1、异常分类
异常分类: 可查异常,运行时异常和错误3种
其中,运行时异常和错误又叫非可查异常
2、可查异常
可查异常: CheckedException
可查异常即必须进行处理的异常,要么try catch住,要么往外抛,谁调用,谁处理,比如 FileNotFoundException
如果不处理,编译器,就不让你通过
package exception;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f= new File("d:/LOL.exe");
try{
System.out.println("试图打开 d:/LOL.exe");
new FileInputStream(f);
System.out.println("成功打开");
}
catch(FileNotFoundException e){
System.out.println("d:/LOL.exe不存在");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3、运行时异常
运行时异常RuntimeException指: 不是必须进行try catch的异常
常见运行时异常:
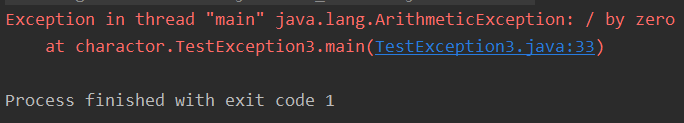
除数不能为0异常:ArithmeticException
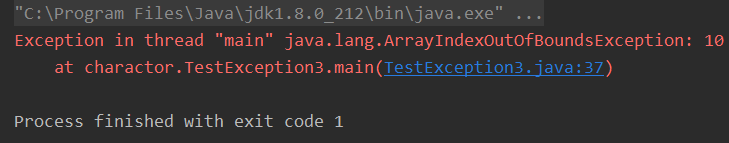
下标越界异常:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
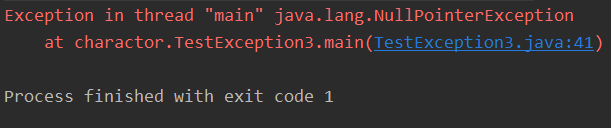
空指针异常:NullPointerException
在编写代码的时候,依然可以使用try catch throws进行处理,与可查异常不同之处在于,即便不进行try catch,也不会有编译错误
Java之所以会设计运行时异常的原因之一,是因为下标越界,空指针这些运行时异常太过于普遍,如果都需要进行捕捉,代码的可读性就会变得很糟糕。
package exception;
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//任何除数不能为0:ArithmeticException
int k = 5/0;
//下标越界异常:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
int j[] = new int[5];
j[10] = 10;
//空指针异常:NullPointerException
String str = null;
str.length();
}
}
- 输出结果
- 除数不能为0的异常
- 下标索引越界
- 空指针异常
4、错误
错误Error,指的是系统级别的异常,通常是内存用光了
在默认设置下,一般java程序启动的时候,最大可以使用16m的内存
如果不停的给StringBuffer追加字符,很快就把内存使用光了。抛出OutOfMemoryError
与运行时异常一样,错误也是不要求强制捕捉的
package exception;
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb =new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE; i++) {
sb.append('a');
}
}
}
5、三种分类
总体上异常分三类:
- 错误
- 运行时异常
- 可查异常

6、练习:异常分类
运行时异常 RuntimeException,能否被捕捉?
错误Error,能否被捕捉?
面试题常问题: 运行时异常与非运行时异常的区别
package exception;
public class exception_test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//内存不足error
try {
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer();
for(int i = 0;i<Integer.MAX_VALUE;i++) {
str.append('1');
}
} catch (Error e) {
System.out.println("这是个错误!!");
e.printStackTrace();
// TODO: handle exception
}
//除数为零异常
try {
int m = (int)Math.random()*10000;
int n = 0;
System.out.println("结果等于:"+m/n);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("除数不可以等于零!!");
e.printStackTrace();
// TODO: handle exception
}
//数组下标异常
try {
int[] a = new int[10];
System.out.println("输出此数组的值:"+a[10]);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("数组下标异常!!");
e.printStackTrace();
// TODO: handle exception
}
//空指针异常
try {
String str = null;
System.out.println("输出此字符串长度:"+str.length());
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("空指针异常!!");
e.printStackTrace();
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
- 运行时异常 RuntimeException 和错误 Error 都能被捕捉
- 运行时异常与非运行时异常的区别?
- 运行时异常是不可查异常,不需要对其进行显式的捕捉
- 非运行时异常是可查异常,必须要对其进行显式的捕捉,抛出,不然编译器会报错不允许程序运行.
