熟悉SpringMVC的启动过程,有助于我们理解相关文件配置的原理,深入理解SpringMVC的设计原理和执行过程。
Web应用部署初始化过程 (Web Application Deployement)
参考Oracle官方文档Java Servlet Specification,可知Web应用部署的相关步骤如下:

web应用部署流程
当一个Web应用部署到容器内时(eg.tomcat),在Web应用开始响应执行用户请求前,以下步骤会被依次执行:
1.部署描述文件中(eg.tomcat的web.xml)由元素标记的事件监听器会被创建和初始化
2.对于所有事件监听器,如果实现了ServletContextListener接口,将会执行其实现的contextInitialized()方法
3.部署描述文件中由元素标记的过滤器会被创建和初始化,并调用其init()方法
4.部署描述文件中由元素标记的servlet会根据的权值按顺序创建和初始化,并调用其init()方法
通过上述官方文档的描述,可绘制如下Web应用部署初始化流程执行图。
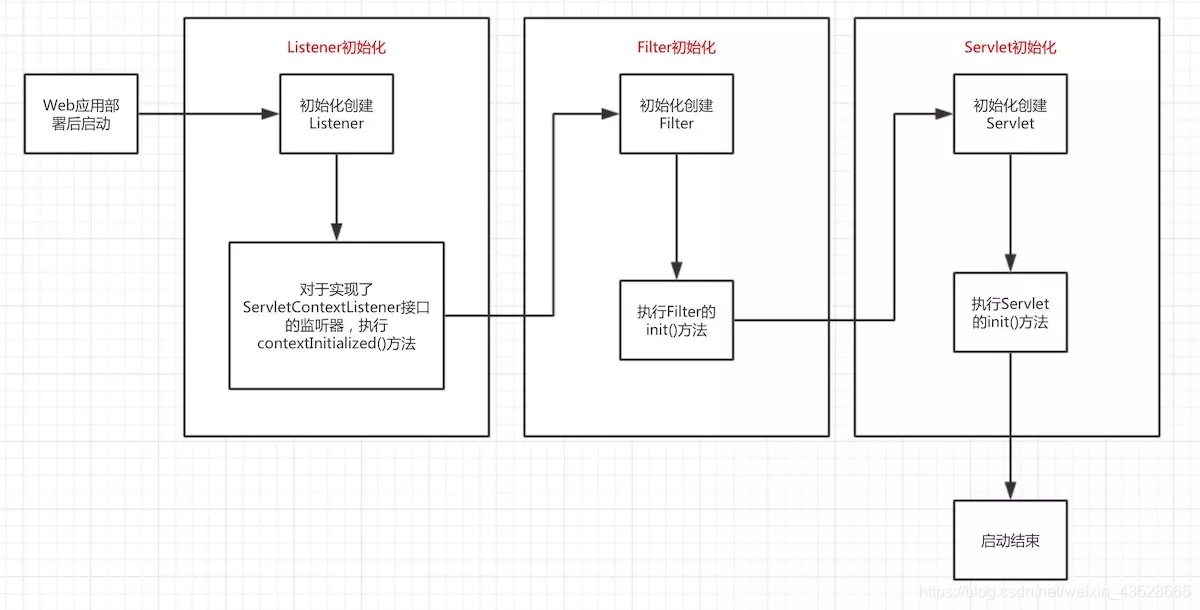
Web应用部署初始化流程图
可以发现,在tomcat下web应用的初始化流程是,先初始化listener接着初始化filter最后初始化servlet,当我们清楚认识到Web应用部署到容器后的初始化过程后,就可以进一步深入探讨SpringMVC的启动过程。
Spring MVC启动过程
接下来以一个常见的简单web.xml配置进行Spring MVC启动过程的分析,web.xml配置内容如下:
<web-app>
<display-name>Web Application</display-name>
<!--全局变量配置-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext-*.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--监听器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!--解决乱码问题的filter-->
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>utf-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!--Restful前端控制器-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springMVC_rest</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springMVC_rest</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Listener的初始化过程
首先定义了标签,用于配置一个全局变量,标签的内容读取后会被放进application中,做为Web应用的全局变量使用,接下来创建listener时会使用到这个全局变量,因此,Web应用在容器中部署后,进行初始化时会先读取这个全局变量,之后再进行上述讲解的初始化启动过程。
接着定义了一个ContextLoaderListener类的listener。查看ContextLoaderListener的类声明源码如下图:
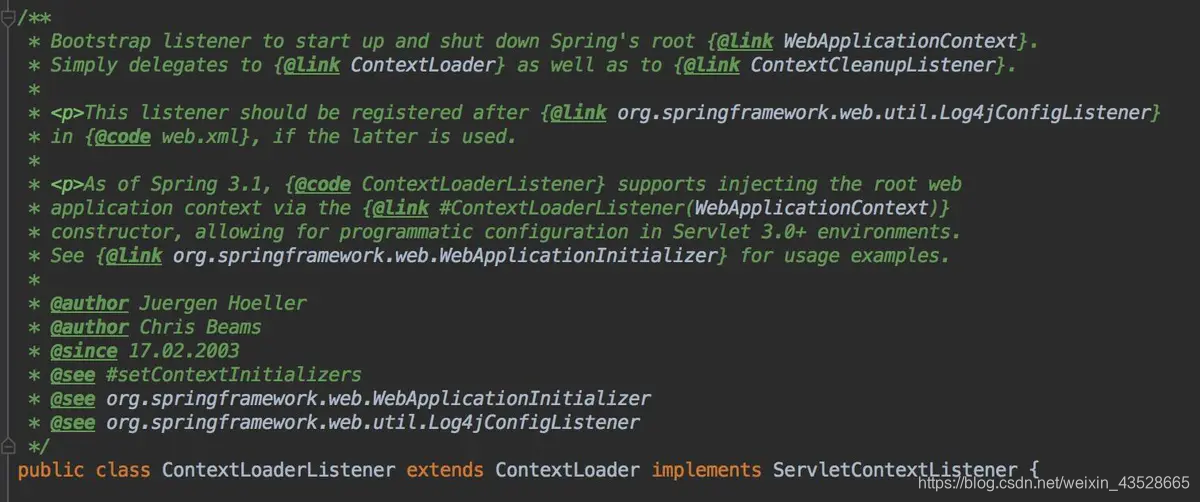
ContextLoaderListener类声明源码
ContextLoaderListener类继承了ContextLoader类并实现了ServletContextListener接口,首先看一下前面讲述的ServletContextListener接口源码:
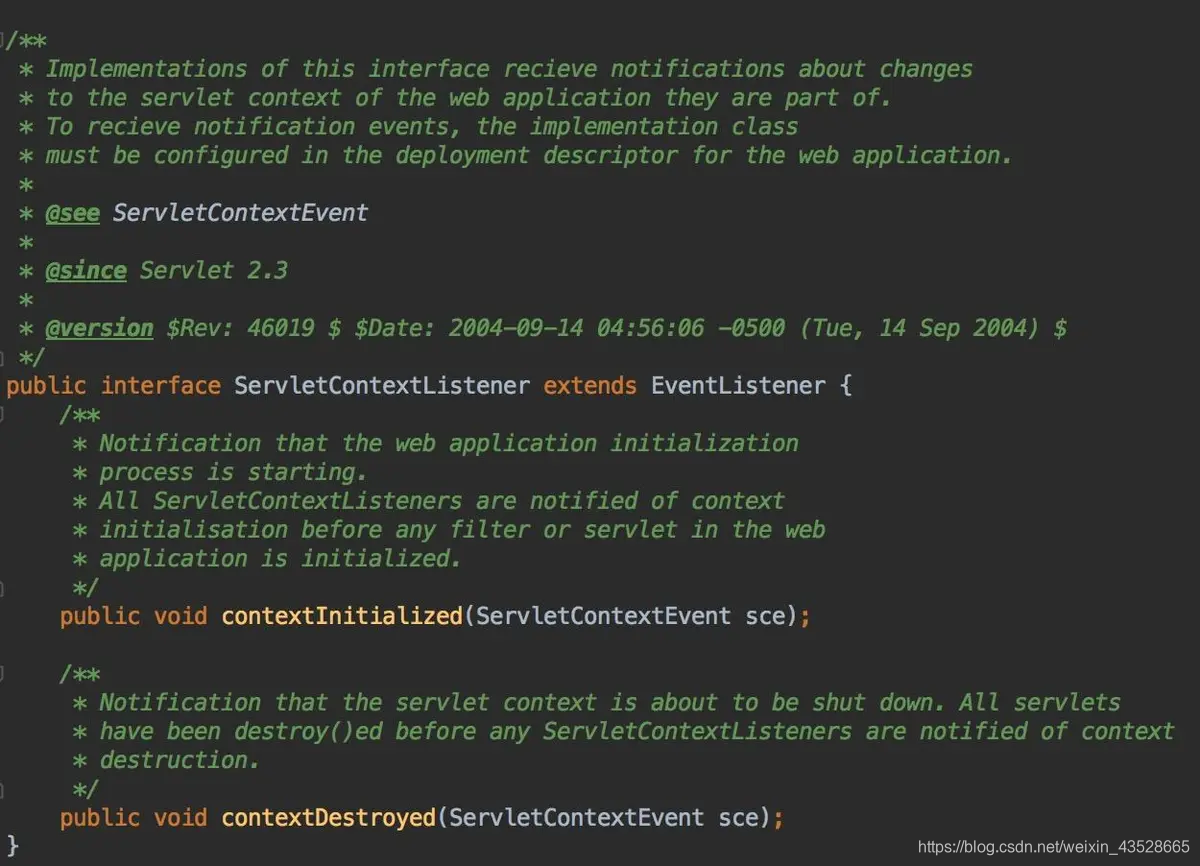
ServletContextListener接口源码
该接口只有两个方法contextInitialized和contextDestroyed,这里采用的是观察者模式,也称为为订阅-发布模式,实现了该接口的listener会向发布者进行订阅,当Web应用初始化或销毁时会分别调用上述两个方法。
继续看ContextLoaderListener,该listener实现了ServletContextListener接口,因此在Web应用初始化时会调用该方法,该方法的具体实现如下:
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
ContextLoaderListener的contextInitialized()方法直接调用了initWebApplicationContext()方法,这个方法是继承自ContextLoader类,通过函数名可以知道,该方法是用于初始化Web应用上下文,即IoC容器,这里使用的是代理模式,继续查看ContextLoader类的initWebApplicationContext()方法的源码如下:
/**
* Initialize Spring's web application context for the given servlet context,
* using the application context provided at construction time, or creating a new one
* according to the "{@link #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM contextClass}" and
* "{@link #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM contextConfigLocation}" context-params.
* @param servletContext current servlet context
* @return the new WebApplicationContext
* @see #ContextLoader(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM
* @see #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM
*/
//servletContext,servlet上下文,即application对象
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
/*
首先通过WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE
这个String类型的静态变量获取一个根IoC容器,根IoC容器作为全局变量
存储在application对象中,如果存在则有且只能有一个
如果在初始化根WebApplicationContext即根IoC容器时发现已经存在
则直接抛出异常,因此web.xml中只允许存在一个ContextLoader类或其子类的对象
*/
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
// 如果当前成员变量中不存在WebApplicationContext则创建一个根WebApplicationContext
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
//为根WebApplicationContext设置一个父容器
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
//配置并刷新整个根IoC容器,在这里会进行Bean的创建和初始化
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
/*
将创建好的IoC容器放入到application对象中,并设置key为WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE
因此,在SpringMVC开发中可以在jsp中通过该key在application对象中获取到根IoC容器,进而获取到相应的Ben
*/
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" +
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);
throw err;
}
}
initWebApplicationContext()方法如上注解讲述,主要目的就是创建root WebApplicationContext对象即根IoC容器,其中比较重要的就是,整个Web应用如果存在根IoC容器则有且只能有一个,根IoC容器作为全局变量存储在ServletContext即application对象中。将根IoC容器放入到application对象之前进行了IoC容器的配置和刷新操作,调用了configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext()方法,该方法源码如下:
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
wac.setServletContext(sc);
/*
CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM = "contextConfigLocation"
获取web.xml中<context-param>标签配置的全局变量,其中key为CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM
也就是我们配置的相应Bean的xml文件名,并将其放入到WebApplicationContext中
*/
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
customizeContext(sc, wac);
wac.refresh();
}
比较重要的就是获取到了web.xml中的标签配置的全局变量contextConfigLocation,并最后一行调用了refresh()方法,ConfigurableWebApplicationContext是一个接口,通过对常用实现类ClassPathXmlApplicationContext逐层查找后可以找到一个抽象类AbstractApplicationContext实现了refresh()方法,其源码如下:
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
该方法主要用于创建并初始化contextConfigLocation类配置的xml文件中的Bean,因此,如果我们在配置Bean时出错,在Web应用启动时就会抛出异常,而不是等到运行时才抛出异常。
整个ContextLoaderListener类的启动过程到此就结束了,可以发现,创建ContextLoaderListener是比较核心的一个步骤,主要工作就是为了创建根IoC容器并使用特定的key将其放入到application对象中,供整个Web应用使用,由于在ContextLoaderListener类中构造的根IoC容器配置的Bean是全局共享的,因此,在标识的contextConfigLocation的xml配置文件一般包括:数据库DataSource、DAO层、Service层、事务等相关Bean。
在JSP中可以通过以下两种方法获取到根IoC容器从而获取相应Bean:
WebApplicationContext applicationContext = (WebApplicationContext) application.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
WebApplicationContext applicationContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
Filter的初始化
在监听器listener初始化完成后,按照文章开始的讲解,接下来会进行filter的初始化操作,filter的创建和初始化中没有涉及IoC容器的相关操作,因此不是本文讲解的重点,本文举例的filter是一个用于编码用户请求和响应的过滤器,采用utf-8编码用于适配中文。
Servlet的初始化
Web应用启动的最后一个步骤就是创建和初始化相关Servlet,在开发中常用的Servlet就是DispatcherServlet类前端控制器,前端控制器作为中央控制器是整个Web应用的核心,用于获取分发用户请求并返回响应,借用网上一张关于DispatcherServlet类的类图,其类图如下所示:
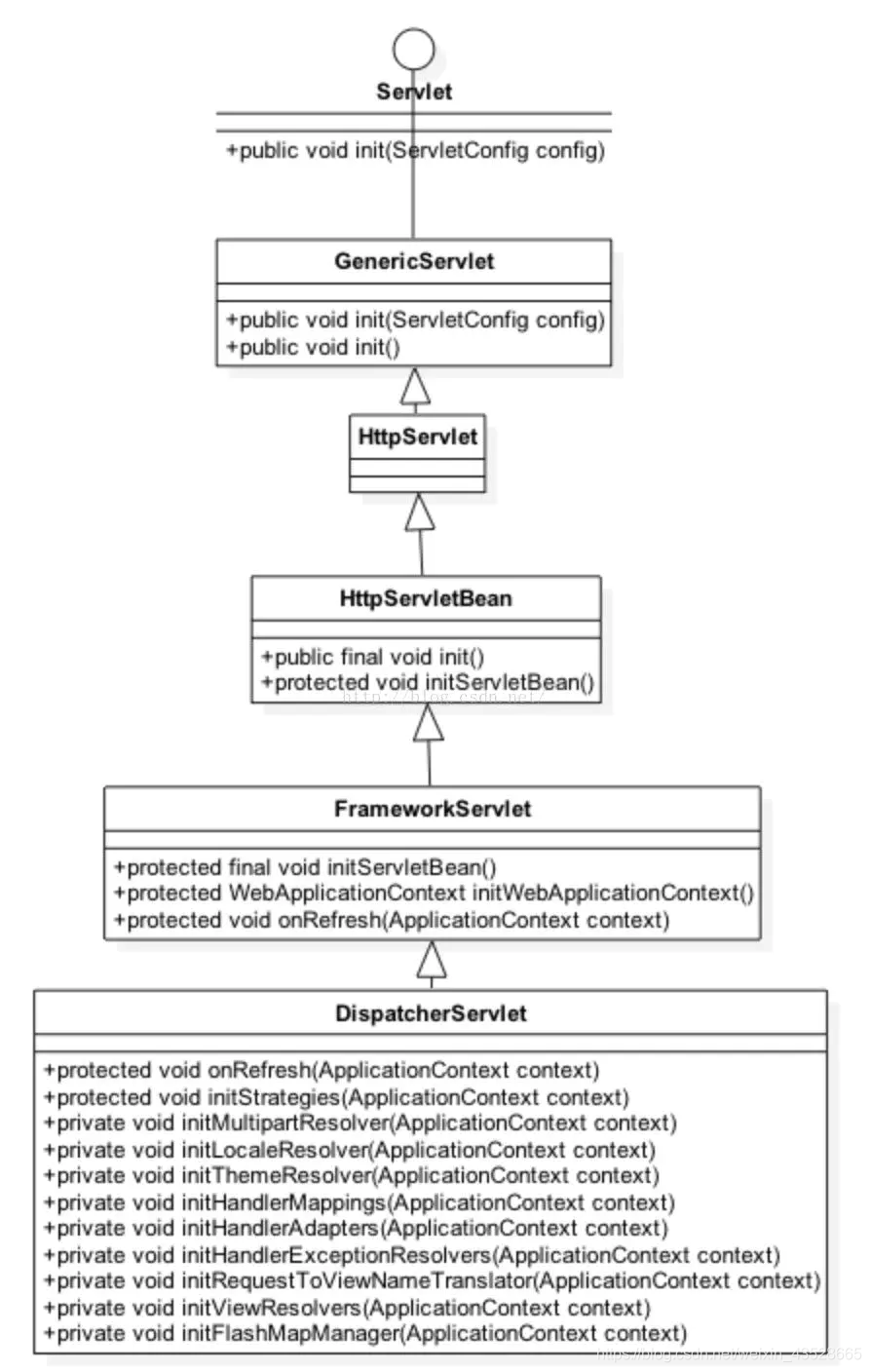
DispatcherServlet类图
通过类图可以看出DispatcherServlet类的间接父类实现了Servlet接口,因此其本质上依旧是一个Servlet。DispatcherServlet类的设计很巧妙,上层父类不同程度的实现了相关接口的部分方法,并留出了相关方法用于子类覆盖,将不变的部分统一实现,将变化的部分预留方法用于子类实现,本文关注的是DispatcherServelt类的初始化过程,没有深入探讨其如何对用户请求做出响应,读者有兴趣可以阅读本系列文章的第二篇SpringMVC DispatcherServlet源码分析。
通过对上述类图中相关类的源码分析可以绘制如下相关初始化方法调用逻辑:
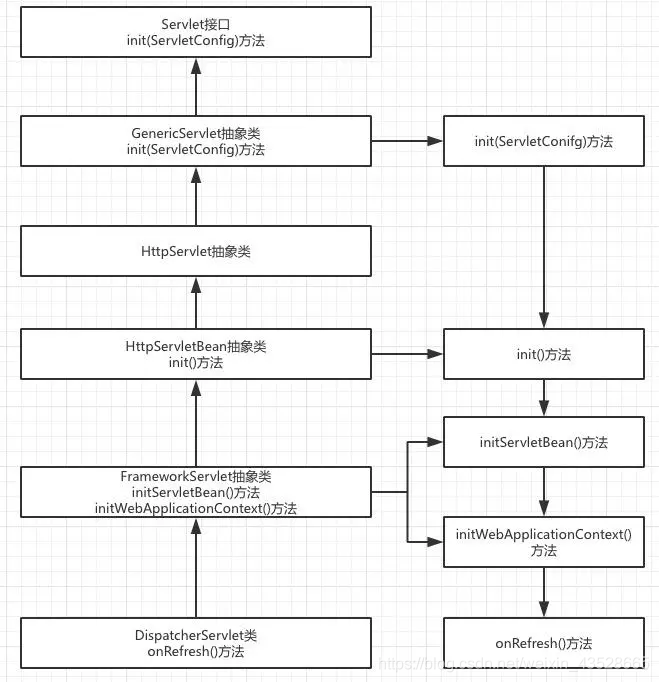
DispatcherServlet类初始化过程函数调用
通过类图和相关初始化函数调用的逻辑来看,DispatcherServlet类的初始化过程将模板方法使用的淋漓尽致,其父类完成不同的统一的工作,并预留出相关方法用于子类覆盖去完成不同的可变工作。
DispatcherServelt类的本质是Servlet,通过文章开始的讲解可知,在Web应用部署到容器后进行Servlet初始化时会调用相关的init(ServletConfig)方法,因此,DispatchServlet类的初始化过程也由该方法开始。上述调用逻辑中比较重要的就是FrameworkServlet抽象类中的initServletBean()方法、initWebApplicationContext()方法以及DispatcherServlet类中的onRefresh()方法,接下来会逐一进行讲解。
首先查看一下initServletBean()的相关源码如下图所示:
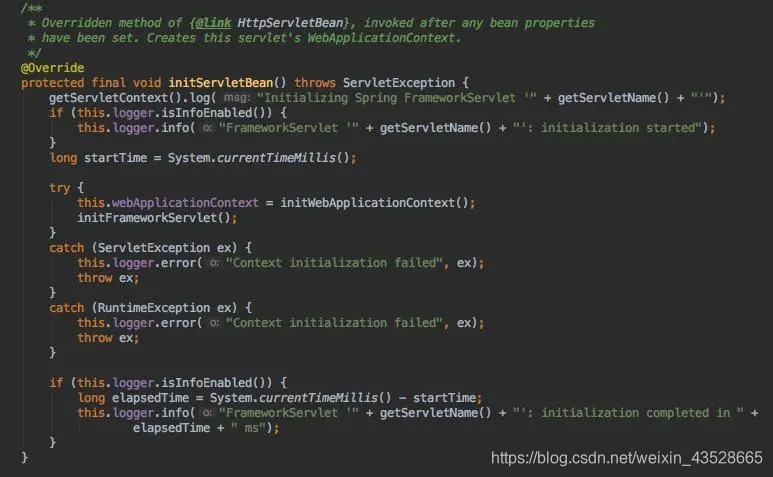
FrameworkServlet initServletBean()方法源码
该方法是重写了FrameworkServlet抽象类父类HttpServletBean抽象类的initServletBean()方法,HttpServletBean抽象类在执行init()方法时会调用initServletBean()方法,由于多态的特性,最终会调用其子类FrameworkServlet抽象类的initServletBean()方法。该方法由final标识,子类就不可再次重写了。该方法中比较重要的就是initWebApplicationContext()方法的调用,该方法仍由FrameworkServlet抽象类实现,继续查看其源码如下所示:
/**
* Initialize and publish the WebApplicationContext for this servlet.
* <p>Delegates to {@link #createWebApplicationContext} for actual creation
* of the context. Can be overridden in subclasses.
* @return the WebApplicationContext instance
* @see #FrameworkServlet(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #setContextClass
* @see #setContextConfigLocation
*/
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
/*
获取由ContextLoaderListener创建的根IoC容器
获取根IoC容器有两种方法,还可通过key直接获取
*/
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
/*
如果当前Servelt存在一个WebApplicationContext即子IoC容器
并且上文获取的根IoC容器存在,则将根IoC容器作为子IoC容器的父容器
*/
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
//配置并刷新当前的子IoC容器,功能与前文讲解根IoC容器时的配置刷新一致,用于构建相关Bean
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
//如果当前Servlet不存在一个子IoC容器则去查找一下
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
//如果仍旧没有查找到子IoC容器则创建一个子IoC容器
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
//调用子类覆盖的onRefresh方法完成“可变”的初始化过程
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}
通过函数名不难发现,该方法的主要作用同样是创建一个WebApplicationContext对象,即Ioc容器,不过前文讲过每个Web应用最多只能存在一个根IoC容器,这里创建的则是特定Servlet拥有的子IoC容器,可能有些读者会有疑问,为什么需要多个Ioc容器,首先介绍一个父子IoC容器的访问特性,有兴趣的读者可以自行实验。
父子IoC容器的访问特性
在学习Spring时,我们都是从读取xml配置文件来构造IoC容器,常用的类有ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类,该类存在一个初始化方法用于传入xml文件路径以及一个父容器,我们可以创建两个不同的xml配置文件并实现如下代码:
//applicationContext1.xml文件中配置一个id为baseBean的Bean
ApplicationContext baseContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext1.xml");
Object obj1 = baseContext.getBean("baseBean");
System.out.println("baseContext Get Bean " + obj1);
//applicationContext2.xml文件中配置一个id未subBean的Bean
ApplicationContext subContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{"applicationContext2.xml"}, baseContext);
Object obj2 = subContext.getBean("baseBean");
System.out.println("subContext get baseContext Bean " + obj2);
Object obj3 = subContext.getBean("subBean");
System.out.println("subContext get subContext Bean " + obj3);
//抛出NoSuchBeanDefinitionException异常
Object obj4 = baseContext.getBean("subBean");
System.out.println("baseContext get subContext Bean " + obj4);
首先创建baseContext没有为其设置父容器,接着可以成功获取id为baseBean的Bean,接着创建subContext并将baseContext设置为其父容器,subContext可以成功获取baseBean以及subBean,最后试图使用baseContext去获取subContext中定义的subBean,此时会抛出异常NoSuchBeanDefinitionException,由此可见,父子容器类似于类的继承关系,子类可以访问父类中的成员变量,而父类不可访问子类的成员变量,同样的,子容器可以访问父容器中定义的Bean,但父容器无法访问子容器定义的Bean。
通过上述实验我们可以理解为何需要创建多个Ioc容器,根IoC容器做为全局共享的IoC容器放入Web应用需要共享的Bean,而子IoC容器根据需求的不同,放入不同的Bean,这样能够做到隔离,保证系统的安全性。
接下来继续讲解DispatcherServlet类的子IoC容器创建过程,如果当前Servlet存在一个IoC容器则为其设置根IoC容器作为其父类,并配置刷新该容器,用于构造其定义的Bean,这里的方法与前文讲述的根IoC容器类似,同样会读取用户在web.xml中配置的中的值,用于查找相关的xml配置文件用于构造定义的Bean,这里不再赘述了。如果当前Servlet不存在一个子IoC容器就去查找一个,如果仍然没有查找到则调用
createWebApplicationContext()方法去创建一个,查看该方法的源码如下图所示:
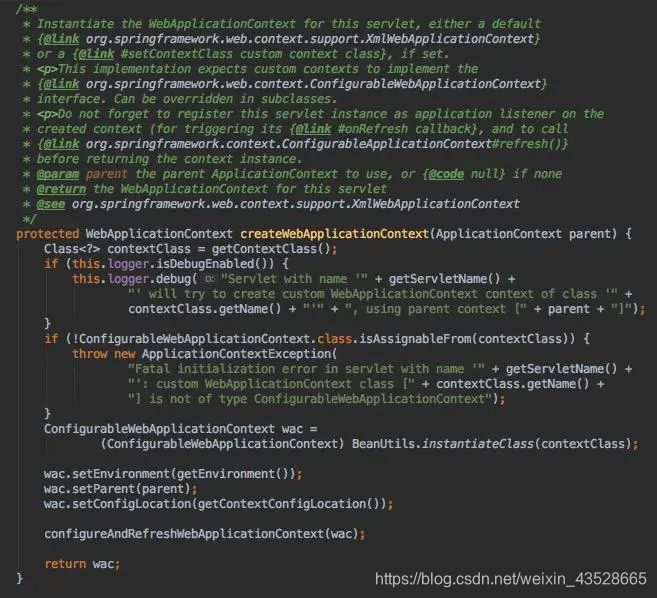
createWebApplicationContext方法源码
该方法用于创建一个子IoC容器并将根IoC容器做为其父容器,接着进行配置和刷新操作用于构造相关的Bean。至此,根IoC容器以及相关Servlet的子IoC容器已经配置完成,子容器中管理的Bean一般只被该Servlet使用,因此,其中管理的Bean一般是“局部”的,如SpringMVC中需要的各种重要组件,包括Controller、Interceptor、Converter、ExceptionResolver等。相关关系如下图所示:
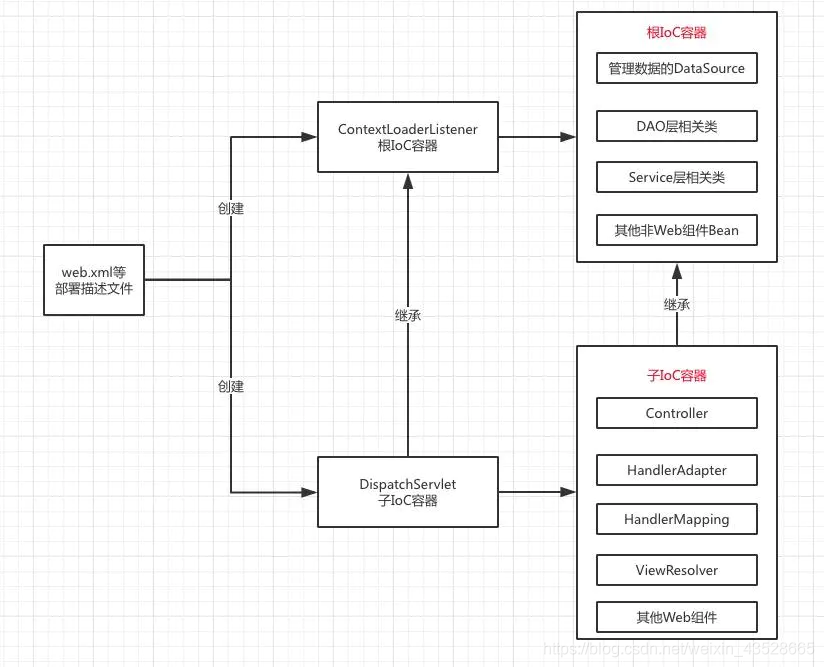
父子容器管理Bean类型
当IoC子容器构造完成后调用了onRefresh()方法,该方法的调用与initServletBean()方法的调用相同,由父类调用但具体实现由子类覆盖,调用onRefresh()方法时将前文创建的IoC子容器作为参数传入,查看DispatcherServletBean类的onRefresh()方法源码如下:
/**
* This implementation calls {@link #initStrategies}.
*/
//context为DispatcherServlet创建的一个IoC子容器
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
onRefresh()方法直接调用了initStrategies()方法,源码如上,通过函数名可以判断,该方法用于初始化创建multipartResovle来支持图片等文件的上传、本地化解析器、主题解析器、HandlerMapping处理器映射器、HandlerAdapter处理器适配器、异常解析器、视图解析器、flashMap管理器等,这些组件都是SpringMVC开发中的重要组件,相关组件的初始化创建过程均在此完成。
由于篇幅问题本文不再进行更深入的探讨,有兴趣的读者可以阅读本系列文章的其他博客内容。
至此,DispatcherServlet类的创建和初始化过程也就结束了,整个Web应用部署到容器后的初始化启动过程的重要部分全部分析清楚了,通过前文的分析我们可以认识到层次化设计的优点,以及IoC容器的继承关系所表现的隔离性。分析源码能让我们更清楚的理解和认识到相关初始化逻辑以及配置文件的配置原理。
总结
这里给出一个简洁的文字描述版SpringMVC启动过程:
tomcat web容器启动时会去读取web.xml这样的部署描述文件,相关组件启动顺序为: 解析 => 解析 => 解析 => 解析,具体初始化过程如下:
1、解析里的键值对。
2、创建一个application内置对象即ServletContext,servlet上下文,用于全局共享。
3、将的键值对放入ServletContext即application中,Web应用内全局共享。
4、读取标签创建监听器,一般会使用ContextLoaderListener类,如果使用了ContextLoaderListener类,Spring就会创建一个WebApplicationContext类的对象,WebApplicationContext类就是IoC容器,ContextLoaderListener类创建的IoC容器是根IoC容器为全局性的,并将其放置在appication中,作为应用内全局共享,键名为WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE,可以通过以下两种方法获取
WebApplicationContext applicationContext = (WebApplicationContext) application.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
WebApplicationContext applicationContext1 = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(application);
这个全局的根IoC容器只能获取到在该容器中创建的Bean不能访问到其他容器创建的Bean,也就是读取web.xml配置的contextConfigLocation参数的xml文件来创建对应的Bean。
5、listener创建完成后如果有则会去创建filter。
6、初始化创建,一般使用DispatchServlet类。
7、DispatchServlet的父类FrameworkServlet会重写其父类的initServletBean方法,并调用initWebApplicationContext()以及onRefresh()方法。
8、initWebApplicationContext()方法会创建一个当前servlet的一个IoC子容器,如果存在上述的全局WebApplicationContext则将其设置为父容器,如果不存在上述全局的则父容器为null。
9、读取标签的配置的xml文件并加载相关Bean。
10、onRefresh()方法创建Web应用相关组件。
