饭前点心:
DFS序,闻名知意就知道这是个跟 DFS 相关的东东,通俗一点说就是
DFS 的序列。
如果您 DFS 不太懂的话,建议先去搞几道走迷宫的题目练练手。
什么是DFS序?

如你当前看到的这幅图,如果我们按照 DFS(深度优先搜索)走这棵树时,
路径就是我们 绿色 所代表的路径。
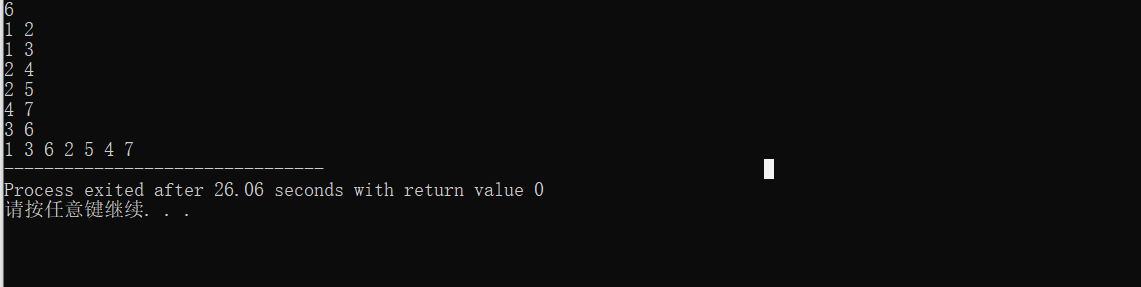
即我们这个树的 DFS 序是 : 1 2 4 7 7 4 5 5 2 3 6 6 3 1
总共有 2 * N 个点,即每个点会经过两次。
另外,我们发现经过的两个点之间经过的路径和节点正好是以该节点为根的一颗
子树,所以 DFS 序经常用来解决树上的一些区间问题。
Code:
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 10;
int head[maxn],Next[maxn],edge[maxn],ver[maxn];
int id[maxn],vis[maxn];
int n,tot,cnt;
void add(int u,int v) {
ver[++ tot] = v,Next[tot] = head[u],head[u] = tot;
return ;
}
// cnt 代表第几次
void DFS(int x) {
// 记录第一个点
id[++ cnt] = x;
vis[x] = 1;
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = Next[i]) {
int y = ver[i];
if(vis[y]) continue;
DFS(y);
}
// 记录第二个点
id[++ cnt] = x;
return ;
}
int main(void) {
scanf("%d",&n);
int u,v;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
// 建立双向边
add(u,v);
add(v,u);
}
DFS(1);
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i ++) {
printf("%d ",id[i]);
}
return 0;
}
效果:
另一种方式:
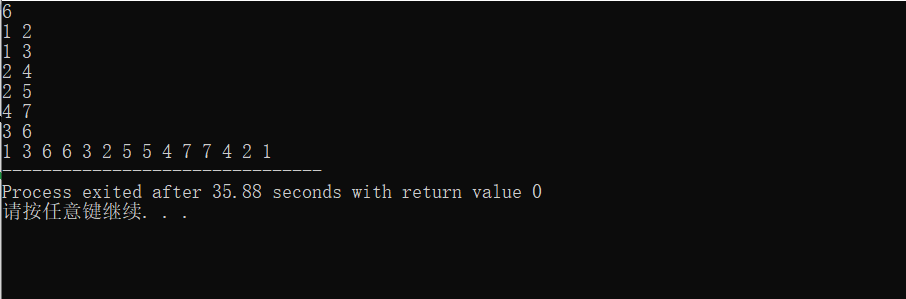
我们发现这种 DFS 序我们输出的同一个节点会输出两次,那么要想只输出一次,要怎么做呢?
修改一下 DFS 函数即可。
Code:
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 10;
int head[maxn],Next[maxn],edge[maxn],ver[maxn];
int id[maxn],vis[maxn];
int st[maxn],ed[maxn];
int n,tot,cnt;
void add(int u,int v) {
ver[++ tot] = v,Next[tot] = head[u],head[u] = tot;
return ;
}
void DFS(int x) {
id[++ cnt] = x;
vis[x] = 1;
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = Next[i]) {
int y = ver[i];
if(vis[y]) continue;
DFS(y);
}
return ;
}
int main(void) {
scanf("%d",&n);
int u,v;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
// 建立双向边
add(u,v);
add(v,u);
}
DFS(1);
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; i ++) {
printf("%d ",id[i]);
}
return 0;
}
效果: