下面来介绍介绍单向链表的一些常见的面试题。拖了好久的题终于写完了。。。。。
前面已经写过一些单向链表的基本实现,在此篇博客中又再次写了一遍,加深记忆。另外还有一些常见的面试题。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct Node
{
struct Node*next;
DataType data;
}Node,*plist,*pNode;
void initLinkList(plist*pplist)//初始化链表,二级指针改变一级指针的指向
{
assert(pplist);//断言pplist是否为NULL
*pplist = NULL;
}
pNode Buynode(DataType data)//创建新节点
{
pNode newnode = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
exit(0);
}
newnode->data = data;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
void PushFront(plist*pplist, DataType data)//头插
{
assert(pplist);
pNode p = Buynode(data);
p->next = *pplist;
*pplist = p;
}
void popFront(plist*pplist)//头删
{
assert(pplist);
pNode cur = *pplist;
if (*pplist == NULL)
{
return;
}
*pplist = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
void PushBack(plist*pplist, DataType data)//尾插
{
assert(pplist);
pNode p = Buynode(data);
pNode cur = *pplist;
if (*pplist == NULL)
{
*pplist = p;
return;
}
while (cur->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = p;
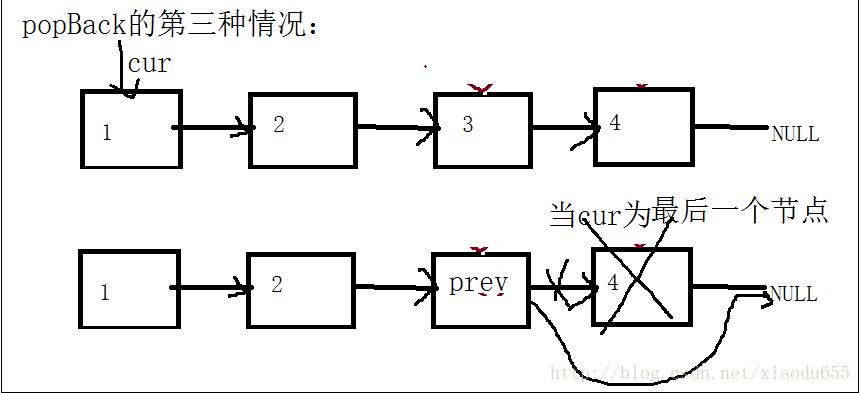
}popBack函数的第三种情况如图所示。
void popBack(plist*pplist)//尾删
{
pNode cur = *pplist;
pNode prev = NULL;
assert(pplist);
//链表没有节点
if (*pplist == NULL)
{
return;
}
//链表有一个节点
if (cur->next == NULL)
{
free(*pplist);
*pplist = NULL;
return;
}
//链表有两个及两个以上节点
while (cur->next != NULL)
{
prev = cur;//prev中保存的是cur之前的那个节点
cur = cur->next;
}
prev->next = NULL;
free(cur);
}pNode Find(plist p, DataType data)//查找节点指向的元素
{
pNode cur = p;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->data == data)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}remove函数的图解如下:
void remove(plist*pplist, DataType data)//删除链表中指定的一个元素的节点
{
assert(pplist);
pNode del = NULL;
pNode cur = Find(*pplist,data);
if (cur == NULL)
{
return;
}
del = cur->next;
cur->data=del->data;
cur->next = del->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
}Insert函数的图解:
void Insert(plist*pplist, pNode pos, DataType data)//指定位置的插入
{
assert(pplist);
pNode newnode = Buynode(data);
assert(pos);
if (*pplist == NULL)//头插
{
newnode->next = *pplist;
*pplist = newnode;
}
newnode->next = pos->next;//插在pos的后面
pos->next = newnode;
}void Erase(plist*pplist, pNode pos)//指定位置的删除
{
assert(pplist);
assert(pos);
//如果是尾节点,则调用尾删函数
if (pos->next == NULL)
{
popBack(pplist);
}
//若不是尾节点
else
{
pNode del = pos->next;
pos->data = del->data;
pos->next = del->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
}
}
void destory(plist*pplist)//销毁链表
{
assert(pplist);
pNode cur = *pplist;
while (cur)
{
pNode del = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
}
}
void display(plist p)//打印链表
{
assert(p);
while (p)
{
printf("%d->", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("NULL");
printf("\n");
}下面为链表的基本实现的测试部分:
void test1()//测试头插及头删
{
plist p1;
initLinkList(&p1);
PushFront(&p1, 1);
PushFront(&p1, 2);
PushFront(&p1, 3);
PushFront(&p1, 4);
display(p1);
popFront(&p1);
popFront(&p1);
popFront(&p1);
display(p1);
destory(&p1);
}
void test2()//测试尾插及尾删
{
plist p2;
initLinkList(&p2);
PushBack(&p2, 1);
PushBack(&p2, 2);
PushBack(&p2, 3);
PushBack(&p2, 4);
display(p2);
popBack(&p2);
display(p2);
destory(&p2);
}
void test3()//测试查找与指定位置的删除函数,和删除链表中指定的一个元素的节点的函数
{
plist p2;
initLinkList(&p2);
PushBack(&p2, 1);
PushBack(&p2, 2);
PushBack(&p2, 3);
PushBack(&p2, 4);
display(p2);
pNode ret = Find(p2, 2);
printf("%d\n", ret->data);
Erase(&p2, ret);
display(p2);
remove(&p2, 3);
display(p2);
destory(&p2);
}
int main()
{
test1();
test2();
test3();
system("pause");
return 0;
}下面为常见的链表面试题的实现。
void printreverse(plist p)//逆序打印单向链表(递归实现)
{
if (p == NULL)
{
return;
}
else if (p->next == NULL)
{
printf("%d->", p->data);
}
else
{
printreverse(p->next);
printf("%d->", p->data);
}
}测试如下:
void test4()
{
plist p2;
initLinkList(&p2);
PushBack(&p2, 1);
PushBack(&p2, 2);
PushBack(&p2, 3);
PushBack(&p2, 4);
printreverse(p2);
destory(&p2);
}void DelNotTail(pNode pos)//删除一个无头单链表的非尾节点(和Erase的第二种情况一样)
{
pNode del = NULL;
assert(pos->next);
del = pos->next;
pos->data = del->data;
pos->next = del->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
}测试部分为:
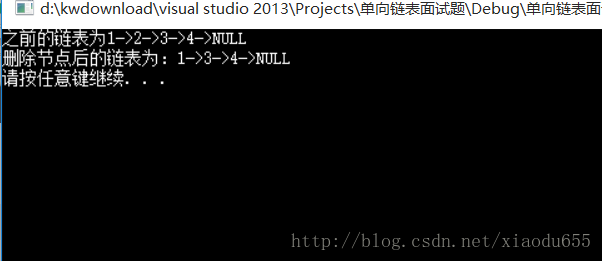
void test5()//删除一个无头单链表的非尾节点
{
plist p2;
initLinkList(&p2);
PushBack(&p2, 1);
PushBack(&p2, 2);
PushBack(&p2, 3);
PushBack(&p2, 4);
printf("之前的链表为");
display(p2);
pNode ret = Find(p2, 2);
DelNotTail(ret);
printf("删除节点后的链表为:");
display(p2);
destory(&p2);
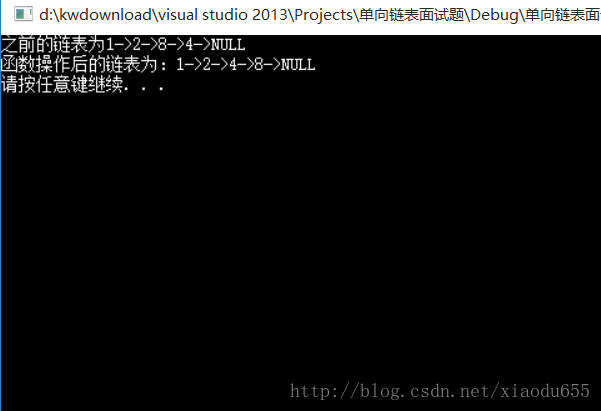
}void insertnode(pNode pos, DataType d)//在无头单链表的一个非头节点前插入一个节点
{
pNode newnode = Buynode(d);
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
newnode->data = d;
DataType temp = 0;
//将两个中的数值进行交换
temp = pos->data;
pos->data = newnode->data;
newnode->data = temp;
}具体图解为:
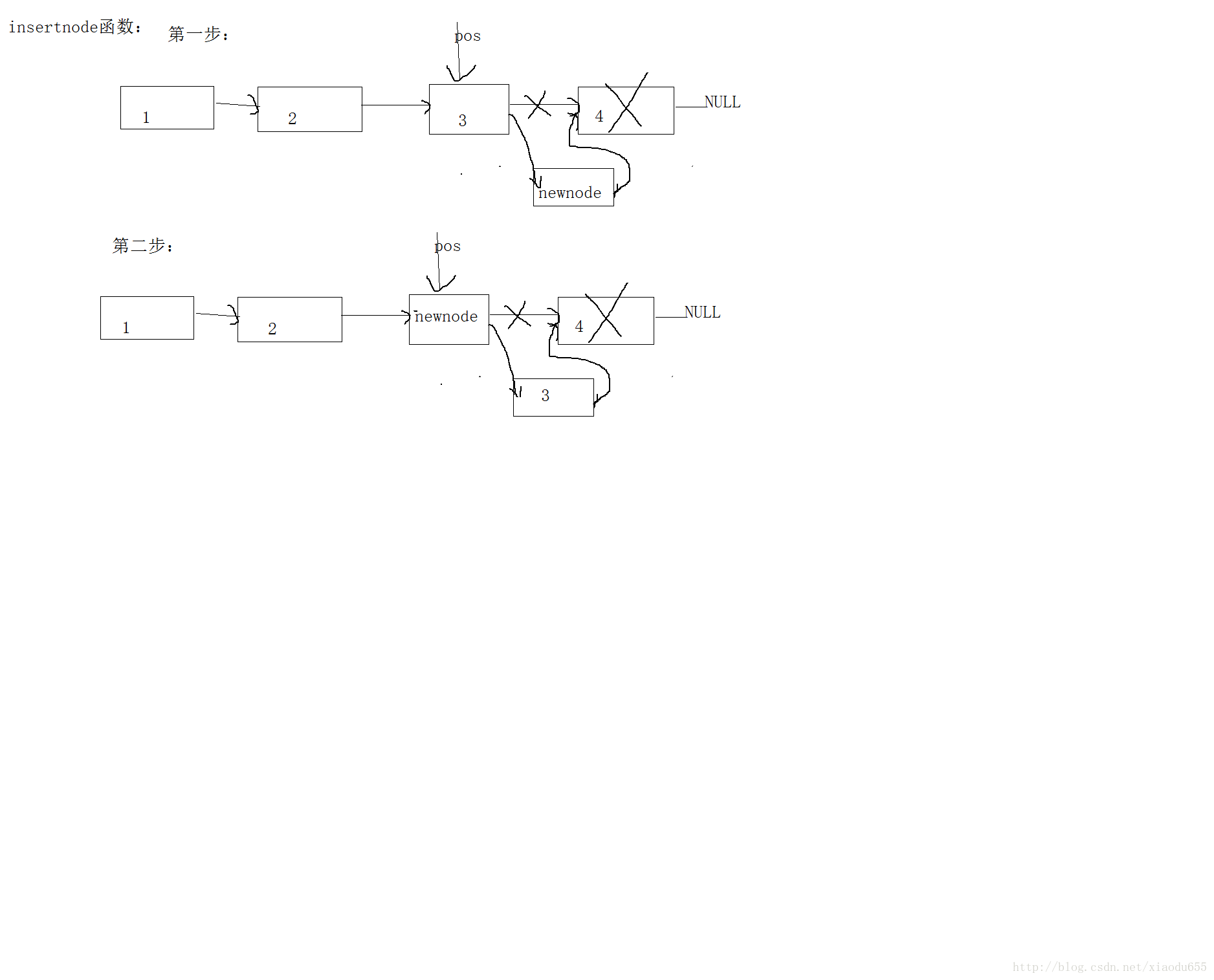
测试部分为:
void test6()
{
plist p2;
initLinkList(&p2);
PushBack(&p2, 1);
PushBack(&p2, 2);
PushBack(&p2, 3);
PushBack(&p2, 4);
printf("之前的链表为");
display(p2);
pNode ret = Find(p2, 2);
insertnode(ret, 6);
printf("函数操作后的链表为:");
display(p2);
destory(&p2);
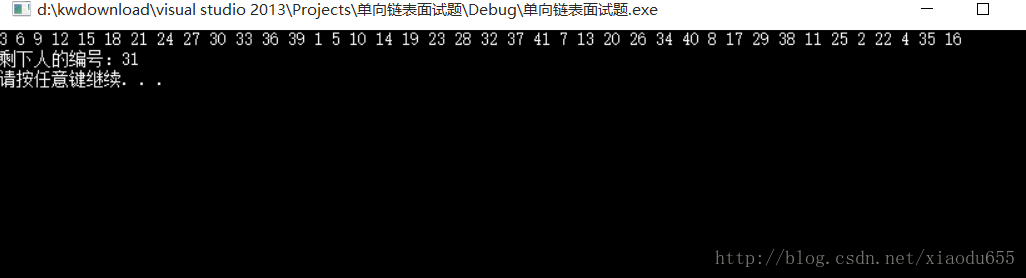
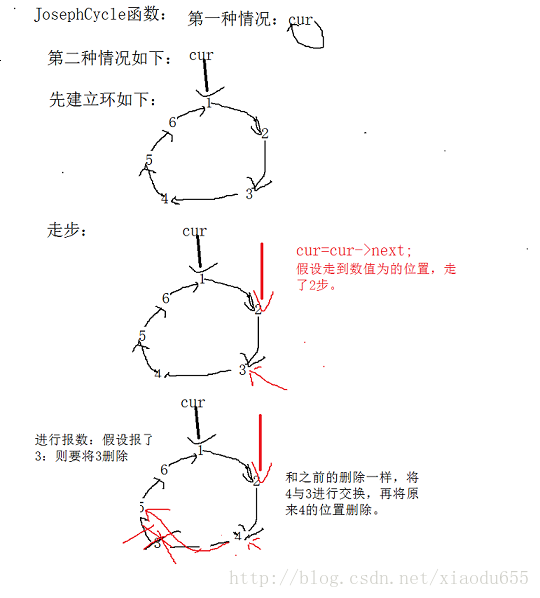
}void JosephCycle(plist p, DataType k)//单链表实现约瑟夫环
{
pNode cur = p;
int count = 0;
while (1)//让其一直循环下去
{
int count = k;
if (cur == cur->next)//如果该环中只有一个元素则跳出
{
//printf("%d", cur->data);
break;
}
while (--count)//走的步数
{
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("%d ",cur->data);//打印要删除的元素
//实现删除,与删除一个无头单链表的非尾节点相同
pNode del = cur->next;
cur->data = del->data;
cur->next = del->next;
free(del);
}
printf("\n剩下人的编号:%d\n", cur->data);
}具体的图解为:
测试部分为:
void test7()
{
plist p2;
initLinkList(&p2);
for (int i = 1; i <= 41; i++)
{
PushBack(&p2, i);
}
pNode ret = Find(p2, 41);
ret->next = p2;
JosephCycle(p2, 3);
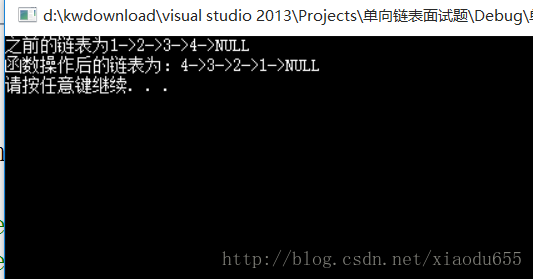
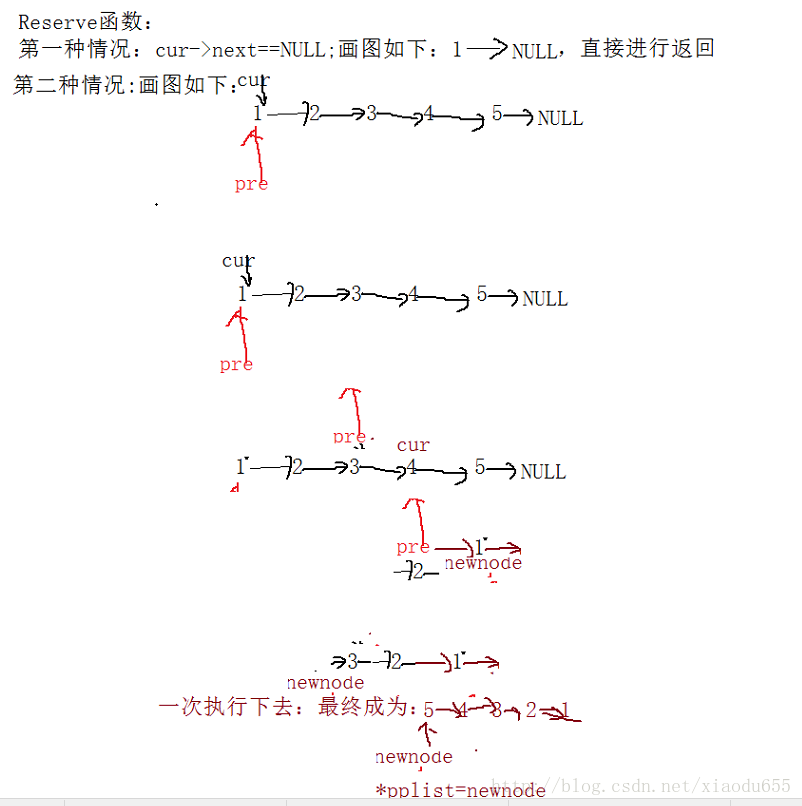
}void Reverse(plist*pplist)//逆置/反转单链表
{
assert(pplist);
pNode cur = *pplist;
pNode newnode = NULL;
if (cur == NULL || (cur->next) == NULL)
{
return;
}
while (cur != NULL)//排除以上两种情况之后
//将此链表的第一个节点取来并保存,之后依次将剩下的节点取下放在第一个节点之前,最后让其指向*pplist
{
pNode pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
pre->next = newnode;
newnode = pre;
}
//最后让newnode指向*pplist
*pplist=newnode;
}图解为:
测试函数为:
void test8()
{
plist p2;
initLinkList(&p2);
PushBack(&p2, 1);
PushBack(&p2, 2);
PushBack(&p2, 3);
PushBack(&p2, 4);
printf("之前的链表为");
display(p2);
Reverse(&p2);
printf("函数操作后的链表为:");
display(p2);
destory(&p2);
}void Bubblesort(plist*pplist)//单链表排序(冒泡排序)
{
assert(pplist);
pNode cur = *pplist;
pNode tail = NULL;
if (cur == NULL || cur->next == NULL)
{
return;
}
//下面是正常的冒泡排序
while ((cur->next)!=tail)//总的趟数
{
while ((cur->next) != tail)
{
if ((cur->data) > (cur->next->data))
{
DataType temp = cur->data;
cur->data = cur->next->data;
cur->next->data = temp;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
tail = cur;
cur = *pplist;
}
}测试部分:
void test9()
{
plist p2;
initLinkList(&p2);
PushBack(&p2, 1);
PushBack(&p2, 2);
PushBack(&p2, 8);
PushBack(&p2, 4);
printf("之前的链表为");
display(p2);
Bubblesort(&p2);
printf("函数操作后的链表为:");
display(p2);
destory(&p2);
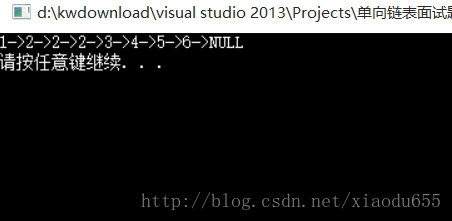
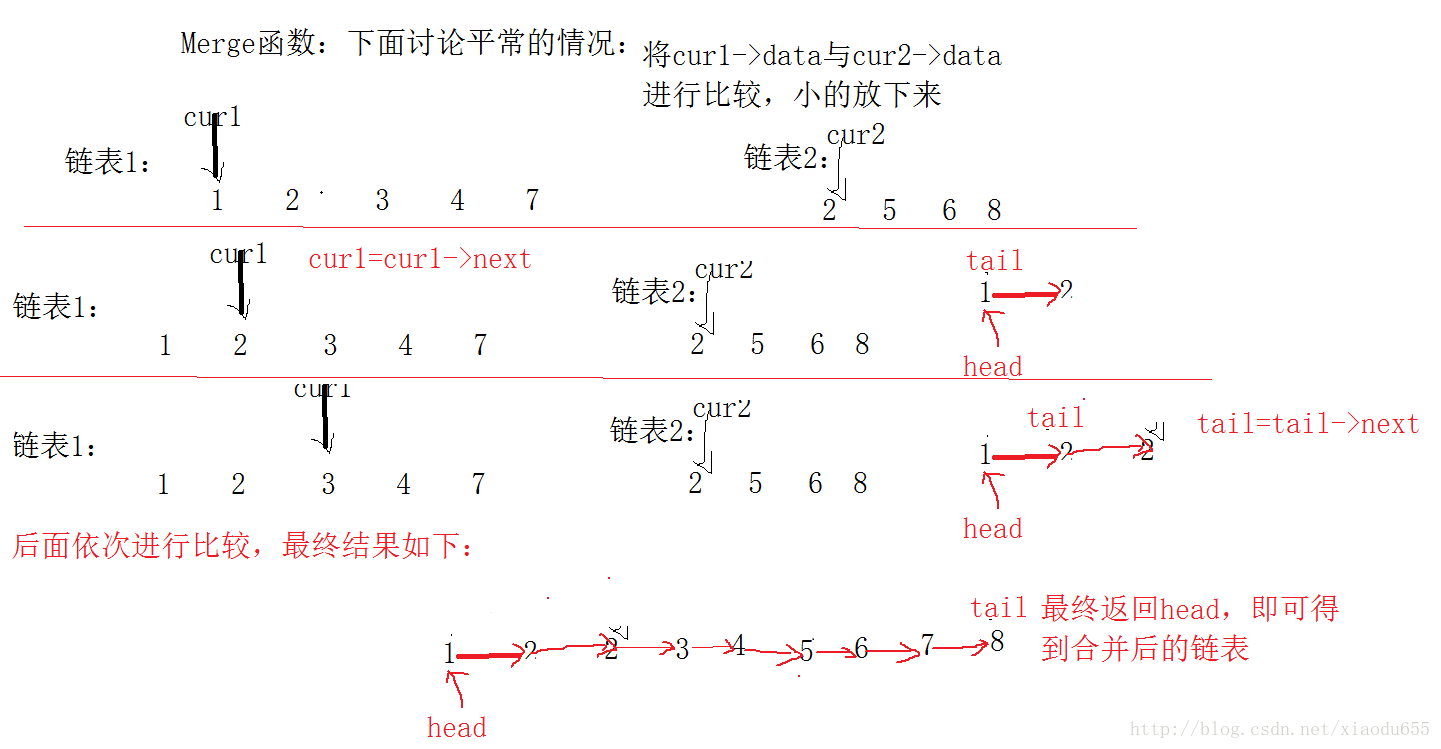
}plist Merge(plist*pplist1, plist *pplist2)//合并两个有序单链表,合并后依然有序
{
assert(pplist1);
assert(pplist2);
pNode cur1 = *pplist1;
pNode cur2 = *pplist2;
pNode head = NULL;
pNode tail = NULL;
if ((*pplist1 == NULL) && (*pplist2 == NULL))//第一种情况
{
return NULL;
}
//第二种情况
if (*pplist1 == NULL)
{
return *pplist2;
}
if ((*pplist2 == NULL) || (*pplist1 == *pplist2))
{
return *pplist1;
}
//正常情况下,第一个元素先进行比较,将两个中小的放在第一个
if ((cur1->data) < (cur2->data))
{
head = cur1;
tail = head;
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
else
{
head = cur2;
tail = head;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
while ((cur1!=NULL)&&(cur2!=NULL))
{
if ((cur1->data) < (cur2->data))
{
tail->next = cur1;
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = cur2;
cur2= cur2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
if (cur1)
{
tail->next = cur1;
}
if (cur2)
{
tail->next = cur2;
}
return head;//返回头指针
}图解为:
测试函数为:
void test10()
{
plist p1;
initLinkList(&p1);
PushBack(&p1, 1);
PushBack(&p1, 2);
PushBack(&p1, 3);
PushBack(&p1, 4);
plist p2;
initLinkList(&p2);
PushBack(&p2, 2);
PushBack(&p2, 2);
PushBack(&p2, 5);
PushBack(&p2, 6);
pNode newlist=Merge(&p1, &p2);
display(newlist);
destory(&newlist);
}pNode FindMidNode(plist p)//查找链表的中间节点
{
//创建两个指针,一个快指针,一个慢指针,当快指针走完整个链表时,慢指针刚好走到中间
pNode fast = p;
pNode slow = p;
if (p == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
while ((fast) && (fast->next))
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}图解为:

测试函数为:
void test11()
{
plist p1;
initLinkList(&p1);
PushBack(&p1, 1);
PushBack(&p1, 2);
PushBack(&p1, 3);
PushBack(&p1, 4);
PushBack(&p1, 5);
PushBack(&p1, 6);
PushBack(&p1, 7);
PushBack(&p1, 8);
pNode ret = FindMidNode(p1);
printf("%d\n", ret->data);
destory(&p1);
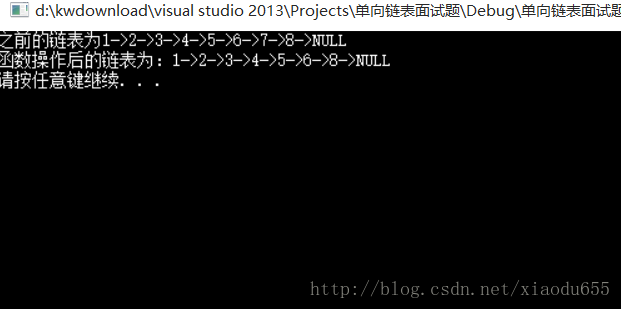
}void DelKNode(plist p, DataType k)//删除链表的倒数第K个节点
{
//该小题也利用快慢指针的方式进行,让快的指针先走k-1步,另一个再开始走,快的到达终点时,慢的刚好走到倒数第k个节点
pNode fast = p;
pNode slow = p;
pNode del = NULL;
if ((p == NULL) && (k == 0))
{
return;
}
while ((fast) && (fast->next))
{
while (--k > 0)
{
fast = fast->next;
}
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
//进行删除
del = slow->next;
slow->data = del->data;
slow->next = del->next;
free(del);
}图解为:
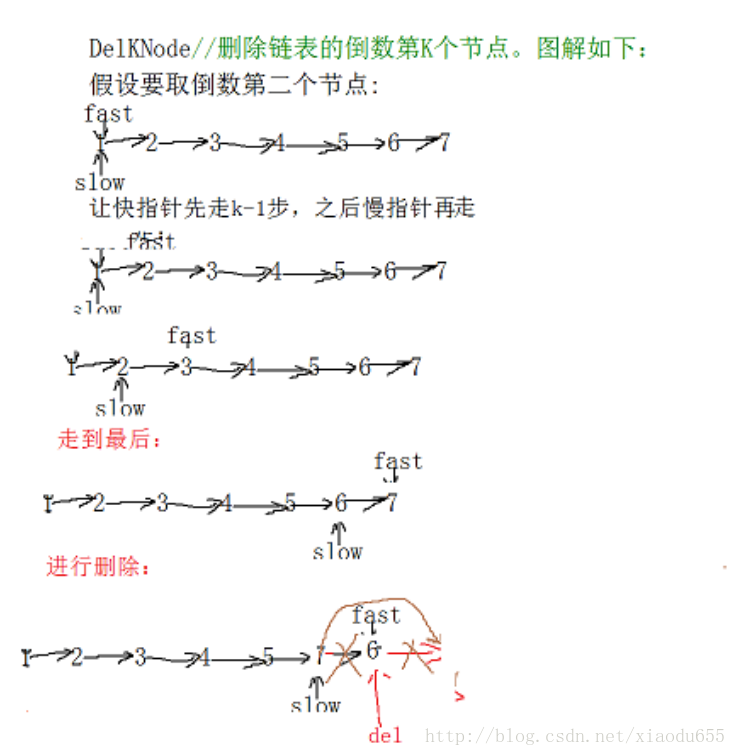
测试函数为:
void test12()
{
plist p1;
initLinkList(&p1);
PushBack(&p1, 1);
PushBack(&p1, 2);
PushBack(&p1, 3);
PushBack(&p1, 4);
PushBack(&p1, 5);
PushBack(&p1, 6);
PushBack(&p1, 7);
PushBack(&p1, 8);
printf("之前的链表为");
display(p1);
DelKNode(p1, 2);
printf("函数操作后的链表为:");
display(p1);
destory(&p1);
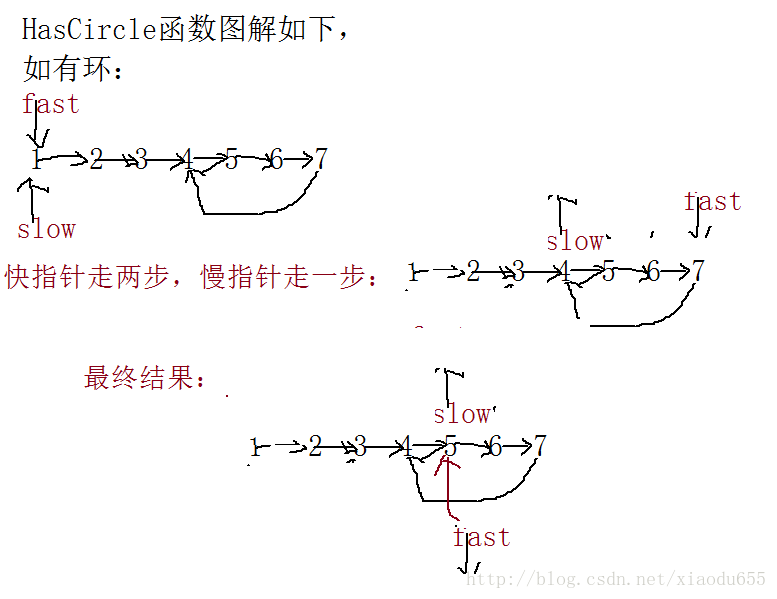
}pNode HasCircle(plist p)//判断链表是否带坏
{
////创建两个指针,一个快指针,一个慢指针,
//如果有环,走着走着快慢指针会相遇,如果没有环,快指针会走到终点
pNode fast = p;
pNode slow = p;
if (p == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
while ((fast) && (fast->next))
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (fast == slow)
{
return fast;//返回快指针
}
}
return NULL;//如果没有环则返回NULL;
}
图解为:
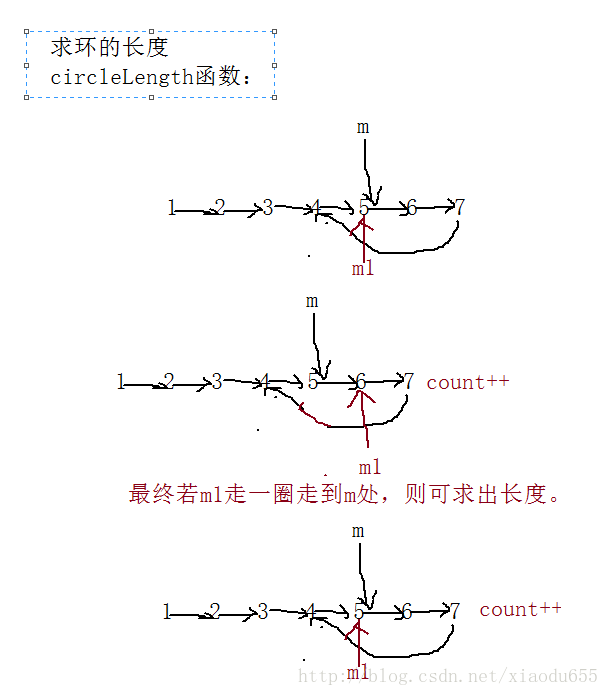
int Circlelength(pNode m)//用一个m(meet)指针记住相遇点,让m从相遇点走步,走一步记一下
//再定义一个指针m1从相遇点走,走一圈后当其等于m时,刚好走了一圈,即可求出长度
{
pNode m1= m;
int count = 0;
do{
count++;
m1 = m1->next;
} while (m1 != m);
return count;
}图解为:
pNode GetCircleEntryNode(pNode m, plist p)//求环的入口处
//定义一个快指针,一个慢指针,快指针先走环的长度步,慢指针开始走,两个指针相遇的地方就为环的入口点
{
pNode fast = p;
pNode slow = p;
int num = Circlelength(m);
while (num--)
{
fast = fast->next;
}
while (fast != slow)
{
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
if (fast == slow)
{
return fast;
}
}图解为:
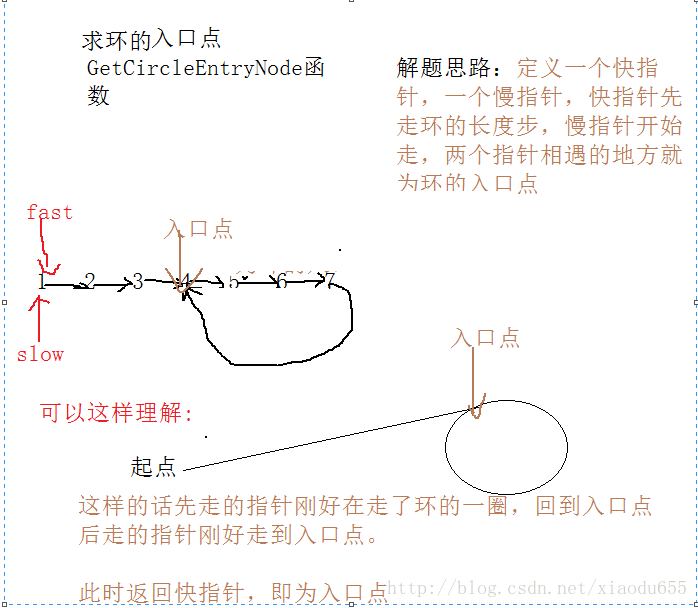
测试函数为:
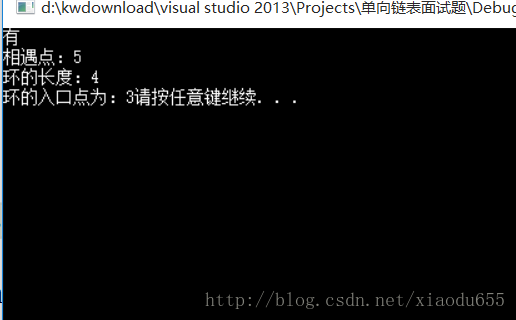
void test13()
{
plist p1;
initLinkList(&p1);
PushBack(&p1, 1);
PushBack(&p1, 2);
PushBack(&p1, 3);
PushBack(&p1, 4);
PushBack(&p1, 5);
PushBack(&p1, 6);
PushBack(&p1, 7);
PushBack(&p1, 8);
pNode ret = Find(p1, 6);
ret->next = Find(p1, 3);
pNode pp = HasCircle(p1);
if (pp == NULL)
{
printf("没有");
}
else
{
printf("有");
}
printf("\n");
printf("相遇点:%d\n", pp->data);
printf("环的长度:%d\n", Circlelength(pp));
pNode m = GetCircleEntryNode(pp, p1);
printf("环的入口点为:%d",m->data);
}pNode CheckListCross(plist p1, plist p2)//判断两个链表是否相交(假设链表不带环)
//将一个链表的尾连到另一个链表的头,将其转变为是否带环问题,如果有交点,则会形成一个环,没有则不相交
{
pNode cur1 = p1;
pNode cur2 = p2;
while (cur1->next)
{
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
cur1->next = cur2;
pNode m = HasCircle(p1);
if (m == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
else
{
pNode ret = GetCircleEntryNode(m, p1);//求得交点
return ret;
}
}测试函数为:
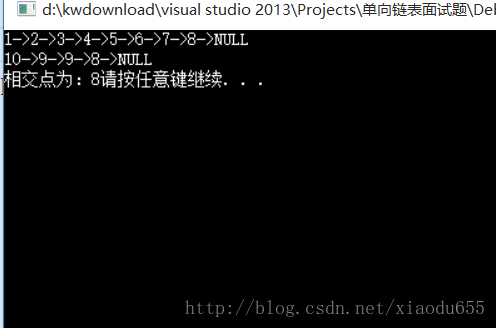
void test14()
{
plist p1;
initLinkList(&p1);
PushBack(&p1, 1);
PushBack(&p1, 2);
PushBack(&p1, 3);
PushBack(&p1, 4);
PushBack(&p1, 5);
PushBack(&p1, 6);
PushBack(&p1, 7);
PushBack(&p1, 8);
display(p1);
plist p2;
initLinkList(&p2);
PushBack(&p2, 10);
PushBack(&p2, 9);
PushBack(&p2, 9);
PushBack(&p2, 8);
display(p2);
Find(p1, 7)->next = Find(p2, 8);
pNode ret = CheckListCross(p1, p2);
if (ret == NULL)
{
printf("不相交\n");
}
else
{
printf("相交点为:%d", ret->data);
}
}