1、读取和输出字节码
1 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
2 //会从classpath中查询该类
3 CtClass cc = pool.get("test.Rectangle");
4 //设置.Rectangle的父类
5 cc.setSuperclass(pool.get("test.Point"));
6 //输出.Rectangle.class文件到该目录中
7 cc.writeFile("c://");
8 //输出成二进制格式
9 //byte[] b=cc.toBytecode();
10 //输出并加载class 类,默认加载到当前线程的ClassLoader中,也可以选择输出的ClassLoader。
11 //Class clazz=cc.toClass();
这里可以看出,Javassist的加载是依靠ClassPool类,输出方式支持三种。
2、新增Class
1 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
2 CtClass cc = pool.makeClass("Point");
3 //新增方法
4 cc.addMethod(m);
5 //新增Field
6 cc.addField(f);
从上面可以看出,对Class的修改主要是依赖于CtClass类。API也比较清楚和简单。
3、冻结Class
当CtClass 调用writeFile()、toClass()、toBytecode() 这些方法的时候,Javassist会冻结CtClass Object,对CtClass object的修改将不允许。这个主要是为了警告开发者该类已经被加载,而JVM是不允许重新加载该类的。如果要突破该限制,方法如下:
1 CtClasss cc = ...; 2 : 3 cc.writeFile(); 4 cc.defrost(); 5 cc.setSuperclass(...); // OK since the class is not frozen.
当 ClassPool.doPruning=true的时候,Javassist 在CtClass object被冻结时,会释放存储在ClassPool对应的数据。这样做可以减少javassist的内存消耗。默认情况ClassPool.doPruning=false。例如
1 CtClasss cc = ...; 2 cc.stopPruning(true); 3 : 4 cc.writeFile(); // convert to a class file. 5 // cc没有被释放
提示:当调试时,可以调用debugWriteFile(),该方法不会导致CtClass被释放。
4、Class 搜索路径
从上面可以看出Class 的载入是依靠ClassPool,而ClassPool.getDefault() 方法的搜索Classpath 只是搜索JVM的同路径下的class。当一个程序运行在JBoss或者Tomcat下,ClassPool Object 可能找到用户的classes。Javassist 提供了四种动态加载classpath的方法。如下
1 //默认加载方式如pool.insertClassPath(new ClassClassPath(this.getClass()));
2 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
3 //从file加载classpath
4 pool.insertClassPath("/usr/local/javalib")
5 //从URL中加载
6 ClassPath cp = new URLClassPath("www.javassist.org", 80, "/java/", "org.javassist.");
7 pool.insertClassPath(cp);
8 //从byte[] 中加载
9 byte[] b = a byte array;
10 String name = class name;
11 cp.insertClassPath(new ByteArrayClassPath(name, b));
12 //可以从输入流中加载class
13 InputStream ins = an input stream for reading a class file;
14 CtClass cc = cp.makeClass(ins);
5、ClassPool
5.1 减少内存溢出
ClassPool是一个CtClass objects的装载容器,当加载了CtClass object后,是不会被ClassPool释放的(默认情况下),这个是因为CtClass object 有可能在下个阶段会被用到,当加载过多的CtClass object的时候,会造成OutOfMemory的异常。为了避免这个异常,javassist提供几种方法,一种是在上面提到的 ClassPool.doPruning这个参数,还有一种方法是调用CtClass.detach()方法,可以把CtClass object 从ClassPool中移除。例如:
1 CtClass cc = ... ; 2 cc.writeFile(); 3 cc.detach();
另外一种方法是不用默认的ClassPool即不用 ClassPool.getDefault()这个方式来生成,这样当ClassPool没被引用的时候,JVM的垃圾收集会收集该类。例如
1 //ClassPool(true) 会默认加载Jvm的ClassPath 2 ClassPool cp = new ClassPool(true); 3 // if needed, append an extra search path by appendClassPath()
5.2 级联ClassPools
javassist支持级联的ClassPool,即类似于继承。例如:
1 ClassPool parent = ClassPool.getDefault();
2 ClassPool child = new ClassPool(parent);
3 child.insertClassPath("./classes");
5.3 修改已有Class的name以创建一个新的Class
当调用setName方法时,会直接修改已有的Class的类名,如果再次使用旧的类名,则会重新在classpath路径下加载。例如:
1 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
2 CtClass cc = pool.get("Point");
3 cc.setName("Pair");
4 //重新在classpath加载
5 CtClass cc1 = pool.get("Point");
对于一个被冻结(Frozen)的CtClass object ,是不可以修改class name的,如果需要修改,则可以重新加载,例如:
1 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
2 CtClass cc = pool.get("Point");
3 cc.writeFile(); // has frozened
4 //cc.setName("Pair"); wrong since writeFile() has been called.
5 CtClass cc2 = pool.getAndRename("Point", "Pair");
6、Class loader
上面也提到,javassist同个Class是不能在同个ClassLoader中加载两次的,所以在输出CtClass的时候需要注意下,例如:
1 // 当Hello未加载的时候,下面是可以运行的。
2 ClassPool cp = ClassPool.getDefault();
3 CtClass cc = cp.get("Hello");
4 Class c = cc.toClass();
5 //下面这种情况,由于Hello2已加载,所以会出错
6 Hello2 h=new Hello2();
7 CtClass cc2 = cp.get("Hello2");
8 Class c2 = cc.toClass();//这里会抛出java.lang.LinkageError 异常
9 //解决加载问题,可以指定一个未加载的ClassLoader
10 Class c3 = cc.toClass(new MyClassLoader());
6.1 使用javassist.Loader
从上面可以看到,如果在同一个ClassLoader加载两次Class抛出异常,为了方便javassist也提供一个Classloader供使用,例如
1 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
2 Loader cl = new Loader(pool);
3 CtClass ct = pool.get("test.Rectangle");
4 ct.setSuperclass(pool.get("test.Point"));
5 Class c = cl.loadClass("test.Rectangle");
6 Object rect = c.newInstance(); :
为了方便监听Javassist自带的ClassLoader的生命周期,javassist也提供了一个listener,可以监听ClassLoader的生命周期,例如:
1 //Translator 为监听器
2 public class MyTranslator implements Translator {
3 void start(ClassPool pool)
4 throws NotFoundException, CannotCompileException {}
5 void onLoad(ClassPool pool, String classname)
6 throws NotFoundException, CannotCompileException
7 {
8 CtClass cc = pool.get(classname);
9 cc.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC);
10 }
11 }
12 //示例
13 public class Main2 {
14 public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
15 Translator t = new MyTranslator();
16 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
17 Loader cl = new Loader();
18 cl.addTranslator(pool, t);
19 cl.run("MyApp", args);
20 }
21 }
22 //输出
23 % java Main2 arg1 arg2...
6.2 修改系统Class
由JVM规范可知,system classloader 是比其他classloader 是优先加载的,而system classloader 主要是加载系统Class,所以要修改系统Class,如果默认参数运行程序是不可能修改的,如果需要修改也有一些办法,即在运行时加入-Xbootclasspath/p: 参数的意义可以参考其他文件。下面修改String的例子如下:
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass cc = pool.get("java.lang.String");
CtField f = new CtField(CtClass.intType, "hiddenValue", cc);
f.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC);
cc.addField(f);
cc.writeFile(".");
//运行脚本
% java -Xbootclasspath/p:. MyApp arg1 arg2...
6.3 动态重载Class
如果JVM运行时开启JPDA(Java Platform Debugger Architecture),则Class是运行被动态重新载入的。具体方式可以参考java.lang.Instrument。javassist也提供了一个运行期重载Class的方法,具体可以看API 中的javassist.tools.HotSwapper。
7、Introspection和定制
javassist封装了很多很方便的方法以供使用,大部分使用只需要用这些API即可,如果不能满足,Javassist也提供了一个低层的API(具体参考javassist.bytecode 包)来修改原始的Class。
7.1 插入source 文本在方法体前或者后
CtMethod 和CtConstructor 提供了 insertBefore()、insertAfter()和 addCatch()方法,它们可以插入一个souce文本到存在的方法的相应的位置。javassist 包含了一个简单的编译器解析这souce文本成二进制插入到相应的方法体里。javassist 还支持插入一个代码段到指定的行数,前提是该行数需要在class 文件里含有。插入的source 可以关联fields 和methods,也可以关联方法的参数。但是关联方法参数的时,需要在程序编译时加上 -g 选项(该选项可以把本地变量的声明保存在class 文件中,默认是不加这个参数的。)。因为默认一般不加这个参数,所以Javassist也提供了一些特殊的变量来代表方法参数:$1,$2,$args...要注意的是,插入的source文本中不能引用方法本地变量的声明,但是可以允许声明一个新的方法本地变量,除非在程序编译时加入-g选项。方法的特殊变量说明:
| $0, $1, $2, ... | this and actual parameters |
| $args | An array of parameters. The type of $args is Object[]. |
| $$ | All actual parameters.For example, m($$) is equivalent to m($1,$2,...) |
| $cflow(...) | cflow variable |
| $r | The result type. It is used in a cast expression. |
| $w | The wrapper type. It is used in a cast expression. |
| $_ | The resulting value |
| $sig | An array of java.lang.Class objects representing the formal parameter types |
| $type | A java.lang.Class object representing the formal result type. |
| $class | A java.lang.Class object representing the class currently edited. |
7.1.1 $0, $1, $2, ...
$0代码的是this,$1代表方法参数的第一个参数、$2代表方法参数的第二个参数,以此类推,$N代表是方法参数的第N个。例如:
1 //实际方法
2 void move(int dx, int dy)
3 //javassist
4 CtMethod m = cc.getDeclaredMethod("move");
5 //打印dx,和dy
6 m.insertBefore("{ System.out.println($1); System.out.println($2); }");
注意:如果javassist改变了$1的值,那实际参数值也会改变。
7.1.2 $args
$args 指的是方法所有参数的数组,类似Object[],如果参数中含有基本类型,则会转成其包装类型。需要注意的时候,$args[0]对应的是$1,而不是$0,$0!=$args[0],$0=this。
7.1.3 $$
$$是所有方法参数的简写,主要用在方法调用上。例如:
1 //原方法 2 move(String a,String b) 3 move($$) 相当于move($1,$2) 4 如果新增一个方法,方法含有move的所有参数,则可以这些写: 5 exMove($$, context) 相当于 exMove($1, $2, context)
7.1.4 $cflow
$cflow意思为控制流(control flow),是一个只读的变量,值为一个方法调用的深度。例如:
1 //原方法
2 int fact(int n) {
3 if (n <= 1)
4 return n;
5 else
6 return n * fact(n - 1);
7 }
8 //javassist调用
9 CtMethod cm = ...;
10 //这里代表使用了cflow
11 cm.useCflow("fact");
12 //这里用了cflow,说明当深度为0的时候,就是开始当第一次调用fact的方法的时候,打印方法的第一个参数
13 cm.insertBefore("if ($cflow(fact) == 0)"
14 + " System.out.println(\"fact \" + $1);");
7.1.5 $r
指的是方法返回值的类型,主要用在类型的转型上。例如:
Object result = ... ;
$_ = ($r)result;
如果返回值为基本类型的包装类型,则该值会自动转成基本类型,如返回值为Integer,则$r为int。如果返回值为void,则该值为null。
7.1.6 $w
$w代表一个包装类型。主要用在转型上。比如:Integer i = ($w)5; 如果该类型不是基本类型,则会忽略。
7.1.7 $_
$_代表的是方法的返回值。
7.1.8 $sig
$sig指的是方法参数的类型(Class)数组,数组的顺序为参数的顺序。
7.1.9 $class
$class 指的是this的类型(Class)。也就是$0的类型。
7.1.10 addCatch()
addCatch() 指的是在方法中加入try catch 块,需要注意的是,必须在插入的代码中,加入return 值。$e代表异常值。比如:
1 CtMethod m = ...;
2 CtClass etype = ClassPool.getDefault().get("java.io.IOException");
3 m.addCatch("{ System.out.println($e); throw $e; }", etype);
实际代码如下:
1 try {
2 the original method body
3 }
4 catch (java.io.IOException e) {
5 System.out.println(e);
6 throw e;
7 }
8、修改方法体
CtMethod 和CtConstructor 提供了 setBody() 的方法,可以替换方法或者构造函数里的所有内容。
支持的变量有:
| $0, $1, $2, ... | this and actual parameters |
| $args | An array of parameters. The type of $args is Object[]. |
| $$ | All actual parameters.For example, m($$) is equivalent to m($1,$2,...) |
| $cflow(...) | cflow variable |
| $r | The result type. It is used in a cast expression. |
| $w | The wrapper type. It is used in a cast expression. |
| $sig | An array of java.lang.Class objects representing the formal parameter types |
| $type | A java.lang.Class object representing the formal result type. |
| $class | A java.lang.Class object representing the class currently edited. |
注意 $_变量不支持。
8.1 替换方法中存在的source
javassist 允许修改方法里的其中一个表达式,javassist.expr.ExprEditor 这个class 可以替换该表达式。例如:
1 CtMethod cm = ... ;
2 cm.instrument(
3 new ExprEditor() {
4 public void edit(MethodCall m)
5 throws CannotCompileException
6 {
7 if (m.getClassName().equals("Point")
8 && m.getMethodName().equals("move"))
9 m.replace("{ $1 = 0; $_ = $proceed($$); }");
10 }
11 });
注意: that the substituted code is not an expression but a statement or a block. It cannot be or contain a try-catch statement.
方法instrument() 可以用来搜索方法体里的内容。比如调用一个方法,field访问,对象创建等。如果你想在某个表达式前后插入方法,则修改的souce如下:
{ before-statements;
$_ = $proceed($$);
after-statements; }
8.2 javassist.expr.MethodCall
MethodCall代表的是一个方法的调用。用replace()方法可以对调用的方法进行替换。
| $0 | The target object of the method call. This is not equivalent to this, which represents the caller-side this object. $0 is null if the method is static. |
| $1, $2, ... | The parameters of the method call. |
| $_ | The resulting value of the method call. |
| $r | The result type of the method call. |
| $class | A java.lang.Class object representing the class declaring the method. |
| $sig | An array of java.lang.Class objects representing the formal parameter types |
| $type | A java.lang.Class object representing the formal result type. |
| $proceed | The name of the method originally called in the expression. |
注意:$w, $args 和 $$也是允许的。$0不是this,是只调用方法的Object。$proceed指的是一个特殊的语法,而不是一个String。
8.3 javassist.expr.ConstructorCall
ConstructorCall 指的是一个构造函数,比如:this()、super()的调用。ConstructorCall.replace()是用来用替换一个块当调用构造方法的时候。
| $0 | The target object of the constructor call. This is equivalent to this. |
| $1, $2, ... | The parameters of the constructor call. |
| $class | A java.lang.Class object representing the class declaring the constructor. |
| $sig | An array of java.lang.Class objects representing the formal parameter types. |
| $proceed | The name of the constructor originally called in the expression. |
$w, $args 和 $$ 也是允许的。
8.4 javassist.expr.FieldAccess
FieldAccess代表的是Field的访问类。
| $0 | The object containing the field accessed by the expression. This is not equivalent to this. this represents the object that the method including the expression is invoked on. $0 is null if the field is static. |
| $1 | The value that would be stored in the field if the expression is write access. Otherwise, $1 is not available. |
| $_ | The resulting value of the field access if the expression is read access. Otherwise, the value stored in $_ is discarded. |
| $r | The type of the field if the expression is read access. Otherwise, $r is void. |
| $class | A java.lang.Class object representing the class declaring the field. |
| $type | A java.lang.Class object representing the field type. |
| $proceed | The name of a virtual method executing the original field access. . |
$w, $args 和 $$ 也是允许的。
8.5 javassist.expr.NewExpr
NewExpr代表的是一个Object 的操作(但不包括数组的创建)。
| $0 | null |
| $1, $2, ... | The parameters to the constructor. |
| $_ | The resulting value of the object creation. A newly created object must be stored in this variable. |
| $r | The type of the created object. |
| $sig | An array of java.lang.Class objects representing the formal parameter types |
| $type | A java.lang.Class object representing the class of the created object. |
| $proceed | The name of a virtual method executing the original object creation. . |
$w, $args 和 $$ 也是允许的。
8.6 javassist.expr.NewArray
NewArray 代表的是数组的创建。
| $0 | null |
| $1, $2, ... | The size of each dimension. |
| $_ | The resulting value of the object creation. A newly created array must be stored in this variable. |
| $r | The type of the created object. |
| $type | A java.lang.Class object representing the class of the created array . |
| $proceed | The name of a virtual method executing the original array creation. . |
$w, $args 和 $$ 也是允许的。
例如:
String[][] s = new String[3][4];
$1 和 $2 的值为 3 和 4, $3 得不到的.
String[][] s = new String[3][];
$1 的值是 3 ,但 $2 得不到的.
8.7 javassist.expr.Instanceof
Instanceof 代表的是Instanceof 表达式。
| $0 | null |
| $1 | The value on the left hand side of the original instanceof operator. |
| $_ | The resulting value of the expression. The type of $_ is boolean. |
| $r | The type on the right hand side of the instanceof operator. |
| $type | A java.lang.Class object representing the type on the right hand side of the instanceof operator. |
| $proceed | The name of a virtual method executing the original instanceof expression. It takes one parameter (the type is java.lang.Object) and returns true if the parameter value is an instance of the type on the right hand side of the original instanceof operator. Otherwise, it returns false. |
$w, $args 和 $$ 也是允许的。
8.8 javassist.expr.Cast
Cast 代表的是一个转型表达式。
| $0 | null |
| $1 | The value the type of which is explicitly cast. |
| $_ | The resulting value of the expression. The type of $_ is the same as the type after the explicit casting, that is, the type surrounded by ( ). |
| $r | the type after the explicit casting, or the type surrounded by ( ). |
| $type | A java.lang.Class object representing the same type as $r. |
| $proceed | The name of a virtual method executing the original type casting. It takes one parameter of the type java.lang.Object and returns it after the explicit type casting specified by the original expression. |
$w, $args 和 $$ 也是允许的。
8.9 javassist.expr.Handler
Handler 代表的是一个try catch 声明。
| $1 | The exception object caught by the catch clause. |
| $r | the type of the exception caught by the catch clause. It is used in a cast expression. |
| $w | The wrapper type. It is used in a cast expression. |
| $type | A java.lang.Class object representing the type of the exception caught by the catch clause. |
9 新增一个方法或者field
Javassist 允许开发者创建一个新的方法或者构造方法。新增一个方法,例如:
1 CtClass point = ClassPool.getDefault().get("Point");
2 CtMethod m = CtNewMethod.make(
3 "public int xmove(int dx) { x += dx; }",
4 point);
5 point.addMethod(m);
6
7 在方法中调用其他方法,例如:
8 CtClass point = ClassPool.getDefault().get("Point");
9 CtMethod m = CtNewMethod.make(
10 "public int ymove(int dy) { $proceed(0, dy); }",
11 point, "this", "move");
12 其效果如下:
13 public int ymove(int dy) { this.move(0, dy); }

下面是javassist提供另一种新增一个方法(未看明白):
Javassist provides another way to add a new method. You can first create an abstract method and later give it a method body:
1 CtClass cc = ... ;
2 CtMethod m = new CtMethod(CtClass.intType, "move",
3 new CtClass[] { CtClass.intType }, cc);
4 cc.addMethod(m);
5 m.setBody("{ x += $1; }");
6 cc.setModifiers(cc.getModifiers() & ~Modifier.ABSTRACT);
7 Since Javassist makes a class abstract if an abstract method is added to the class, you have to explicitly change the class back to a non-abstract one after calling setBody().
9.1 递归方法
1 CtClass cc = ... ;
2 CtMethod m = CtNewMethod.make("public abstract int m(int i);", cc);
3 CtMethod n = CtNewMethod.make("public abstract int n(int i);", cc);
4 cc.addMethod(m);
5 cc.addMethod(n);
6 m.setBody("{ return ($1 <= 0) ? 1 : (n($1 - 1) * $1); }");
7 n.setBody("{ return m($1); }");
8 cc.setModifiers(cc.getModifiers() & ~Modifier.ABSTRACT);
9.2 新增field
如下:
1 CtClass point = ClassPool.getDefault().get("Point");
2 CtField f = new CtField(CtClass.intType, "z", point);
3 point.addField(f);
4 //point.addField(f, "0"); // initial value is 0.
5 或者:
6 CtClass point = ClassPool.getDefault().get("Point");
7 CtField f = CtField.make("public int z = 0;", point);
8 point.addField(f);
9.3 移除方法或者field
1 调用removeField()或者removeMethod()。
10 注解
获取注解信息:
1 //注解
2 public @interface Author {
3 String name();
4 int year();
5 }
6 //javassist代码
7 CtClass cc = ClassPool.getDefault().get("Point");
8 Object[] all = cc.getAnnotations();
9 Author a = (Author)all[0];
10 String name = a.name();
11 int year = a.year();
12 System.out.println("name: " + name + ", year: " + year);
11 javassist.runtime
12 import
引用包:
1 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
2 pool.importPackage("java.awt");
3 CtClass cc = pool.makeClass("Test");
4 CtField f = CtField.make("public Point p;", cc);
5 cc.addField(f);
13 限制
(1)不支持java5.0的新增语法。不支持注解修改,但可以通过底层的javassist类来解决,具体参考:javassist.bytecode.annotation
(2)不支持数组的初始化,如String[]{"1","2"},除非只有数组的容量为1
(3)不支持内部类和匿名类
(4)不支持continue和btreak 表达式。
(5)对于继承关系,有些不支持。例如
class A {}
class B extends A {}
class C extends B {}
class X {
void foo(A a) { .. }
void foo(B b) { .. }
}
如果调用 x.foo(new C()),可能会调用foo(A) 。
(6)推荐开发者用#分隔一个class name和static method或者 static field。例如:
javassist.CtClass.intType.getName()推荐用javassist.CtClass#intType.getName()
14.完整实例
14.1 创建类实例
1 package com.swust.javassist;
2
3 import javassist.ClassPool;
4 import javassist.CtClass;
5 import javassist.CtConstructor;
6 import javassist.CtField;
7 import javassist.CtMethod;
8
9 public class Example1 {
10 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
11 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
12 CtClass cc = pool.makeClass("bean.User");
13
14 //创建属性
15 CtField field01 = CtField.make("private int id;",cc);
16 CtField field02 = CtField.make("private String name;", cc);
17 cc.addField(field01);
18 cc.addField(field02);
19
20 //创建方法
21 CtMethod method01 = CtMethod.make("public String getName(){return name;}", cc);
22 CtMethod method02 = CtMethod.make("public void setName(String name){this.name = name;}", cc);
23 cc.addMethod(method01);
24 cc.addMethod(method02);
25
26 //添加有参构造器
27 CtConstructor constructor = new CtConstructor(new CtClass[]{CtClass.intType,pool.get("java.lang.String")},cc);
28 constructor.setBody("{this.id=id;this.name=name;}");
29 cc.addConstructor(constructor);
30 //无参构造器
31 CtConstructor cons = new CtConstructor(null,cc);
32 cons.setBody("{}");
33 cc.addConstructor(cons);
34
35 cc.writeFile("E:/workspace/TestCompiler/src");
36 }
37 }
14.2 访问类实例变量
1 package com.swust.javassist;
2
3 import java.lang.reflect.Field;
4 import java.lang.reflect.Method;
5 import java.util.Arrays;
6
7 import javassist.ClassPool;
8 import javassist.CtClass;
9 import javassist.CtConstructor;
10 import javassist.CtField;
11 import javassist.CtMethod;
12 import javassist.CtNewMethod;
13 import javassist.Modifier;
14
15 public class Example2 {
16 //获取类的简单信息
17 public static void test01() throws Exception{
18 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
19 CtClass cc = pool.get("com.swust.beans.Person");
20 //得到字节码
21 byte[] bytes = cc.toBytecode();
22 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
23 System.out.println(cc.getName());//获取类名
24 System.out.println(cc.getSimpleName());//获取简要类名
25 System.out.println(cc.getSuperclass());//获取父类
26 System.out.println(cc.getInterfaces());//获取接口
27 System.out.println(cc.getMethods());//获取
28 }
29 //新生成一个方法
30 public static void test02() throws Exception{
31 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
32 CtClass cc = pool.get("com.swust.beans.Person");
33 //第一种
34 //CtMethod cm = CtMethod.make("public String getName(){return name;}", cc);
35 //第二种
36 //参数:返回值类型,方法名,参数,对象
37 CtMethod cm = new CtMethod(CtClass.intType,"add",new CtClass[]{CtClass.intType,CtClass.intType},cc);
38 cm.setModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC);//访问范围
39 cm.setBody("{return $1+$2;}");
40 //cc.removeMethod(m) 删除一个方法
41 cc.addMethod(cm);
42 //通过反射调用方法
43 Class clazz = cc.toClass();
44 Object obj = clazz.newInstance();//通过调用无参构造器,生成新的对象
45 Method m = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("add", int.class,int.class);
46 Object result = m.invoke(obj, 2,3);
47 System.out.println(result);
48 }
49
50 //修改已有的方法
51 public static void test03() throws Exception{
52 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
53 CtClass cc = pool.get("bean.User");
54
55 CtMethod cm = cc.getDeclaredMethod("hello",new CtClass[]{pool.get("java.lang.String")});
56 cm.insertBefore("System.out.println(\"调用前\");");//调用前
57 cm.insertAt(29, "System.out.println(\"29\");");//行号
58 cm.insertAfter("System.out.println(\"调用后\");");//调用后
59
60 //通过反射调用方法
61 Class clazz = cc.toClass();
62 Object obj = clazz.newInstance();
63 Method m = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("hello", String.class);
64 Object result = m.invoke(obj, "张三");
65 System.out.println(result);
66 }
67
68 //修改已有属性
69 public static void test04() throws Exception{
70 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
71 CtClass cc = pool.get("bean.User");
72
73 //属性
74 CtField cf = new CtField(CtClass.intType,"age",cc);
75 cf.setModifiers(Modifier.PRIVATE);
76 cc.addField(cf);
77 //增加响应的get set方法
78 cc.addMethod(CtNewMethod.getter("getAge",cf));
79 cc.addMethod(CtNewMethod.setter("setAge",cf));
80
81 //访问属性
82 Class clazz = cc.toClass();
83 Object obj = clazz.newInstance();
84 Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("age");
85 System.out.println(field);
86 Method m = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("setAge", int.class);
87 m.invoke(obj, 16);
88 Method m2 = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("getAge", null);
89 Object resutl = m2.invoke(obj,null);
90 System.out.println(resutl);
91 }
92
93 //操作构造方法
94 public static void test05() throws Exception{
95 ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
96 CtClass cc = pool.get("com.swust.beans.Person");
97
98 CtConstructor[] cons = cc.getConstructors();
99 for(CtConstructor con:cons){
100 System.out.println(con);
101 }
102 }
103 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
104 test01();
105 //test02();
106 //test03();
107 //test04();
108 test05();
109 }
110 }
调用方法1获取类的基本信息,结果如下:
1 完整类名为:com.swust.beans.Person 2 类名为:Person 3 父类名称为:java.lang.Object 4 ***************************** 5 ***************************** 6 属性方法为:wait 7 属性方法为:wait 8 属性方法为:setName 9 属性方法为:notifyAll 10 属性方法为:wait 11 属性方法为:toString 12 属性方法为:getName 13 属性方法为:setAge 14 属性方法为:equals 15 属性方法为:main 16 属性方法为:getAge 17 属性方法为:getClass 18 属性方法为:clone 19 属性方法为:finalize 20 属性方法为:hashCode 21 属性方法为:notify
调用方法2添加新方法:
1 方法执行结果为:5
1 这是在原有方法体执行之前增加的内容 2 张三 3 这是在原有方法体执行之后增加的内容 4 null
调用方法4修改已有属性:
1 增添的属性为:private int com.swust.beans.Person.age 2 getAge方法执行后的结果为:16 3 增添的属性为:private int com.swust.beans.Person.height 4 getHeight方法执行后的结果为:176
调用方法5操作构造函数:
1 javassist.CtConstructor@180cb01[public Person ()V]Dubbo原理解析-代理之Javassist生成的伪代码
下面我们以伪代码来展示下生成的代理类
比如我们要对如下接口生成代理
public interface DemoService {
String sayHello(String name);
String sayHelloAgain(Stringname);
}生成的代理对象
public class DemoService.proxy10001implements DemoService {
public static Method[] methods =new Metod[]{“sayHello”, “sayHelloAgain”};
private InvocationHandlerhandler;
public voidDemoService.proxy10001() {}
public voidDemoService.proxy10001(InvocationHandler handler) {
this.handler= handler;
}
public String sayHello(String name){
Objectret = handler.invoke(this, methods[0], new Object[]{name})
}
public String sayHello(String name){
Objectret = handler.invoke(this, methods[1], new Object[]{name})
}
}生成创建代理对象的代理
public class Proxy10001 extends Proxy {
public void Proxy10001(){}
public ObjectnewInstance(InvocationHandler h) {
returnnew DemoService.proxy10001(h);
}
}Proxy.getProxy(DemoService).newInstance(newInvokerInvocationHndler(invoker))代码最终创建了基于DemoService接口的代理对象
ClassGenerator是dubbo提供的基于javassist之上的封装,方便dubbo用于生成字节码操作,ClassGenerator主要用来收集java的类信息如接口,字段,方法,构造器等等信息,具体如何利用javassist生成字节码不在本文档介绍范围,如有兴趣请谷歌百度
Wrapper:抽象类定义了Class类中的常用的获取类信息的一些方法, Wrapper包装了一个接口或者一个类可以,可以通过Wrapper对实例对象进行赋值取值以及指定方法调用, 如果对spring原理有了解的话spring中对bean的操作都是通过BeanWrapper这个包装器进行了的, Dubbo的Wrapper的功能与它类似。
Wrapper生成包装类的过程其实同上面生成代理类过程类似,有兴趣的同学阅读下源代码即可, 下面我们通过伪代码来展示下生成的包装类的来了解它要达到的功能。
如我们要Wrapper的类
public class Impl1 implements I1{
private String name = "youname";
public String getName(){return name;}
public void setName(String name){this.name = name; }
public void hello(String name) {System.out.println("hello " + name);}
}生成的包装类
public class Wrapper1234 extends Wrapper {
public static String[] pns = newString[]{“name”};
publicstatic Map pts = {“name” : “java.lang.String”};
publicstatic String[] mns= new String[] {“getName”, “setName”, “hello” };
publicstatic String[] dmns= new String[] {“getName”, “setName”, “hello” };
publicString[] getPropertyNames(){ return pns; }
publicboolean hasProperty(String n){ return pts.containsKey(n); }
publicClass getPropertyType(String n){ return (Class)pts.get(n); }
publicString[] getMethodNames(){ return mns; }
publicString[] getDeclaredMethodNames(){ return dmns; }
publicvoid setPropertyValue(Object o, String n, Object v) {
Wrapper1234w;
try { w= ((Wrapper1234) o);}
catch(Throwable e) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(e); }
if (n.equals("name")){
w.setName((java.lang.String) v);
return;
}
throw 方法不存在异常
}
public ObjectgetPropertyValue(Object o, String n) {
Wrapper1234w;
try { w= ((Wrapper1234) o);
} catch(Throwable e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(e); }
if (n.equals("name")){
return w.getName();
}
抛方法不存在异常、
}
public ObjectinvokeMethod(Object o, String n, Class[] p, Object[] v) throws java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException{
Wrapper1234w;
try { w= ((Wrapper1234) o);
} catch(Throwable e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(e); }
try {
if("getName".equals(n) && p.length == 0) {
return w.getName();
}
if("setName".equals(n) && p.length == 1) {
w.setName((java.lang.String) v[0]);
return null;
}
if("hello".equals(n) && p.length == 1) {
w.hello((java.lang.String) v[0]);
return null;
}
}catch (Throwable e) {
throw new java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException(e);
}
throw new com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.NoSuchMethodException( "Not found method " + n+ " in class Wrapper1234.");
}
}Wrapper1234是Wapper生成Impl1的包装对象, 对dubbo来说把各种无法预知的接口或者类转换成对dubbo可知的Wrapper对象子类, dubbo内部在向Invoker模型靠拢,Invoker是dubbo内部通用可执行对象, 这样一个远程调用只要根据请求invocation对象获取调用方法参数即可完成调用返回调用结果。
Dubbo学习-理解动态代理
在之前的一篇post中了解了spring可扩展的XML配置是怎么一会事,接下来继续研究dubbo consumer端如何解析service并执行远程调用。
本次研究目标
- 代理如何创建的。仅仅只是配置了
<dubbo:reference interface="x.y.z.ServiceInterface" id="serviceId"/>并将其交给了spring container,然后直接注入并使用该接口的方法就可以完成调用了,然而我并没有为该接口实现具体的类,how does it works? - 远程调用如何执行的。假设已经有了具体的实现类,怎么实现远程调用的呢,Thingking? 由于第一个分析就很长,这个目标列入下一次分析。
预备知识
为了顺利的研究上述两个目标,需要了解以下知识:
- SPI. 官方教程。用于服务扩展。
- Netty. User Guide。用于远程调用。
- Javassist. 官方Tutorial。动态类生成。
How to dig in?
从何处入手是个问题,我的习惯是顺藤摸瓜,所以从service被注入开始:
dubbo service配置:
<!-- DemoService is just a interface -->
<dubbo:reference interface="x.y.z.DemoService" id="demoService"/>Service注入:
@Resource
private DemoService demoService;当使用这个demoService的时候可以肯定的是一定有个DemoService的具体实现可供使用,DubboNamespaceHandler中有这样一段代码:
registerBeanDefinitionParser("reference", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ReferenceBean.class,false));解析上面配置在namespace dubbo下的reference。DubboBeanDefinitionParser相关代码如下:
public DubboBeanDefinitionParser(Class<?> beanClass, boolean required) {
this.beanClass = beanClass;
this.required = required;
}
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
return parse(element, parserContext, beanClass, required);
}
// 关键部分
private static BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext, Class<?> beanClass, boolean required) {
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
// 设置bean class,in this case it is ReferenceBean.class
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(beanClass);
beanDefinition.setLazyInit(false);
String id = element.getAttribute("id");
// some ops...
if (id != null && id.length() > 0) {
if (parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(id)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate spring bean id " + id);
}
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(id, beanDefinition);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("id", id);
}
// some ops...
// 遍历setter and getter设置属性值
for (Method setter : beanClass.getMethods()) {
String name = setter.getName();
if (name.length() > 3 && name.startsWith("set")
&& Modifier.isPublic(setter.getModifiers())
&& setter.getParameterTypes().length == 1) {
Class<?> type = setter.getParameterTypes()[0];
String property = StringUtils.camelToSplitName(name.substring(3, 4).toLowerCase() + name.substring(4), "-");
if(...){
// some ops...
}else {
String value = element.getAttribute(property);
if (value != null) {
value = value.trim();
if (value.length() > 0) {
// 部分省略...
Object reference;
if (isPrimitive(type)) {
if ("async".equals(property) && "false".equals(value)
|| "timeout".equals(property) && "0".equals(value)
|| "delay".equals(property) && "0".equals(value)
|| "version".equals(property) && "0.0.0".equals(value)
|| "stat".equals(property) && "-1".equals(value)
|| "reliable".equals(property) && "false".equals(value)) {
// 兼容旧版本xsd中的default值
value = null;
}
reference = value;
}
// 大批省略...
// 这里会将interface这个attribute的值设置在ReferenceBean的父类ReferenceConfig的interfaceName上通过method:setInterface(String)
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(property, reference);
}
}
}
}
}
}
// 省略...
return beanDefinition;
}上面两个关键的属性值id,interface都设置在了bean上,后面会用到。ReferenceConfig中的settter:setInterface用来设置interface:
public void setInterface(String interfaceName) {
this.interfaceName = interfaceName;
if (id == null || id.length() == 0) {
id = interfaceName;
}
}参考ReferenceBean Hierarchy:
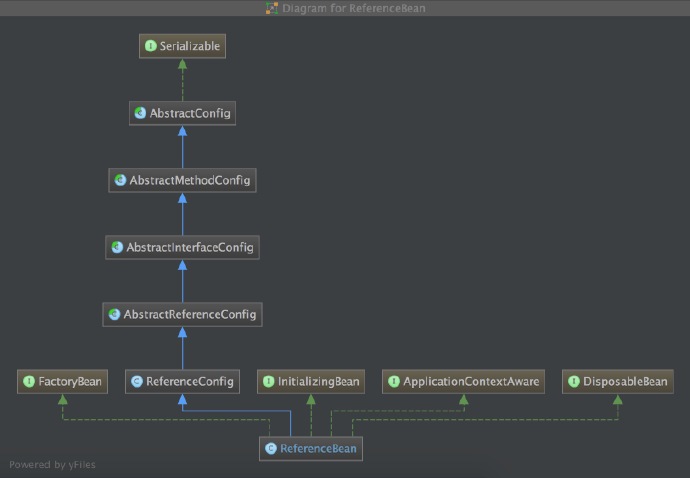
ReferenceBean中包含以几个两个方法:
@Override
// inherit from ApplicationContextAware
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
SpringExtensionFactory.addApplicationContext(applicationContext);
}
@Override
// inherit from FactoryBean
public Object getObject() throws Exception {
return get();// 调用ReferenceConfig#get()方法创建类型为getObjectType()的对象,which in this case is instance of x.y.z.DemoService
}
// inherit from FactoryBean
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return getInterfaceClass();
}如此,重点关注ReferenceConfig#get(),follow up:
public synchronized T get() {
if (destroyed){
throw new IllegalStateException("Already destroyed!");
}
if (ref == null) {
init();
}
return ref;
}进入init():
private void init() {
// some ops...
{
try {
// 之前设置的interface:x.y.z.DemoService
interfaceClass = Class.forName(interfaceName, true, Thread.currentThread()
.getContextClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
checkInterfaceAndMethods(interfaceClass, methods);
}
// a lot of ops...
ref = createProxy(map);
}进入createProxy(Map):
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) {
//some ops...
if (urls.size() == 1) {
invoker = refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, urls.get(0));
}
// some ops...
// 创建服务代理
return (T) proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker);
}到这里已经知道代理是由ProxyFactory创建了,接下重点看看ProxyFactory.
ProxyFactory
ProxyFactory Hierarchy:
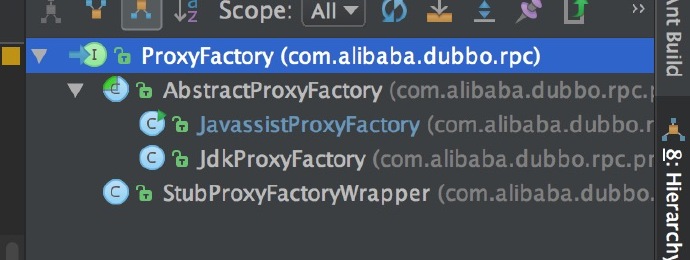
AbstractProxyFactory
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException {
Class<?>[] interfaces = null;
// createProxy时创建invoker时已将interface传入
String config = invoker.getUrl().getParameter("interfaces");
if (config != null && config.length() > 0) {
String[] types = Constants.COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(config);
if (types != null && types.length > 0) {
interfaces = new Class<?>[types.length + 2];
interfaces[0] = invoker.getInterface();
interfaces[1] = EchoService.class;
for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i ++) {
interfaces[i + 1] = ReflectUtils.forName(types[i]);
}
}
}
if (interfaces == null) {
interfaces = new Class<?>[] {invoker.getInterface(), EchoService.class};
}
// 调用子类的实现
return getProxy(invoker, interfaces);JavassistProxyFactory
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
return (T) Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}getProxy的相关代码:
public static Proxy getProxy(Class<?>... ics)
{
return getProxy(ClassHelper.getCallerClassLoader(Proxy.class), ics);
}动态类的实现:
public static Proxy getProxy(ClassLoader cl, Class<?>... ics)
{
//some ops...
try
{
ccp = ClassGenerator.newInstance(cl);
Set<String> worked = new HashSet<String>();
List<Method> methods = new ArrayList<Method>();
// 反射获取interface的相关信息并build code string,然后交给javassist动态生成实现类。
for(int i=0;i<ics.length;i++)
{
if( !Modifier.isPublic(ics[i].getModifiers()) )
{
String npkg = ics[i].getPackage().getName();
if( pkg == null )
{
pkg = npkg;
}
else
{
if( !pkg.equals(npkg) )
throw new IllegalArgumentException("non-public interfaces from different packages");
}
}
ccp.addInterface(ics[i]);
for( Method method : ics[i].getMethods() )
{
String desc = ReflectUtils.getDesc(method);
if( worked.contains(desc) )
continue;
worked.add(desc);
int ix = methods.size();
Class<?> rt = method.getReturnType();
Class<?>[] pts = method.getParameterTypes();
StringBuilder code = new StringBuilder("Object[] args = new Object[").append(pts.length).append("];");
for(int j=0;j<pts.length;j++)
code.append(" args[").append(j).append("] = ($w)$").append(j+1).append(";");
// 注意这里 handler.invoke(),代理的统一处理
code.append(" Object ret = handler.invoke(this, methods[" + ix + "], args);");
if( !Void.TYPE.equals(rt) )
code.append(" return ").append(asArgument(rt, "ret")).append(";");
methods.add(method);
ccp.addMethod(method.getName(), method.getModifiers(), rt, pts, method.getExceptionTypes(), code.toString());
}
}
if( pkg == null )
pkg = PACKAGE_NAME;
// 接口的实现类
String pcn = pkg + ".proxy" + id;
ccp.setClassName(pcn);
ccp.addField("public static java.lang.reflect.Method[] methods;");
ccp.addField("private " + InvocationHandler.class.getName() + " handler;");
ccp.addConstructor(Modifier.PUBLIC, new Class<?>[]{ InvocationHandler.class }, new Class<?>[0], "handler=$1;"); // $1等表示传入的参数,具体参考javassist官方文档
ccp.addDefaultConstructor();
Class<?> clazz = ccp.toClass();
clazz.getField("methods").set(null, methods.toArray(new Method[0]));
// 生成当前Proxy的子类,实现newInstance()方法
String fcn = Proxy.class.getName() + id;
ccm = ClassGenerator.newInstance(cl);
ccm.setClassName(fcn);
ccm.addDefaultConstructor();
ccm.setSuperClass(Proxy.class);
ccm.addMethod("public Object newInstance(" + InvocationHandler.class.getName() + " h){ return new " + pcn + "($1); }");
Class<?> pc = ccm.toClass();
proxy = (Proxy)pc.newInstance();
}
// some ops...
return proxy;
}toClass() 为ClassGenerator的方法,实现也是通过javassist生成动态类。 这儿返回的是Proxy的子类实例。JavassistProxyFactory的getProxy中Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));这儿的newInstance()就属于这个子类实例。该方法的定义:
abstract public Object newInstance(InvocationHandler handler);再来看看InvocationHandler的实现:
public class InvokerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private final Invoker<?> invoker;
public InvokerInvocationHandler(Invoker<?> handler){
this.invoker = handler;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return method.invoke(invoker, args);
}
if ("toString".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.toString();
}
if ("hashCode".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.hashCode();
}
if ("equals".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 1) {
return invoker.equals(args[0]);
}
// 返回远程调用的结果
return invoker.invoke(new RpcInvocation(method, args)).recreate();
}
}看到这儿可能还有点迷糊,invoke是在哪里调用的呢?回头看看动态类生成部分有这样一段代码:
code.append(" Object ret = handler.invoke(this, methods[" + ix + "], args);");这就将代理调用衔接起来了。看起来可能有点抽象,待下面来试验一把。
试验
DemoService.java
package com.alibaba.dubbo.examples.x.y.z;
/**
* Created by tangwei on 2016/11/23.
*/
public interface DemoService {
void sayHi(String name);
}Main.java
package com.alibaba.dubbo.examples.demo;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.URL;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.examples.x.y.z.DemoService;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.proxy.javassist.JavassistProxyFactory;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.support.MockInvoker;
/**
* Created by tangwei on 2016/11/22.
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JavassistProxyFactory().getProxy(new MockInvoker<DemoService>(new URL("", "", 8888)),
new Class[]{DemoService.class});
}
}在ClassGenerator中 toClass返回前加入以下代码:
try {
// 将class写入文件
mCtc.writeFile("/path/to/save/classfile/"+mSuperClass);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return mCtc.toClass(loader, pd);debug一下main,在动态生成类的时候将类写入文件中,结果如下:
DemoService的实现:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.ClassGenerator.DC;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.examples.x.y.z.DemoService;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class proxy0 implements DC, DemoService {
public static Method[] methods;
private InvocationHandler handler;
public void sayHi(String var1) {
Object[] var2 = new Object[]{var1};
this.handler.invoke(this, methods[0], var2);
}
public proxy0() {
}
public proxy0(InvocationHandler var1) {
this.handler = var1;
}
}Proxy的子类:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.Proxy;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.proxy0;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.ClassGenerator.DC;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
public class Proxy0 extends Proxy implements DC {
public Object newInstance(InvocationHandler var1) {
// 返回的是DemoService的实例
return new proxy0(var1);
}
public Proxy0() {
}
}其中DC接口只是一个标识接口,表示该类是动态生成的。这样看起来就比较清晰明了了。下面再来看看jdk的proxy。
JdkProxyFactory
相关代码如下:
public class JdkProxyFactory extends AbstractProxyFactory {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(), interfaces, new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}
public <T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) {
return new AbstractProxyInvoker<T>(proxy, type, url) {
@Override
protected Object doInvoke(T proxy, String methodName,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
Object[] arguments) throws Throwable {
Method method = proxy.getClass().getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
return method.invoke(proxy, arguments);
}
};
}
}可以看到Proxy.newProxyInstance直接使用的是JDK的动态代理机制,因此就不再跟下去了。
总结
至此,对dubbo本地动态代理有一个清晰的理解了,总的来说一路顺藤摸瓜还算顺畅。对于选择哪一中方式作为生产使用,Dubbo推荐使用Javassist的代理机制,因为jdk原生的动态代理性能较差,生产环境不宜使用。
性能比较
因服务框架需要用动态代理生成客户端接口的stub,所以做了一下性能评测,
动态代理工具比较成熟的产品有:
JDK自带的,ASM,CGLIB(基于ASM包装),JAVAASSIST,
使用的版本分别为:
JDK-1.6.0_18-b07, ASM-3.3, CGLIB-2.2, JAVAASSIST-3.11.0.GA
(一) 测试结果:
数据为执行三次,每次调用一千万次代理方法的结果,测试代码后面有贴出。
(1) PC机测试结果:Linux 2.6.9-42.ELsmp(32bit), 2 Cores CPU(Intel Pentium4 3.06GHz)
Java代码
Create JDK Proxy: 13 ms
Create CGLIB Proxy: 217 ms
Create JAVAASSIST Proxy: 99 ms
Create JAVAASSIST Bytecode Proxy: 168 ms
Create ASM Proxy: 3 ms
================
Run JDK Proxy: 2224 ms, 634,022 t/s
Run CGLIB Proxy: 1123 ms, 1,255,623 t/s
Run JAVAASSIST Proxy: 3212 ms, 438,999 t/s
Run JAVAASSIST Bytecode Proxy: 206 ms, 6,844,977 t/s
Run ASM Bytecode Proxy: 209 ms, 6,746,724 t/s
----------------
Run JDK Proxy: 2169 ms, 650,099 t/s
Run CGLIB Proxy: 1059 ms, 1,331,506 t/s
Run JAVAASSIST Proxy: 3328 ms, 423,697 t/s
Run JAVAASSIST Bytecode Proxy: 202 ms, 6,980,521 t/s
Run ASM Bytecode Proxy: 206 ms, 6,844,977 t/s
----------------
Run JDK Proxy: 2174 ms, 648,604 t/s
Run CGLIB Proxy: 1032 ms, 1,366,342 t/s
Run JAVAASSIST Proxy: 3119 ms, 452,088 t/s
Run JAVAASSIST Bytecode Proxy: 207 ms, 6,811,910 t/s
Run ASM Bytecode Proxy: 207 ms, 6,811,910 t/s
----------------
(2) 服务器测试结果:Linux 2.6.18-128.el5xen(64bit), 16 Cores CPU(Intel Xeon E5520 2.27GHz)
Create JDK Proxy: 7 ms
Create CGLIB Proxy: 86 ms
Create JAVAASSIST Proxy: 36 ms
Create JAVAASSIST Bytecode Proxy: 57 ms
Create ASM Proxy: 1 ms
================
Run JDK Proxy: 235 ms, 6,000,278 t/s
Run CGLIB Proxy: 234 ms, 6,025,920 t/s
Run JAVAASSIST Proxy: 459 ms, 3,072,037 t/s
Run JAVAASSIST Bytecode Proxy: 71 ms, 19,860,076 t/s
Run ASM Bytecode Proxy: 72 ms, 19,584,241 t/s
----------------
Run JDK Proxy: 298 ms, 4,731,763 t/s
Run CGLIB Proxy: 134 ms, 10,522,876 t/s
Run JAVAASSIST Proxy: 406 ms, 3,473,067 t/s
Run JAVAASSIST Bytecode Proxy: 67 ms, 21,045,752 t/s
Run ASM Bytecode Proxy: 66 ms, 21,364,627 t/s
----------------
Run JDK Proxy: 282 ms, 5,000,231 t/s
Run CGLIB Proxy: 133 ms, 10,601,995 t/s
Run JAVAASSIST Proxy: 406 ms, 3,473,067 t/s
Run JAVAASSIST Bytecode Proxy: 67 ms, 21,045,752 t/s
Run ASM Bytecode Proxy: 67 ms, 21,045,752 t/s
----------------
(二) 测试结论:
1. ASM和JAVAASSIST字节码生成方式不相上下,都很快,是CGLIB的5倍。
2. CGLIB次之,是JDK自带的两倍。
3. JDK自带的再次之,因JDK1.6对动态代理做了优化,如果用低版本JDK更慢,要注意的是JDK也是通过字节码生成来实现动态代理的,而不是反射。
4. JAVAASSIST提供者动态代理接口最慢,比JDK自带的还慢。
(这也是为什么网上有人说JAVAASSIST比JDK还慢的原因,用JAVAASSIST最好别用它提供的动态代理接口,而可以考虑用它的字节码生成方式)
(三) 差异原因:
各方案生成的字节码不一样,
像JDK和CGLIB都考虑了很多因素,以及继承或包装了自己的一些类,
所以生成的字节码非常大,而我们很多时候用不上这些,
而手工生成的字节码非常小,所以速度快,
具体的字节码对比,后面有贴出,可自行分析。
(四) 最终选型:
最终决定使用JAVAASSIST的字节码生成代理方式,
虽然ASM稍快,但并没有快一个数量级,
而JAVAASSIST的字节码生成方式比ASM方便,
JAVAASSIST只需用字符串拼接出Java源码,便可生成相应字节码,
而ASM需要手工写字节码。
(五) 测试代码:
public interface CountService {
int count();
} public class CountServiceImpl implements CountService {
private int count = 0;
public int count() {
return count ++;
}
} import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import javassist.ClassPool;
import javassist.CtClass;
import javassist.CtField;
import javassist.CtNewConstructor;
import javassist.CtNewMethod;
import javassist.util.proxy.MethodHandler;
import javassist.util.proxy.ProxyFactory;
import javassist.util.proxy.ProxyObject;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import org.objectweb.asm.ClassWriter;
import org.objectweb.asm.FieldVisitor;
import org.objectweb.asm.MethodVisitor;
import org.objectweb.asm.Opcodes;
public class DynamicProxyPerformanceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CountService delegate = new CountServiceImpl();
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
CountService jdkProxy = createJdkDynamicProxy(delegate);
time = System.currentTimeMillis() - time;
System.out.println("Create JDK Proxy: " + time + " ms");
time = System.currentTimeMillis();
CountService cglibProxy = createCglibDynamicProxy(delegate);
time = System.currentTimeMillis() - time;
System.out.println("Create CGLIB Proxy: " + time + " ms");
time = System.currentTimeMillis();
CountService javassistProxy = createJavassistDynamicProxy(delegate);
time = System.currentTimeMillis() - time;
System.out.println("Create JAVAASSIST Proxy: " + time + " ms");
time = System.currentTimeMillis();
CountService javassistBytecodeProxy = createJavassistBytecodeDynamicProxy(delegate);
time = System.currentTimeMillis() - time;
System.out.println("Create JAVAASSIST Bytecode Proxy: " + time + " ms");
time = System.currentTimeMillis();
CountService asmBytecodeProxy = createAsmBytecodeDynamicProxy(delegate);
time = System.currentTimeMillis() - time;
System.out.println("Create ASM Proxy: " + time + " ms");
System.out.println("================");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
test(jdkProxy, "Run JDK Proxy: ");
test(cglibProxy, "Run CGLIB Proxy: ");
test(javassistProxy, "Run JAVAASSIST Proxy: ");
test(javassistBytecodeProxy, "Run JAVAASSIST Bytecode Proxy: ");
test(asmBytecodeProxy, "Run ASM Bytecode Proxy: ");
System.out.println("----------------");
}
}
private static void test(CountService service, String label)
throws Exception {
service.count(); // warm up
int count = 10000000;
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
service.count();
}
time = System.currentTimeMillis() - time;
System.out.println(label + time + " ms, " + new DecimalFormat().format(count * 1000 / time) + " t/s");
}
private static CountService createJdkDynamicProxy(final CountService delegate) {
CountService jdkProxy = (CountService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(),
new Class[] { CountService.class }, new JdkHandler(delegate));
return jdkProxy;
}
private static class JdkHandler implements InvocationHandler {
final Object delegate;
JdkHandler(Object delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
}
public Object invoke(Object object, Method method, Object[] objects)
throws Throwable {
return method.invoke(delegate, objects);
}
}
private static CountService createCglibDynamicProxy(final CountService delegate) throws Exception {
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setCallback(new CglibInterceptor(delegate));
enhancer.setInterfaces(new Class[] { CountService.class });
CountService cglibProxy = (CountService) enhancer.create();
return cglibProxy;
}
private static class CglibInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
final Object delegate;
CglibInterceptor(Object delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
}
public Object intercept(Object object, Method method, Object[] objects,
MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
return methodProxy.invoke(delegate, objects);
}
}
private static CountService createJavassistDynamicProxy(final CountService delegate) throws Exception {
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setInterfaces(new Class[] { CountService.class });
Class<?> proxyClass = proxyFactory.createClass();
CountService javassistProxy = (CountService) proxyClass.newInstance();
((ProxyObject) javassistProxy).setHandler(new JavaAssitInterceptor(delegate));
return javassistProxy;
}
private static class JavaAssitInterceptor implements MethodHandler {
final Object delegate;
JavaAssitInterceptor(Object delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
}
public Object invoke(Object self, Method m, Method proceed,
Object[] args) throws Throwable {
return m.invoke(delegate, args);
}
}
private static CountService createJavassistBytecodeDynamicProxy(CountService delegate) throws Exception {
ClassPool mPool = new ClassPool(true);
CtClass mCtc = mPool.makeClass(CountService.class.getName() + "JavaassistProxy");
mCtc.addInterface(mPool.get(CountService.class.getName()));
mCtc.addConstructor(CtNewConstructor.defaultConstructor(mCtc));
mCtc.addField(CtField.make("public " + CountService.class.getName() + " delegate;", mCtc));
mCtc.addMethod(CtNewMethod.make("public int count() { return delegate.count(); }", mCtc));
Class<?> pc = mCtc.toClass();
CountService bytecodeProxy = (CountService) pc.newInstance();
Field filed = bytecodeProxy.getClass().getField("delegate");
filed.set(bytecodeProxy, delegate);
return bytecodeProxy;
}
private static CountService createAsmBytecodeDynamicProxy(CountService delegate) throws Exception {
ClassWriter classWriter = new ClassWriter(ClassWriter.COMPUTE_FRAMES | ClassWriter.COMPUTE_MAXS);
String className = CountService.class.getName() + "AsmProxy";
String classPath = className.replace('.', '/');
String interfacePath = CountService.class.getName().replace('.', '/');
classWriter.visit(Opcodes.V1_5, Opcodes.ACC_PUBLIC, classPath, null, "java/lang/Object", new String[] {interfacePath});
MethodVisitor initVisitor = classWriter.visitMethod(Opcodes.ACC_PUBLIC, "<init>", "()V", null, null);
initVisitor.visitCode();
initVisitor.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 0);
initVisitor.visitMethodInsn(Opcodes.INVOKESPECIAL, "java/lang/Object", "<init>", "()V");
initVisitor.visitInsn(Opcodes.RETURN);
initVisitor.visitMaxs(0, 0);
initVisitor.visitEnd();
FieldVisitor fieldVisitor = classWriter.visitField(Opcodes.ACC_PUBLIC, "delegate", "L" + interfacePath + ";", null, null);
fieldVisitor.visitEnd();
MethodVisitor methodVisitor = classWriter.visitMethod(Opcodes.ACC_PUBLIC, "count", "()I", null, null);
methodVisitor.visitCode();
methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 0);
methodVisitor.visitFieldInsn(Opcodes.GETFIELD, classPath, "delegate", "L" + interfacePath + ";");
methodVisitor.visitMethodInsn(Opcodes.INVOKEINTERFACE, interfacePath, "count", "()I");
methodVisitor.visitInsn(Opcodes.IRETURN);
methodVisitor.visitMaxs(0, 0);
methodVisitor.visitEnd();
classWriter.visitEnd();
byte[] code = classWriter.toByteArray();
CountService bytecodeProxy = (CountService) new ByteArrayClassLoader().getClass(className, code).newInstance();
Field filed = bytecodeProxy.getClass().getField("delegate");
filed.set(bytecodeProxy, delegate);
return bytecodeProxy;
}
private static class ByteArrayClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
public ByteArrayClassLoader() {
super(ByteArrayClassLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
public synchronized Class<?> getClass(String name, byte[] code) {
if (name == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("");
}
return defineClass(name, code, 0, code.length);
}
}
}
(六) 字节码对比
(1) JDK生成的字节码:
public final class $Proxy0 extends java.lang.reflect.Proxy implements com.alibaba.test.performance.dynamicproxy.CountService{
public $Proxy0(java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler) throws ;
Code:
0: aload_0
1: aload_1
2: invokespecial #8; //Method java/lang/reflect/Proxy."":(Ljava/lang/reflect/InvocationHandler;)V
5: return
public final boolean equals(java.lang.Object) throws ;
Code:
0: aload_0
1: getfield #16; //Field java/lang/reflect/Proxy.h:Ljava/lang/reflect/InvocationHandler;
4: aload_0
5: getstatic #20; //Field m1:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
8: iconst_1
9: anewarray #22; //class java/lang/Object
12: dup
13: iconst_0
14: aload_1
15: aastore
16: invokeinterface #28, 4; //InterfaceMethod java/lang/reflect/InvocationHandler.invoke:(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
21: checkcast #30; //class java/lang/Boolean
24: invokevirtual #34; //Method java/lang/Boolean.booleanValue:()Z
27: ireturn
28: athrow
29: astore_2
30: new #42; //class java/lang/reflect/UndeclaredThrowableException
33: dup
34: aload_2
35: invokespecial #45; //Method java/lang/reflect/UndeclaredThrowableException."":(Ljava/lang/Throwable;)V
38: athrow
Exception table:
from to target type
0 28 28 Class java/lang/Error
0 28 28 Class java/lang/RuntimeException
0 28 29 Class java/lang/Throwable
public final int count() throws ;
Code:
0: aload_0
1: getfield #16; //Field java/lang/reflect/Proxy.h:Ljava/lang/reflect/InvocationHandler;
4: aload_0
5: getstatic #50; //Field m3:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
8: aconst_null
9: invokeinterface #28, 4; //InterfaceMethod java/lang/reflect/InvocationHandler.invoke:(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
14: checkcast #52; //class java/lang/Integer
17: invokevirtual #55; //Method java/lang/Integer.intValue:()I
20: ireturn
21: athrow
22: astore_1
23: new #42; //class java/lang/reflect/UndeclaredThrowableException
26: dup
27: aload_1
28: invokespecial #45; //Method java/lang/reflect/UndeclaredThrowableException."":(Ljava/lang/Throwable;)V
31: athrow
Exception table:
from to target type
0 21 21 Class java/lang/Error
0 21 21 Class java/lang/RuntimeException
0 21 22 Class java/lang/Throwable
public final int hashCode() throws ;
Code:
0: aload_0
1: getfield #16; //Field java/lang/reflect/Proxy.h:Ljava/lang/reflect/InvocationHandler;
4: aload_0
5: getstatic #59; //Field m0:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
8: aconst_null
9: invokeinterface #28, 4; //InterfaceMethod java/lang/reflect/InvocationHandler.invoke:(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
14: checkcast #52; //class java/lang/Integer
17: invokevirtual #55; //Method java/lang/Integer.intValue:()I
20: ireturn
21: athrow
22: astore_1
23: new #42; //class java/lang/reflect/UndeclaredThrowableException
26: dup
27: aload_1
28: invokespecial #45; //Method java/lang/reflect/UndeclaredThrowableException."":(Ljava/lang/Throwable;)V
31: athrow
Exception table:
from to target type
0 21 21 Class java/lang/Error
0 21 21 Class java/lang/RuntimeException
0 21 22 Class java/lang/Throwable
public final java.lang.String toString() throws ;
Code:
0: aload_0
1: getfield #16; //Field java/lang/reflect/Proxy.h:Ljava/lang/reflect/InvocationHandler;
4: aload_0
5: getstatic #64; //Field m2:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
8: aconst_null
9: invokeinterface #28, 4; //InterfaceMethod java/lang/reflect/InvocationHandler.invoke:(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
14: checkcast #66; //class java/lang/String
17: areturn
18: athrow
19: astore_1
20: new #42; //class java/lang/reflect/UndeclaredThrowableException
23: dup
24: aload_1
25: invokespecial #45; //Method java/lang/reflect/UndeclaredThrowableException."":(Ljava/lang/Throwable;)V
28: athrow
Exception table:
from to target type
0 18 18 Class java/lang/Error
0 18 18 Class java/lang/RuntimeException
0 18 19 Class java/lang/Throwable
static {} throws ;
Code:
0: ldc #70; //String java.lang.Object
2: invokestatic #76; //Method java/lang/Class.forName:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Class;
5: ldc #77; //String equals
7: iconst_1
8: anewarray #72; //class java/lang/Class
11: dup
12: iconst_0
13: ldc #70; //String java.lang.Object
15: invokestatic #76; //Method java/lang/Class.forName:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Class;
18: aastore
19: invokevirtual #81; //Method java/lang/Class.getMethod:(Ljava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/Class;)Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
22: putstatic #20; //Field m1:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
25: ldc #83; //String com.alibaba.test.performance.dynamicproxy.CountService
27: invokestatic #76; //Method java/lang/Class.forName:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Class;
30: ldc #84; //String count
32: iconst_0
33: anewarray #72; //class java/lang/Class
36: invokevirtual #81; //Method java/lang/Class.getMethod:(Ljava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/Class;)Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
39: putstatic #50; //Field m3:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
42: ldc #70; //String java.lang.Object
44: invokestatic #76; //Method java/lang/Class.forName:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Class;
47: ldc #85; //String hashCode
49: iconst_0
50: anewarray #72; //class java/lang/Class
53: invokevirtual #81; //Method java/lang/Class.getMethod:(Ljava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/Class;)Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
56: putstatic #59; //Field m0:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
59: ldc #70; //String java.lang.Object
61: invokestatic #76; //Method java/lang/Class.forName:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Class;
64: ldc #86; //String toString
66: iconst_0
67: anewarray #72; //class java/lang/Class
70: invokevirtual #81; //Method java/lang/Class.getMethod:(Ljava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/Class;)Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
73: putstatic #64; //Field m2:Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
76: return
77: astore_1
78: new #90; //class java/lang/NoSuchMethodError
81: dup
82: aload_1
83: invokevirtual #93; //Method java/lang/Throwable.getMessage:()Ljava/lang/String;
86: invokespecial #96; //Method java/lang/NoSuchMethodError."":(Ljava/lang/String;)V
89: athrow
90: astore_1
91: new #100; //class java/lang/NoClassDefFoundError
94: dup
95: aload_1
96: invokevirtual #93; //Method java/lang/Throwable.getMessage:()Ljava/lang/String;
99: invokespecial #101; //Method java/lang/NoClassDefFoundError."":(Ljava/lang/String;)V
102: athrow
Exception table:
from to target type
0 77 77 Class java/lang/NoSuchMethodException
0 77 90 Class java/lang/ClassNotFoundException
}
(2) CGLIB生成的字节码:
public class net.sf.cglib.core.MethodWrapper$MethodWrapperKey$$KeyFactoryByCGLIB$$d45e49f7 extends net.sf.cglib.core.KeyFactory implements net.sf.cglib.core.MethodWrapper$MethodWrapperKey{
public net.sf.cglib.core.MethodWrapper$MethodWrapperKey$$KeyFactoryByCGLIB$$d45e49f7();
Code:
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #11; //Method net/sf/cglib/core/KeyFactory."":()V
4: return
public java.lang.Object newInstance(java.lang.String, java.lang.String[], java.lang.String);
Code:
0: new #2; //class net/sf/cglib/core/MethodWrapper$MethodWrapperKey$$KeyFactoryByCGLIB$$d45e49f7
3: dup
4: aload_1
5: aload_2
6: aload_3
7: invokespecial #16; //Method "":(Ljava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;)V
10: areturn
public net.sf.cglib.core.MethodWrapper$MethodWrapperKey$$KeyFactoryByCGLIB$$d45e49f7(java.lang.String, java.lang.String[], java.lang.String);
Code:
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #11; //Method net/sf/cglib/core/KeyFactory."":()V
4: aload_0
5: dup
6: aload_1
7: putfield #20; //Field FIELD_0:Ljava/lang/String;
10: dup
11: aload_2
12: putfield #24; //Field FIELD_1:[Ljava/lang/String;
15: dup
16: aload_3
17: putfield #27; //Field FIELD_2:Ljava/lang/String;
20: return
public int hashCode();
Code:
0: ldc #30; //int 938313161
2: aload_0
3: getfield #20; //Field FIELD_0:Ljava/lang/String;
6: swap
7: ldc #31; //int 362693231
9: imul
10: swap
11: dup
12: ifnull 21
15: invokevirtual #35; //Method java/lang/Object.hashCode:()I
18: goto 23
21: pop
22: iconst_0
23: iadd
24: aload_0
25: getfield #24; //Field FIELD_1:[Ljava/lang/String;
28: dup
29: ifnull 71
32: astore_1
33: iconst_0
34: istore_2
35: goto 62
38: aload_1
39: iload_2
40: aaload
41: swap
42: ldc #31; //int 362693231
44: imul
45: swap
46: dup
47: ifnull 56
50: invokevirtual #35; //Method java/lang/Object.hashCode:()I
53: goto 58
56: pop
57: iconst_0
58: iadd
59: iinc 2, 1
62: iload_2
63: aload_1
64: arraylength
65: if_icmplt 38
68: goto 72
71: pop
72: aload_0
73: getfield #27; //Field FIELD_2:Ljava/lang/String;
76: swap
77: ldc #31; //int 362693231
79: imul
80: swap
81: dup
82: ifnull 91
85: invokevirtual #35; //Method java/lang/Object.hashCode:()I
88: goto 93
91: pop
92: iconst_0
93: iadd
94: ireturn
public boolean equals(java.lang.Object);
Code:
0: aload_1
1: instanceof #2; //class net/sf/cglib/core/MethodWrapper$MethodWrapperKey$$KeyFactoryByCGLIB$$d45e49f7
4: ifeq 181
7: aload_0
8: getfield #20; //Field FIELD_0:Ljava/lang/String;
11: aload_1
12: checkcast #2; //class net/sf/cglib/core/MethodWrapper$MethodWrapperKey$$KeyFactoryByCGLIB$$d45e49f7
15: getfield #20; //Field FIELD_0:Ljava/lang/String;
18: dup2
19: ifnonnull 29
22: ifnonnull 35
25: pop2
26: goto 45
29: ifnull 35
32: goto 39
35: pop2
36: goto 181
39: invokevirtual #39; //Method java/lang/Object.equals:(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z
42: ifeq 181
45: aload_0
46: getfield #24; //Field FIELD_1:[Ljava/lang/String;
49: aload_1
50: checkcast #2; //class net/sf/cglib/core/MethodWrapper$MethodWrapperKey$$KeyFactoryByCGLIB$$d45e49f7
53: getfield #24; //Field FIELD_1:[Ljava/lang/String;
56: dup2
57: ifnonnull 67
60: ifnonnull 73
63: pop2
64: goto 141
67: ifnull 73
70: goto 77
73: pop2
74: goto 181
77: dup2
78: arraylength
79: swap
80: arraylength
81: if_icmpeq 88
84: pop2
85: goto 181
88: astore_2
89: astore_3
90: iconst_0
91: istore 4
93: goto 134
96: aload_2
97: iload 4
99: aaload
100: aload_3
101: iload 4
103: aaload
104: dup2
105: ifnonnull 115
108: ifnonnull 121
111: pop2
112: goto 131
115: ifnull 121
118: goto 125
121: pop2
122: goto 181
125: invokevirtual #39; //Method java/lang/Object.equals:(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z
128: ifeq 181
131: iinc 4, 1
134: iload 4
136: aload_2
137: arraylength
138: if_icmplt 96
141: aload_0
142: getfield #27; //Field FIELD_2:Ljava/lang/String;
145: aload_1
146: checkcast #2; //class net/sf/cglib/core/MethodWrapper$MethodWrapperKey$$KeyFactoryByCGLIB$$d45e49f7
149: getfield #27; //Field FIELD_2:Ljava/lang/String;
152: dup2
153: ifnonnull 163
156: ifnonnull 169
159: pop2
160: goto 179
163: ifnull 169
166: goto 173
169: pop2
170: goto 181
173: invokevirtual #39; //Method java/lang/Object.equals:(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z
176: ifeq 181
179: iconst_1
180: ireturn
181: iconst_0
182: ireturn
public java.lang.String toString();
Code:
0: new #43; //class java/lang/StringBuffer
3: dup
4: invokespecial #44; //Method java/lang/StringBuffer."":()V
7: aload_0
8: getfield #20; //Field FIELD_0:Ljava/lang/String;
11: dup
12: ifnull 24
15: invokevirtual #46; //Method java/lang/Object.toString:()Ljava/lang/String;
18: invokevirtual #50; //Method java/lang/StringBuffer.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuffer;
21: goto 30
24: pop
25: ldc #52; //String null
27: invokevirtual #50; //Method java/lang/StringBuffer.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuffer;
30: ldc #54; //String ,
32: invokevirtual #50; //Method java/lang/StringBuffer.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuffer;
35: aload_0
36: getfield #24; //Field FIELD_1:[Ljava/lang/String;
39: dup
40: ifnull 110
43: swap
44: ldc #56; //String {
46: invokevirtual #50; //Method java/lang/StringBuffer.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuffer;
49: swap
50: astore_1
51: iconst_0
52: istore_2
53: goto 86
56: aload_1
57: iload_2
58: aaload
59: dup
60: ifnull 72
63: invokevirtual #46; //Method java/lang/Object.toString:()Ljava/lang/String;
66: invokevirtual #50; //Method java/lang/StringBuffer.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuffer;
69: goto 78
72: pop
73: ldc #52; //String null
75: invokevirtual #50; //Method java/lang/StringBuffer.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuffer;
78: ldc #54; //String ,
80: invokevirtual #50; //Method java/lang/StringBuffer.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuffer;
83: iinc 2, 1
86: iload_2
87: aload_1
88: arraylength
89: if_icmplt 56
92: dup
93: dup
94: invokevirtual #59; //Method java/lang/StringBuffer.length:()I
97: iconst_2
98: isub
99: invokevirtual #63; //Method java/lang/StringBuffer.setLength:(I)V
102: ldc #65; //String }
104: invokevirtual #50; //Method java/lang/StringBuffer.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuffer;
107: goto 116
110: pop
111: ldc #52; //String null
113: invokevirtual #50; //Method java/lang/StringBuffer.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuffer;
116: ldc #54; //String ,
118: invokevirtual #50; //Method java/lang/StringBuffer.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuffer;
121: aload_0
122: getfield #27; //Field FIELD_2:Ljava/lang/String;
125: dup
126: ifnull 138
129: invokevirtual #46; //Method java/lang/Object.toString:()Ljava/lang/String;
132: invokevirtual #50; //Method java/lang/StringBuffer.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuffer;
135: goto 144
138: pop
139: ldc #52; //String null
141: invokevirtual #50; //Method java/lang/StringBuffer.append:(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/StringBuffer;
144: invokevirtual #66; //Method java/lang/StringBuffer.toString:()Ljava/lang/String;
147: areturn
}
(3) JAVAASSIST动态代理接口生成的字节码:
public class com.alibaba.test.performance.dynamicproxy.CountService_$$_javassist_0 extends java.lang.Object implements com.alibaba.test.performance.dynamicproxy.CountService,javassist.util.proxy.ProxyObject{
public static javassist.util.proxy.MethodHandler default_interceptor;
public static javassist.util.proxy.MethodFilter _method_filter;
public com.alibaba.test.performance.dynamicproxy.CountService_$$_javassist_0();
Code:
0: aload_0
1: getstatic #19; //Field default_interceptor:Ljavassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler;
4: putfield #21; //Field handler:Ljavassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler;
7: getstatic #23; //Field default_interceptor:Ljavassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler;
10: ifnonnull 20
13: aload_0
14: getstatic #27; //Field javassist/util/proxy/RuntimeSupport.default_interceptor:Ljavassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler;
17: putfield #29; //Field handler:Ljavassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler;
20: aload_0
21: invokespecial #31; //Method java/lang/Object."":()V
24: return
public final boolean _d0equals(java.lang.Object);
Code:
0: aload_0
1: aload_1
2: invokespecial #38; //Method java/lang/Object.equals:(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z
5: ireturn
public final boolean equals(java.lang.Object);
Code:
0: getstatic #42; //Field _methods_:[Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
3: astore_2
4: aload_0
5: ldc #43; //String equals
7: ldc #44; //String _d0equals
9: iconst_0
10: ldc #45; //String (Ljava/lang/Object;)Z
12: aload_2
13: invokestatic #49; //Method javassist/util/proxy/RuntimeSupport.find2Methods:(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;ILjava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;)V
16: aload_0
17: getfield #51; //Field handler:Ljavassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler;
20: aload_0
21: aload_2
22: iconst_0
23: aaload
24: aload_2
25: iconst_1
26: aaload
27: iconst_1
28: anewarray #52; //class java/lang/Object
31: dup
32: iconst_0
33: aload_1
34: aastore
35: invokeinterface #58, 5; //InterfaceMethod javassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler.invoke:(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
40: checkcast #60; //class java/lang/Boolean
43: invokevirtual #64; //Method java/lang/Boolean.booleanValue:()Z
46: ireturn
public final java.lang.Object _d1clone() throws java.lang.CloneNotSupportedException;
Code:
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #72; //Method java/lang/Object.clone:()Ljava/lang/Object;
4: areturn
protected final java.lang.Object clone() throws java.lang.CloneNotSupportedException;
Code:
0: getstatic #74; //Field _methods_:[Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
3: astore_1
4: aload_0
5: ldc #75; //String clone
7: ldc #76; //String _d1clone
9: iconst_2
10: ldc #77; //String ()Ljava/lang/Object;
12: aload_1
13: invokestatic #79; //Method javassist/util/proxy/RuntimeSupport.find2Methods:(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;ILjava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;)V
16: aload_0
17: getfield #81; //Field handler:Ljavassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler;
20: aload_0
21: aload_1
22: iconst_2
23: aaload
24: aload_1
25: iconst_3
26: aaload
27: iconst_0
28: anewarray #52; //class java/lang/Object
31: invokeinterface #83, 5; //InterfaceMethod javassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler.invoke:(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
36: checkcast #4; //class java/lang/Object
39: areturn
public final int _d2hashCode();
Code:
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #88; //Method java/lang/Object.hashCode:()I
4: ireturn
public final int hashCode();
Code:
0: getstatic #90; //Field _methods_:[Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
3: astore_1
4: aload_0
5: ldc #91; //String hashCode
7: ldc #92; //String _d2hashCode
9: iconst_4
10: ldc #93; //String ()I
12: aload_1
13: invokestatic #95; //Method javassist/util/proxy/RuntimeSupport.find2Methods:(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;ILjava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;)V
16: aload_0
17: getfield #97; //Field handler:Ljavassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler;
20: aload_0
21: aload_1
22: iconst_4
23: aaload
24: aload_1
25: iconst_5
26: aaload
27: iconst_0
28: anewarray #52; //class java/lang/Object
31: invokeinterface #99, 5; //InterfaceMethod javassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler.invoke:(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
36: checkcast #101; //class java/lang/Integer
39: invokevirtual #104; //Method java/lang/Integer.intValue:()I
42: ireturn
public final int count();
Code:
0: getstatic #107; //Field _methods_:[Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
3: astore_1
4: aload_0
5: ldc #108; //String count
7: aconst_null
8: bipush 6
10: ldc #109; //String ()I
12: aload_1
13: invokestatic #111; //Method javassist/util/proxy/RuntimeSupport.find2Methods:(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;ILjava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;)V
16: aload_0
17: getfield #113; //Field handler:Ljavassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler;
20: aload_0
21: aload_1
22: bipush 6
24: aaload
25: aload_1
26: bipush 7
28: aaload
29: iconst_0
30: anewarray #52; //class java/lang/Object
33: invokeinterface #115, 5; //InterfaceMethod javassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler.invoke:(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
38: checkcast #101; //class java/lang/Integer
41: invokevirtual #117; //Method java/lang/Integer.intValue:()I
44: ireturn
public final void _d4finalize() throws java.lang.Throwable;
Code:
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #123; //Method java/lang/Object.finalize:()V
4: return
protected final void finalize() throws java.lang.Throwable;
Code:
0: getstatic #125; //Field _methods_:[Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
3: astore_1
4: aload_0
5: ldc #126; //String finalize
7: ldc #127; //String _d4finalize
9: bipush 8
11: ldc #128; //String ()V
13: aload_1
14: invokestatic #130; //Method javassist/util/proxy/RuntimeSupport.find2Methods:(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;ILjava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;)V
17: aload_0
18: getfield #132; //Field handler:Ljavassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler;
21: aload_0
22: aload_1
23: bipush 8
25: aaload
26: aload_1
27: bipush 9
29: aaload
30: iconst_0
31: anewarray #52; //class java/lang/Object
34: invokeinterface #134, 5; //InterfaceMethod javassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler.invoke:(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
39: pop
40: return
public final java.lang.String _d5toString();
Code:
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #139; //Method java/lang/Object.toString:()Ljava/lang/String;
4: areturn
public final java.lang.String toString();
Code:
0: getstatic #141; //Field _methods_:[Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
3: astore_1
4: aload_0
5: ldc #142; //String toString
7: ldc #143; //String _d5toString
9: bipush 10
11: ldc #144; //String ()Ljava/lang/String;
13: aload_1
14: invokestatic #146; //Method javassist/util/proxy/RuntimeSupport.find2Methods:(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;ILjava/lang/String;[Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;)V
17: aload_0
18: getfield #148; //Field handler:Ljavassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler;
21: aload_0
22: aload_1
23: bipush 10
25: aaload
26: aload_1
27: bipush 11
29: aaload
30: iconst_0
31: anewarray #52; //class java/lang/Object
34: invokeinterface #150, 5; //InterfaceMethod javassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler.invoke:(Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;[Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;
39: checkcast #152; //class java/lang/String
42: areturn
static {};
Code:
0: bipush 12
2: anewarray #155; //class java/lang/reflect/Method
5: putstatic #157; //Field _methods_:[Ljava/lang/reflect/Method;
8: return
public void setHandler(javassist.util.proxy.MethodHandler);
Code:
0: aload_0
1: aload_1
2: putfield #161; //Field handler:Ljavassist/util/proxy/MethodHandler;
5: return
java.lang.Object writeReplace() throws java.io.ObjectStreamException;
Code:
0: aload_0
1: invokestatic #168; //Method javassist/util/proxy/RuntimeSupport.makeSerializedProxy:(Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljavassist/util/proxy/SerializedProxy;
4: areturn
}
(5) JAVAASSIST拼接源码生成的字节码:
public class com.alibaba.test.performance.dynamicproxy.CountServiceJavaassistProxy extends java.lang.Object implements com.alibaba.test.performance.dynamicproxy.CountService{
public com.alibaba.test.performance.dynamicproxy.CountService delegate;
public com.alibaba.test.performance.dynamicproxy.CountServiceJavaassistProxy();
Code:
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #12; //Method java/lang/Object."":()V
4: return
public int count();
Code:
0: aload_0
1: getfield #19; //Field delegate:Lcom/alibaba/test/performance/dynamicproxy/CountService;
4: invokeinterface #21, 1; //InterfaceMethod com/alibaba/test/performance/dynamicproxy/CountService.count:()I
9: ireturn
}
(6) 用ASM自行生成的字节码:
public class com.alibaba.test.performance.dynamicproxy.CountServiceAsmProxy extends java.lang.Object implements com.alibaba.test.performance.dynamicproxy.CountService{
public com.alibaba.test.performance.dynamicproxy.CountService delegate;
public com.alibaba.test.performance.dynamicproxy.CountServiceAsmProxy();
Code:
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #10; //Method java/lang/Object."":()V
4: return
public int count();
Code:
0: aload_0
1: getfield #16; //Field delegate:Lcom/alibaba/test/performance/dynamicproxy/CountService;
4: invokeinterface #18, 1; //InterfaceMethod com/alibaba/test/performance/dynamicproxy/CountService.count:()I
9: ireturn
}