在Spring中实现依赖注入有两种方式,分别是通过注解的方式和通过xml的方式,以下案例是在Spring3.x版本进行讲解。
一、使用注解的方式实现IOC
1.1、导入Spring类库
1.2、编写数据访问层DAO
这里面只是提供了一个空的类,我们的目的是为了测试在Service层中是否可以成功的将这个Dao类注入。通过@Repository注解来标注Dao
package com.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
/**
*
* 配置DAO
*
* @author thinkpad
*
*/
@Repository("userDao")
public class UserDao {
}
1.3、编写服务层Service
我们通过@Service注解来标注Service
package com.service;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.dao.UserDao;
/**
* 配置Service
*
* @author thinkpad
*
*/
@Service("userService")
@Scope("singleton") //单实例
//@Scope("prototype") //多实例
public class UserService {
@Value("用户服务")
private String info;
// @Autowired
// @Qualifier("userDao")
@Resource(name = "userDao")
private UserDao dao;
/**
* 初始化注解
*/
@PostConstruct
public void setup() {
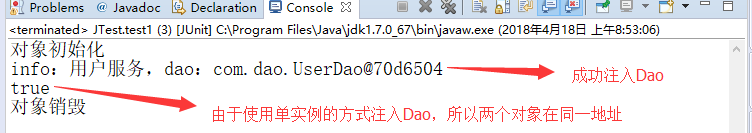
System.out.println("对象初始化");
}
/**
* 销毁注解
*/
@PreDestroy
public void teardown() {
System.out.println("对象销毁");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "info:" + this.info + ",dao:" + this.dao;
}
}
1.4、在applicationContext.xml中配置注解扫描
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--
在是用xml+注解混合开发时,必须配置annotation-config,完全使用注解开发,是不需要配置的
<context:annotation-config/>
-->
<!-- 扫描entity包下的所有类,寻找注解 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com" />
</beans>
1.5、测试
package test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.service.UserService;
public class JTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService en = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userService");
System.out.println(en);
UserService en2 = (UserService) ctx.getBean("userService");
System.out.println(en.equals(en2));
ctx.close();
}
}
1.6、运行结果
二、使用XML的方式实现IOC
1.1、导入Spring类库
1.2、要注入的实体对象
package test.entity;
public class EntityInner {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Inner姓名:" + this.name;
}
}
package test.entity;
public class Entity1 {
private String name;
public Entity1(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "姓名:" + this.name;
}
}
package test.entity;
public class Entity2 {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "姓名:" + this.name;
}
}
package test.entity;
public class Entity3 {
private String name;
private EntityInner inner;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setInner(EntityInner inner) {
this.inner = inner;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "姓名:"+this.name + ",inner:"+this.inner.toString();
}
}
package test.entity;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Entity4 {
private List<String> cities;
private Map<String, Integer> persons;
private Properties users;
public List<String> getCities() {
return cities;
}
public void setCities(List<String> cities) {
this.cities = cities;
}
public Map<String, Integer> getPersons() {
return persons;
}
public void setPersons(Map<String, Integer> persons) {
this.persons = persons;
}
public Properties getUsers() {
return users;
}
public void setUsers(Properties users) {
this.users = users;
}
}
1.3、在applicationContext.xml中配置注解扫描
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
>
<!--
bean标签的属性:
id:遵守xml约束的id约束,id约束保证这个属性值是唯一的,而且必须以字母开始,可以使用字母、数字、连接符、下划线、句号、冒号
name:功能和id属性一直,但是name属性没有xml的id约束,如果bean中没有配置id,则name属性可以代替id
scope:类的作用域,
-singleton:(默认)表示以单实例的方式来创建该类的实例
-prototype:多实例
-request:web开发中,创建了一个对象,将这个对象存入request范围,相当于request.setAttribute()
-session:web开发中,创建了一个对象,将这个对象存入session范围,相当于session.setAttribute()
-globalSession:web开发,一般用于Porlet应用环境,指的是分布式开发,不是Porlet环境,globalSession相当于session
-->
<!-- 使用setter方法注入 -->
<bean id="entity1" class="test.entity.Entity2" scope="singleton">
<property name="name" value="张三" />
</bean>
<!-- 使用构造器注入 -->
<bean id="entity2" class="test.entity.Entity1" scope="prototype">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="李四" />
</bean>
<!-- 使用setter方法注入实体 -->
<bean id="entity3" class="test.entity.Entity3">
<property name="inner" ref="entity_innner"/>
</bean>
<bean id="entity_innner" class="test.entity.EntityInner">
<property name="name" value="嘿嘿嘿"/>
</bean>
<!--
通过名称空间(2.5以后),使用setter方法注入实体
注意:
使用名称控件,需要在<beans>标签中引入p空间属性
-->
<bean id="entity4" class="test.entity.Entity3" p:name="王五" p:inner-ref="entity_innner"/>
<!--
通过SpEL(3.0以后)[Spring表达式语言],使用setter方法注入实体
-->
<bean id="entity5" class="test.entity.Entity3">
<property name="name" value="#{entity_innner.name}"/>
<property name="inner" value="#{entity_innner}"/>
</bean>
<!-- 引入外部配置文件 -->
<import resource="applicationContext2.xml"/>
</beans>
applicationContext2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
>
<!-- 注入集合 -->
<bean id="entity6" class="test.entity.Entity4">
<property name="cities">
<list>
<value>北京</value>
<value>上海</value>
<value>杭州</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="persons">
<map>
<entry key="张三" value="18" value-type="int"/>
<entry key="李四" value="23" value-type="int"/>
<entry key="王五" value="19" value-type="int"/>
</map>
</property>
<property name="users">
<props>
<prop key="张三">admin</prop>
<prop key="李四">123456</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
1.4、测试
package test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import test.entity.Entity1;
import test.entity.Entity2;
import test.entity.Entity3;
import test.entity.Entity4;
public class JTest {
/**
* 通过Setter方法注入依赖对象
*/
@Test
public void test1() {
ApplicationContext cxt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Entity1 en = (Entity1) cxt.getBean("entity2");
System.out.println(en.toString());
}
/**
* 通过构造器注入依赖对象
*/
@Test
public void test1_1() {
ApplicationContext cxt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Entity2 en = (Entity2) cxt.getBean("entity1");
System.out.println(en.toString());
}
/**
* 注入实体
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
ApplicationContext cxt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Entity3 en = (Entity3) cxt.getBean("entity5");
System.out.println(en.toString());
}
/**
* 注入集合
*/
@Test
public void test3() {
ApplicationContext cxt = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Entity4 en = (Entity4) cxt.getBean("entity6");
System.out.println(en.getCities());
System.out.println(en.getPersons());
System.out.println(en.getUsers());
}
}
四、源代码