- Spring的使命:简化Java开发。
Spring为简化Java开发采取的4个关键策略:
①基于POJO的轻量级和最小侵入性编程;
②通过依赖注入和面向接口实现松耦合;
③通过切面和惯例进行声明式编程;
④通过切面和模板减少样板式代码;Spring容器管理bean对象的生命周期和协作关系,Spring通过上下文对象将你对bean的配置加载进Spring容器,比如你在JavaConfig中配置,或者XML中,或者隐式配置(使用@Component等注解),这样容器就可以管理你的对象。
- 几种上下文对象:
① AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:从一个或多个基于java的配置类中加载上下文定义,适用于java注解的方式;@Configuration
② ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从类路径下的一个或多个xml配置文件中加载上下文定义,适用于xml配置的方式;
③ FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:从文件系统下的一个或多个xml配置文件中加载上下文定义,也就是说系统盘符中加载xml配置文件;
④ AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext:专门为web应用准备的,适用于注解方式;
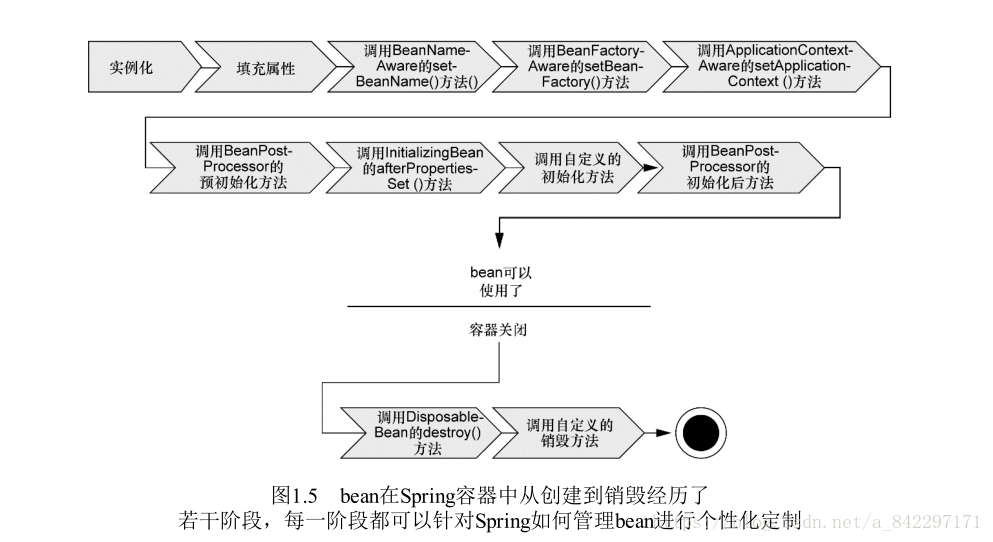
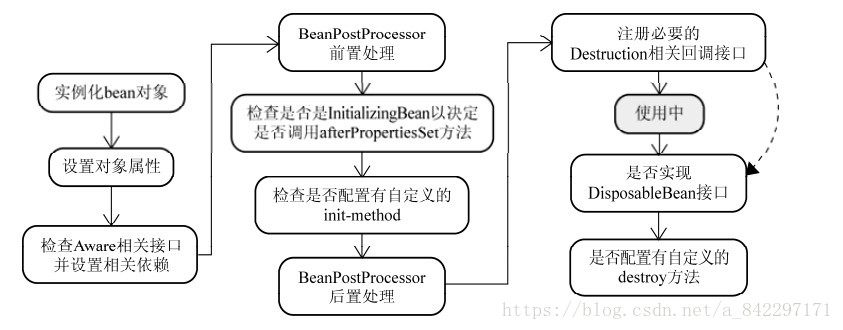
⑤ XmlWebApplicationContext:从web应用下的一个或多个xml配置文件加载上下文定义,适用于xml配置方式。 - bean的生命周期
- JavaConfig
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
//不指定值默认扫描自己所在的包以及子包
@ComponentScan
public class CDPlayerConfig {
}import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
//指定特定的包作为基础包
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.Chapter2"})
public class CDPlayerConfig2 {
}import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.Chapter2.CompactDisc;
@Configuration
//指定为特定的类和接口
@ComponentScan(basePackageClasses = {CompactDisc.class})
public class CDPlayerConfig3 {
}import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.Chapter2.CDPlayer;
import com.Chapter2.CompactDisc;
import com.Chapter2.SgtPeppers;
@Configuration //表明这个类是一个配置类,该类应该包含在Spring应用上下文中如何创建bean的细节。
public class CDPlayerConfig4 {
@Bean(name="lonelyHeartsClub")
public CompactDisc sgtPeppers() {
return new SgtPeppers();
}
@Bean
public CDPlayer cdPlayer() {
return new CDPlayer(sgtPeppers());
}
/*@Bean
public CDPlayer cdPlayer(CompactDisc compactDisc) {
//构造器注入
return new CDPlayer(compactDisc);
}*/
@Bean
public CDPlayer cdPlayer(CompactDisc compactDisc) {
CDPlayer cdPlayer = new CDPlayer(compactDisc);
//setter方法注入
cdPlayer.setCd(compactDisc);
return cdPlayer;
}
}- @Profile:多种环境下的不同bean
不同环境下的不同bean创建,每个profile代表一种环境,spring通过spring.profiles.active和spring.profiles.default属性来设置,如果active有设置值则是active,不然则是default设置的值,如果default也没有设置值,则@Profile定义的bean不会被创建。
有多种方式来设置这两个属性:
①作为DispatcherServlet的初始化参数;
②作为web应用的上下文参数;
③作为JNDI条目;
④作为环境变量;
⑤作为JVM的系统属性;
⑥在集成测试类上,使用@ActiveProfiles注解配置。
public interface Person {
public void speak();
}
@Component
@Profile("China")
//Profile是China才会实例化这个bean
public class Chinese implements Person {
public void speak() {
System.out.println("我说中文");
}
}
@Component
@Profile("England")
//Profile是England才会实例化这个bean
public class English implements Person {
public void speak() {
System.out.println("I speak english");
}
}
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes=ProfileConfig.class)
//集成测试类上,使用@ActiveProfiles注解设置
@ActiveProfiles({"England"/*,"China"*/})
public class ProfileTest {
@Autowired
Person p;
@Test
public void testProfile() {
p.speak();
}
}
输出:I speak english- @Conditional满足条件才创建bean
@Conditional用到带有@bean注解的方法上,只有满足条件,才创建bean。
只有matches方法返回true,bean才会创建。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Condition {
/**
* Determine if the condition matches.
* @param context the condition context
* @param metadata metadata of the {@link org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata class}
* or {@link org.springframework.core.type.MethodMetadata method} being checked
* @return {@code true} if the condition matches and the component can be registered,
* or {@code false} to veto the annotated component's registration
*/
boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata);
}public interface ConditionContext {
/**
* Return the {@link BeanDefinitionRegistry} that will hold the bean definition
* should the condition match.
*/
BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry();
/**
* Return the {@link ConfigurableListableBeanFactory} that will hold the bean
* definition should the condition match.
*/
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory();
/**
* Return the {@link Environment} for which the current application is running.
*/
Environment getEnvironment();
/**
* Return the {@link ResourceLoader} currently being used.
*/
ResourceLoader getResourceLoader();
/**
* Return the {@link ClassLoader} that should be used to load additional classes.
*/
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}下面是一个例子:
public interface RunEnvironment {
public void where();
}
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata;
/**
* bean是否加载的条件
* @author hasee
*
*/
public class WindowsConditional implements Condition {
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata am) {
//可以检查bean定义
BeanDefinitionRegistry register = context.getRegistry();
//可以检查bean是否存在,甚至探查bean的属性
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
//检查环境变量是否存在以及它的值是什么
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
//返回类加载器,可以检查类是否存在
ClassLoader classLoader = context.getClassLoader();
//检查所加载的资源
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = context.getResourceLoader();
String osName = context.getEnvironment().getProperty("os.name");
System.out.println(osName);
return osName.contains("Windows");
}
}import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata;
/**
* bean是否加载的条件
* @author hasee
*
*/
public class LinuxConditional implements Condition {
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata arg1) {
String osName = context.getEnvironment().getProperty("os.name");
System.out.println(osName);
return osName.contains("Linux");
}
}public class WindowsEnvironment implements RunEnvironment {
public void where() {
System.out.println("Run in Windows");
}
}public class LinuxEnvironment implements RunEnvironment {
public void where() {
System.out.println("Run in Linux");
}
}@Configuration
public class ConditionalConfig {
//spring会遍历下面的条件,只生成符合的bean
@Bean
//只有满足WindowsConditional的条件此类才加载
@Conditional(WindowsConditional.class)
public RunEnvironment getWindows() {
return new WindowsEnvironment();
}
@Bean
@Conditional(LinuxConditional.class)
public RunEnvironment getLinux() {
return new LinuxEnvironment();
}
}import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import com.Chapter3.conditional.config.ConditionalConfig;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes= {ConditionalConfig.class})
public class ConditionalTest {
@Autowired
private RunEnvironment runEnvironment;
@Test
public void conditionalTest() {
runEnvironment.where();
}
}
结果输出为:
Windows 8.1
Windows 8.1
Run in Windows