组实现的速度更快 假如长度为8,当添加到第12个元素的时候在哪个序号上呢?用12%8决定 当Buffer被填满的时候到底是覆盖还是等待,由Producer决定 长度设为2的n次幂,利于二进制计算,例如:12%8 = 12 & (8 - 1) pos = num & (size -1) Disruptor开发步骤 1. 定义Event - 队列中需要处理的元素 2. 定义Event工厂,用于填充队列 这里牵扯到效率问题:disruptor初始化的时候,会调用Event工厂,对ringBuffer进行内存的提前分配 GC产频率会降低 3. 定义EventHandler(消费者),处理容器中的元素 源码地址: https://github.com/koukay/JUC.git https://github.com/koukay/TestJMH.git