简介
Protobuf是google提供的一个开源序列化框架,类似于XML,JSON这样的数据表示语言。
支持多种编程语言,现:java、c#、c++、go 和 python。
基于二进制,因此比传统的XML表示高效短小得多
作为一种效率和兼容性都很优秀的二进制数据传输格式,可以用于诸如网络传输、配置文件、数据存储等诸多领域。
使用
1、下载地址:http://code.google.com/p/protobuf/downloads/
2、proto文件格式
package 对应于c#中的命名空间
required 对应类的属性
optional 创建一个具有默认值的属性,通过[default=XXX]设置默认值,不添加默认为空置。如string默认为“”,int默认为0
enum 创建枚举
message 创建自定义类或内部类
repeated 对应list列表数据
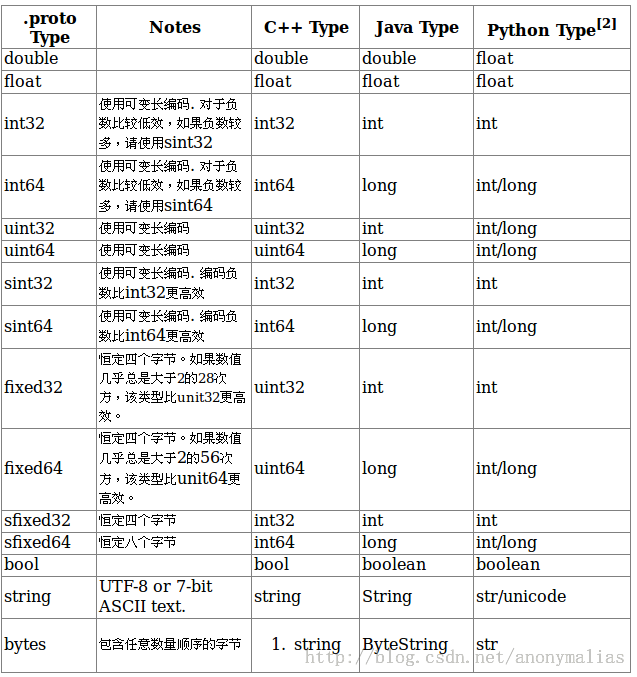
proto数据类型:
示例:
package test;
message Person {
required string name=1;
required int32 id=2;
optional string email=3 ;
enum PhoneType {
MOBILE=0;
HOME=1;
WORK=2;
}
message PhoneNumber {
required string number=1;
optional PhoneType type=2 [default=HOME];
}
repeated PhoneNumber phone=4;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
proto文件编辑的命令:
protogen -i:input.proto -o:output.cs
protogen -i:input.proto -o:output.xml -t:xml
protogen -i:input.proto -o:output.cs -p:datacontract -q
protogen -i:input.proto -o:output.cs -p:observable=true
转换之后的文件:
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// <auto-generated>
// This code was generated by a tool.
//
// Changes to this file may cause incorrect behavior and will be lost if
// the code is regenerated.
// </auto-generated>
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Generated from: input/test.proto
namespace input.test
{
[global::System.Serializable, global::ProtoBuf.ProtoContract(Name=@"Person")]
public partial class Person : global::ProtoBuf.IExtensible
{
public Person() {}
private string _name;
[global::ProtoBuf.ProtoMember(1, IsRequired = true, Name=@"name", DataFormat = global::ProtoBuf.DataFormat.Default)]
public string name
{
get { return _name; }
set { _name = value; }
}
private int _id;
[global::ProtoBuf.ProtoMember(2, IsRequired = true, Name=@"id", DataFormat = global::ProtoBuf.DataFormat.TwosComplement)]
public int id
{
get { return _id; }
set { _id = value; }
}
private string _email = "";
[global::ProtoBuf.ProtoMember(3, IsRequired = false, Name=@"email", DataFormat = global::ProtoBuf.DataFormat.Default)]
[global::System.ComponentModel.DefaultValue("")]
public string email
{
get { return _email; }
set { _email = value; }
}
private readonly global::System.Collections.Generic.List<Person.PhoneNumber> _phone = new global::System.Collections.Generic.List<Person.PhoneNumber>();
[global::ProtoBuf.ProtoMember(4, Name=@"phone", DataFormat = global::ProtoBuf.DataFormat.Default)]
public global::System.Collections.Generic.List<Person.PhoneNumber> phone
{
get { return _phone; }
}
[global::System.Serializable, global::ProtoBuf.ProtoContract(Name=@"PhoneNumber")]
public partial class PhoneNumber : global::ProtoBuf.IExtensible
{
public PhoneNumber() {}
private string _number;
[global::ProtoBuf.ProtoMember(1, IsRequired = true, Name=@"number", DataFormat = global::ProtoBuf.DataFormat.Default)]
public string number
{
get { return _number; }
set { _number = value; }
}
private Person.PhoneType _type = Person.PhoneType.HOME;
[global::ProtoBuf.ProtoMember(2, IsRequired = false, Name=@"type", DataFormat = global::ProtoBuf.DataFormat.TwosComplement)]
[global::System.ComponentModel.DefaultValue(Person.PhoneType.HOME)]
public Person.PhoneType type
{
get { return _type; }
set { _type = value; }
}
private global::ProtoBuf.IExtension extensionObject;
global::ProtoBuf.IExtension global::ProtoBuf.IExtensible.GetExtensionObject(bool createIfMissing)
{ return global::ProtoBuf.Extensible.GetExtensionObject(ref extensionObject, createIfMissing); }
}
[global::ProtoBuf.ProtoContract(Name=@"PhoneType")]
public enum PhoneType
{
[global::ProtoBuf.ProtoEnum(Name=@"MOBILE", Value=0)]
MOBILE = 0,
[global::ProtoBuf.ProtoEnum(Name=@"HOME", Value=1)]
HOME = 1,
[global::ProtoBuf.ProtoEnum(Name=@"WORK", Value=2)]
WORK = 2
}
private global::ProtoBuf.IExtension extensionObject;
global::ProtoBuf.IExtension global::ProtoBuf.IExtensible.GetExtensionObject(bool createIfMissing)
{ return global::ProtoBuf.Extensible.GetExtensionObject(ref extensionObject, createIfMissing); }
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
3、proto转化后的.cs文件的序列化和反序列化
首先,将生成的.cs文件复制到自己的项目文件中
然后添加动态链接库文件protobuf-net.dll(该文件位于下载的proto文件的protobuf-net_r668\ProtoGen目录下)
然后在程序中引用,相关程序如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using ProtoBuf;
using input.test;
using System.IO;
using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary;
namespace test1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Person p = new Person();
p.name = "zhang san";
p.email = "[email protected]";
p.id = 12;
//序列化操作
MemoryStream ms=new MemoryStream();
//BinaryFormatter bm = new BinaryFormatter();
//bm.Serialize(ms, p);
Serializer.Serialize<Person>(ms, p);
byte[] data = ms.ToArray();//length=27 709
//反序列化操作
MemoryStream ms1 = new MemoryStream(data);
// BinaryFormatter bm1 = new BinaryFormatter();
//Person p1= bm.Deserialize(ms1) as Person;
Person p1 = Serializer.Deserialize<Person>(ms1);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36