一、概念
在前面的案例中,将对象就交给spring的ioc容器来管理,这样可以有效地解决程序之间的耦合依赖问题。但是这样还是无法解决问题,因为如果要让业务层调用持久层,那么还需要在业务层创建持久层的对象,但是业务层我们交给了Spring来处理,理所当然业务层中持久层的对象也应交给Spring来管理。让我们的业务层对象被创建时,其中的持久层实例变量也被创建。
前面说到,spring创建bean的几种方式中,需要该bean提供默认的无参构造函数,也就是说Spring在创建对象时,使用的是无参构造函数,那么如果我们想在创建对象时,给该对象赋值一些参数,这个时候就需要依赖注入。
- 依赖注入:Dependency Injection。它是 spring 框架核心 ioc 的具体实现
例如:
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
AccountDao accountDao = ac.getBean("accountDao", AccountDao.class);
AccountService accountService = ac.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class);
accountService.saveAccount();
System.out.println(accountService);
结果报错:NullPointerException
因为在AccountService对象中没有去创建AccountDao中的实例。
二、构造函数注入
使用构造函数注入,这里是提供有参构造函数,通过配置的方式,让Spring给我们注入参数
例如下面的一个实体类:
/**
* author by four and ten
* create by 2020/3/29 15:05
*/
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private Date birthday;
public User(String name, int age, Date birthday) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public User(){}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", birthday=" + birthday +
'}';
}
}
bean.xml
<bean id="user" class="com.SpringDemo1.Domain.User">
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="name" value="zhangsan"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="birthday" ref="date"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="date" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
标签详解:
- constructor-arg:使用构造函数注入
属性:
-
index:指定参数在构造函数参数列表的索引位置
-
type:指定参数在构造函数中的数据类型
-
name:指定参数在构造函数中的名称
-
value:它能赋的值是基本数据类型和 String 类型
-
ref:它能赋的值是其他 bean 类型,也就是说,必须得是在配置文件中配置过的 bean
测试结果
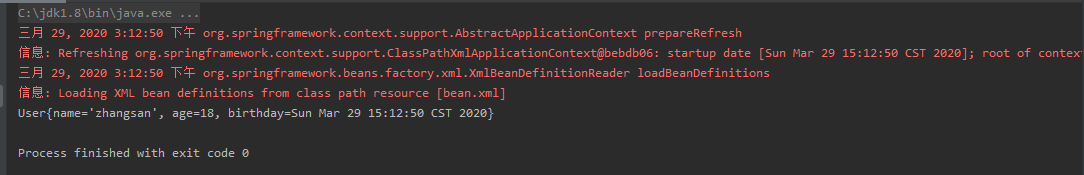
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
User user = ac.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println(user);
三、set方法注入
set方式注入,需要在类中提供set方法
/**
* author by four and ten
* create by 2020/3/29 15:05
*/
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private Date birthday;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public User(){}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", birthday=" + birthday +
'}';
}
}
bean.xml
<bean id="user" class="com.SpringDemo1.Domain.User">
<property name="age" value="21"></property>
<property name="birthday" ref="date"></property>
<property name="name" value="lisi"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="date" class="java.util.Date"></bean>
标签详解
- property:使用set方式注入的标签
属性:
- name:找的是类中 set 方法后面的部分,也就是一个类的属性
- ref:它能赋的值是其他 bean 类型,也就是说,必须得是在配置文件中配置过的 bean
- value:它能赋的值是基本数据类型和 String 类型
测试代码
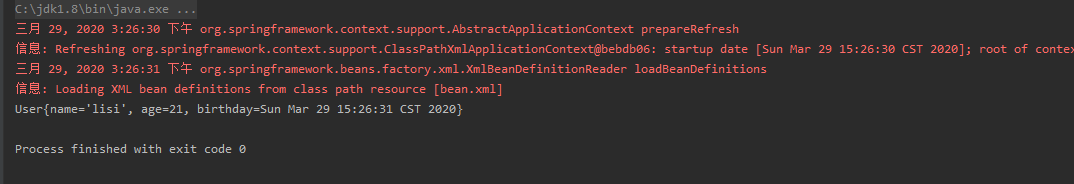
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
User user = ac.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println(user);
四、注入集合属性
也就是在注入时,该变量是集合类型
/**
* author by four and ten
* create by 2020/3/29 15:05
*/
public class User {
private String[] alias;
private List<String> list;
private Set<String> set;
private Map<String, String> map;
private Properties properties;
public void setAlias(String[] alias) {
this.alias = alias;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public void setSet(Set<String> set) {
this.set = set;
}
public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) {
this.map = map;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"alias=" + Arrays.toString(alias) +
", list=" + list +
", set=" + set +
", map=" + map +
", properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
}
bean.xml
<bean id="user" class="com.SpringDemo1.Domain.User">
<property name="alias">
<array>
<value>aaa</value>
<value>bbb</value>
<value>ccc</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>list1</value>
<value>list2</value>
<value>list3</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="testA" value="map1"></entry>
<entry key="testB">
<value>map2</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="properties">
<map>
<entry key="testC" value="properties1"></entry>
<entry key="testD" value="properties2"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>set1</value>
<value>set2</value>
<value>set3</value>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
注意:在注入集合数据时,只要数据结构相同,那么标签可以互换
List 结构的:
array,list,set
Map 结构的:
map,entry,props,prop
测试:

