RPC概念
RPC(Remote Procedure Call)远程过程调用,通过这个rpc协议,调用远程计算机上的服务,就像调用本地的服务一样。

不同的服务部署在不同的机器上面,并且在启动后在注册中心进行注册,如果要调用,可以通过rpc调用对应的服务。如图,在不同的Controller中可以从注册中心(可以使用eureka,zookeeper实现,本文例子使用简单的hashmap作为实现)获取可以调用的服务,然后通过rpc进行调用。
RMI远程调用
java本身提供了一种RPC框架——RMI(即Remote Method Invoke 远程方法调用),在编写一个接口需要作为远程调用时,都需要继承了Remote,Remote 接口用于标识其方法可以从非本地虚拟机上调用的接口,只有在“远程接口”(扩展 java.rmi.Remote 的接口)中指定的这些方法才可远程使用,下面通过一
个简单的示例,来讲解RMI原理以及开发流程:
代码示例
1、项目结构

2、server端
User:用于远程调用时pojo对象的传输,该对象必须实现Serializable接口,否则在调用过程中,会抛出NotSerializableException异常
package com.ty.dto; import lombok.Data; import lombok.ToString; import java.io.Serializable; /** * 用户信息,用于远程调用传输,必须实现Serializable接口 */ @Data @ToString public class User implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private String name; private int age; }
IHello:远程接口,该接口需要继承Remote接口,并且接口中的方法全都要抛出RemoteException异常
package com.ty.service; import com.ty.dto.User; import java.rmi.Remote; import java.rmi.RemoteException; /** * 定义一个远程接口,必须继承Remote接口,其中需要远程调用的方法必须抛出RemoteException异常 */ public interface IHello extends Remote { /** * 更新user信息 * @param user * @return * @throws RemoteException */ User updateUser(User user) throws RemoteException; }
HelloImpl:远程接口实现类,必须继承UnicastRemoteObject,只有继承UnicastRemoteObject类,才表明其可以作为远程对象,被注册到注册表中供客户端远程调用(补充:客户端lookup找到的对象,只是该远程对象的Stub(存根对象),而服务端的对象有一个对应的骨架Skeleton(用于接收客户端stub的请求,以及调用真实的对象)对应,Stub是远程对象的客户端代理,Skeleton是远程对象的服务端代理,他们之间协作完成客户端与服务器之间的方法调用时的通信。)
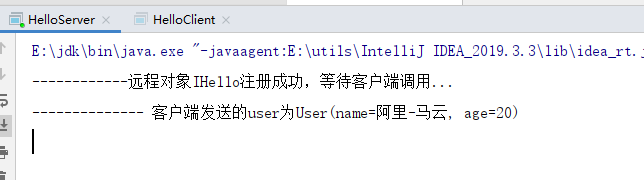
package com.ty.service.impl; import com.ty.dto.User; import com.ty.service.IHello; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject; /** * 远程的接口的实现,继承了UnicastRemoteObject,表明该类作为一个远程对象 */ public class HelloImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements IHello { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; /** * 因为UnicastRemoteObject的构造方法抛出了RemoteException异常,因此这里默认的构造方法必须写,必须声明抛出RemoteException异常 * * @throws RemoteException */ public HelloImpl() throws RemoteException { } public User updateUser(User user) throws RemoteException { System.out.println("-------------- 客户端发送的user为" + user.toString()); user.setName("阿里-马云"); user.setAge(30); return user; } }
HelloServer:服务端启动类,用于创建远程对象注册表以及注册远程对象
package com.ty.server; import com.ty.service.IHello; import com.ty.service.impl.HelloImpl; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.rmi.AlreadyBoundException; import java.rmi.Naming; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry; public class HelloServer { public static void main(String args[]) { try { // 本地主机上的远程对象注册表Registry的实例,并指定端口为8888,这一步必不可少(Java默认端口是1099) LocateRegistry.createRegistry(8888); // 把远程对象注册到RMI注册服务器上,并命名为RHello // 绑定的URL标准格式为:rmi://host:port/name(其中协议名可以省略,下面两种写法都是正确的) IHello rhello = new HelloImpl(); Naming.bind("rmi://localhost:8888/RHello", rhello); // Naming.bind("//localhost:8888/RHello",rhello); System.out.println("------------远程对象IHello注册成功,等待客户端调用..."); } catch (RemoteException e) { System.out.println("创建远程对象发生异常!"); e.printStackTrace(); } catch (AlreadyBoundException e) { System.out.println("发生重复绑定对象异常!"); e.printStackTrace(); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { System.out.println("发生URL畸形异常!"); e.printStackTrace(); } } }
补充说明:为何HelloImpl继承了UnicastRemoteObject就可以被作为远程对象发布,查阅UnicastRemoteObject的源码可以发现:
protected UnicastRemoteObject() throws RemoteException { this(0); } protected UnicastRemoteObject(int port) throws RemoteException { this.port = port; exportObject((Remote) this, port); }
其实在启动server端的时候,new了HelloImpl对象,因为继承了UnicastRemoteObject,会先调用父类的构造方法,这时候,就会将this(当前对象)通过exportObject方法注册。
所以,如果在被导出的对象需要继承其它的类,那么就可以不采用集成UnicastRemoteObject的方式,而是通过exportObject方法将其导出为远程对象:
... // 创建一个远程对象 IHello rhello = new HelloImpl(); //HelloImpl不需要继承UnicastRemoteObject类,通过exportObject将其显示导出 UnicastRemoteObject.exportObject(rhello,0); ...
3、client端
实际应用开发中,客户端的User.java和IHello.java应该是从服务端导出jar包的形式添加到依赖库里
HelloClient
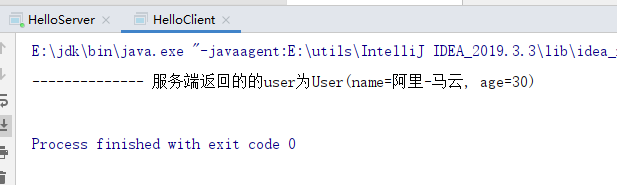
package com.ty.client; import com.ty.dto.User; import com.ty.service.IHello; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.rmi.Naming; import java.rmi.NotBoundException; import java.rmi.RemoteException; public class HelloClient { public static void main(String args[]) { try { // 在RMI服务注册表中查找名称为RHello的对象,并调用其上的方法 IHello rhello = (IHello) Naming.lookup("rmi://localhost:8888/RHello"); // 构造user对象,测试远程对象传输 User user = new User(); user.setAge(20); user.setName("阿里-马云"); System.out.println("-------------- 服务端返回的的user为" + rhello.updateUser(user).toString()); } catch (NotBoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (RemoteException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
4、测试
启动Server与client
RMI的问题:
其实rmi的思想是非常棒的,但是使用的时候必须要继承remote接口,另外还得继承UnicastRemoteObject类,使业务代码与框架代码耦合在了一起。优秀的框架应该是无侵入的,业务层无需关注框架层实现。
手写rpc框架
技术方案
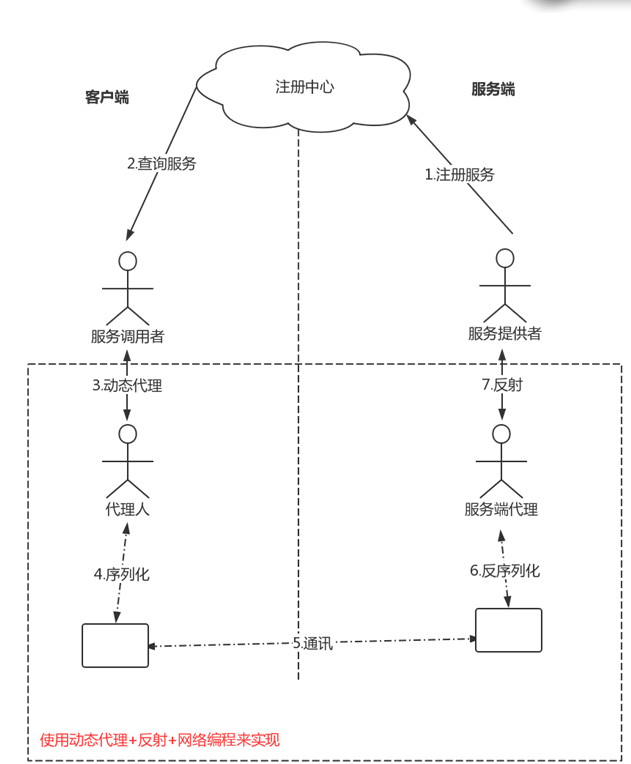
设计技术点:Socket通讯、动态代理与反射、Java序列化
RPC本质是使用动态代理,通过网络通信技术进行增强。
图示:
代码示例
服务端
1、项目结构

2、代码
1.//服务端定义要调用的服务接口 package service; public interface TechInterface { //洗脚服务 String XJ(String name); } 2.//服务端定义要调用的服务的接口实现类 package service.impl; import service.TechInterface; public class TechImpl implements TechInterface { public String XJ(String name) { return "您好,13号技师为你服务:"+name; } }
package server; import java.io.IOException; import javax.imageio.spi.RegisterableService; import register.RegisterCenter; import service.TechInterface; import service.impl.TechImpl; /** * rpc的服务端,提供服务 * @author hasee * */ public class Server { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { RegisterCenter registerCenter = new RegisterCenter(8888); //注册技师对象至注册中心 registerCenter.register(TechInterface.class, TechImpl.class); registerCenter.start(); } }
package register; /** * 注册中心,这个例子使用一个hashmap作为实现 * @author hasee * */ import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class RegisterCenter { //线程池 private static ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()); //定义注册中心的静态对象 private static Map<String, Class> serviceRegistry = new HashMap<String, Class>(); //服务端口 private static int port = 8888; /** * 注册服务 * @param serviceInterface 接口名字 * @param impl 实现类的class对象 */ public void register(Class serviceInterface, Class impl) { //服务的注册:socket通讯+反射 serviceRegistry.put(serviceInterface.getSimpleName(), impl); } public RegisterCenter(int port) { this.port = port; } /** * 启动服务端 * @throws IOException */ public static void start() throws IOException { // 创建ServerSocket实例监听端口 ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port); System.out.println("start server"); // 1.监听客户端的TCP连接,接到TCP连接后将其封装成task,由线程池执行,并且同时将socket送入(server.accept()=socket) try { while (true) { //serverSocket.accept()会阻塞直到服务端接受到客户端的请求。 executorService.execute(new ServiceTask(serverSocket.accept())); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 将客户端的每一个请求都封装成一个线程ServiceTask,投放到线程池里面进行执行。 * @author hasee * */ private static class ServiceTask implements Runnable { private Socket client; public ServiceTask(Socket client) { this.client = client; } public void run() { //读取socket中的流数据 ObjectInputStream inputStream = null; ObjectOutputStream outputStream = null; try { // 类名、方法名、参数类型、参数值 inputStream = new ObjectInputStream(client.getInputStream()); //获取调用服务名称 String serviceName = inputStream.readUTF(); //获取调用方法的名称 String methodName = inputStream.readUTF(); //获取参数类型列表 Class<?>[] requiresTypes = (Class<?>[]) inputStream.readObject(); //获取参数列表 Object[] args = (Object[]) inputStream.readObject(); Class serviceClass = serviceRegistry.get(serviceName); //反射调用方法 Method method = serviceClass.getMethod(methodName, requiresTypes); Object result = method.invoke(serviceClass.newInstance(), args); //把结果反馈到客户端 outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); outputStream.writeObject(result); outputStream.flush(); //关闭io资源 inputStream.close(); client.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
客户端
1、项目结构

2、代码
package main.java.rpc; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.Socket; //rpc框架的客户端代理部分 public class RpcClientFrame { public static<T> T getRemoteProxyObj(final Class<?> serviceInterface) throws Exception { //默认端口8888 InetSocketAddress serviceAddr = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8888); //1、将本地的接口调用转换成jdk的动态代理,在动态代理中实现接口的远程调用,进行实际的服务调用 return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(serviceInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[] {serviceInterface}, new DynProxy(serviceInterface, serviceAddr)); } /*动态代理类,实现了对远程服务的访问*/ private static class DynProxy implements InvocationHandler{ //远程调用的服务 private Class serviceClass; //远程调用地址 private final InetSocketAddress addr; public DynProxy(Class serviceClass,InetSocketAddress addr) { this.serviceClass = serviceClass; this.addr = addr; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { ObjectInputStream inputStream = null; ObjectOutputStream outputStream = null; Socket socket = null; try { socket = new Socket(); socket.connect(addr); //类名 方法名 方法类型列表 方法入参列表 outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream()); outputStream.writeUTF(serviceClass.getSimpleName()); outputStream.writeUTF(method.getName()); outputStream.writeObject(method.getParameterTypes()); outputStream.writeObject(args); outputStream.flush(); inputStream = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream()); //我们要把调用的细节打印出来 System.out.println("远程调用成功!" + serviceClass.getName()); //最后要网络的请求返回给返回 return inputStream.readObject(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { socket.close(); inputStream.close(); outputStream.close(); } return null; } }
//定义客户端要定义的服务 package enjoyedu.service; /** * 享学课堂 *类说明:服务员接口 */ public interface TechInterface { //洗脚服务 String XJ(String name); }
package main.java; import main.java.rpc.RpcClientFrame; import main.java.service.TechInterface; /** * rpc的客户端调用远程服务 * @author hasee * */ public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { //动态代理获取我们的对象 TechInterface techInterface = (TechInterface) RpcClientFrame.getRemoteProxyObject(TechInterface.class); //进远程调用我们的对象 System.out.println(techInterface.XJ("luke")); } }