- 隐式使用工作项
#include <iostream> #include <windows.h> int g_nCount = 0; VOID NTAPI SimpleCallback(PTP_CALLBACK_INSTANCE pInstance, PVOID pvContext) { g_nCount++; printf("test:%d\n", g_nCount); } void main() { int nCount = 500; PTP_SIMPLE_CALLBACK pFunc = SimpleCallback; while (0 != nCount) { TrySubmitThreadpoolCallback(pFunc, NULL, NULL); nCount--; } getchar(); }
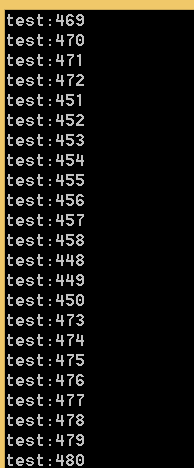
通过结果观察发现,利用了线程池,输出并非有序:
显式地控制工作项
void main() { g_pWorkItem = CreateThreadpoolWork(TaskHandler, NULL, NULL); if (NULL == g_pWorkItem) { return; } int nCount = 5000; while (nCount) { SubmitThreadpoolWork(g_pWorkItem); nCount--; } WaitForThreadpoolWorkCallbacks(g_pWorkItem, FALSE); CloseThreadpoolWork(g_pWorkItem); getchar(); }
如果改为下面这样,则会报错:
int g_nCount = 0; PTP_WORK g_pWorkItem = NULL; void NTAPI TaskHandler(PTP_CALLBACK_INSTANCE Instance, PVOID Context, PTP_WORK work) { g_nCount++; printf("test:%d..\n", g_nCount); } unsigned int _stdcall testthread(PVOID pParam) { int nCount = 500; while (nCount) { SubmitThreadpoolWork(g_pWorkItem); nCount--; } return 0; } void main() { g_pWorkItem = CreateThreadpoolWork(TaskHandler, NULL, NULL); if (NULL == g_pWorkItem) { return; }
_beginthreadex(NULL, 0, testthread, NULL, 0, NULL); WaitForThreadpoolWorkCallbacks(g_pWorkItem, FALSE); CloseThreadpoolWork(g_pWorkItem); getchar(); }
因为据书上说,只能取消或等待本线程中的工作项。