作用域:
用于确定创建spring创建bean实例个数。
案例实现代码:
测试类:
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestFactory {
@Test
public void demo02() {
//spring工厂
String xmlPath = "com/spring/d_scope/beans.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
UserService userService1 = applicationContext.getBean("UserServiceId", UserService.class);
UserService userService2 = applicationContext.getBean("UserServiceId", UserService.class);
System.out.println(userService1);
System.out.println(userService2);
}
}
UserService接口与UserServiceImpl实现类:
public interface UserService {
public void addUser();
}
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void addUser() {
System.out.println("d_scope");
}
}
bean.xml配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- scope="prototype"使得多例 -->
<bean id="UserServiceId" class="com.spring.d_scope.UserServiceImpl" scope="prototype"></bean>
</beans>
运行结果及比较:
当是单例的情况时===》
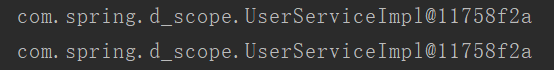
当是多例的情况时===》
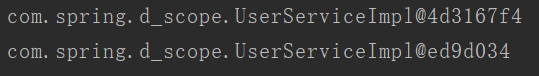
生命周期:
指目标方法执行前后执行后,将进行初始化或销毁。
案例实现代码:
UserService接口与UserServiceImpl实现类:
public interface UserService {
public void addUser();
}
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void addUser() {
System.out.println("e_lifecycle");
}
public void myInit(){
System.out.println("初始化");
}
public void myDestory(){
System.out.println("销毁");
}
}
spring 提供一种机制,只要实现接口BeanPostProcessor,并将实现类提供给spring容器,spring容器将自动执行,则在初始化方法前执行before(),在初始化方法后执行after() 。
BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类:
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean,String beanName) throws BeansException{
if ("userServiceId".equals(beanName)){
System.out.println("前方法:"+beanName);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(final Object bean,String beanName) throws BeansException{
System.out.println("后方法:"+beanName);
//bean目标对象
//生成jdk代理
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(MyBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader(), bean.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("------开启事务");
//执行目标方法
Object obj = method.invoke(bean,args);
System.out.println("------提交事务");
return obj;
}
});
}
}
bean.xml配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- init-method 用于配置初始方法,准备数据等
destroy-method 用于配置销毁方法,清理数据等
-->
<bean id="UserServiceId" class="com.spring.e_lifecycle.UserServiceImpl"
init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestory"></bean>
<!--将后处理的实现类注册给spring-->
<bean class="com.spring.e_lifecycle.MyBeanPostProcessor"></bean>
</beans>
测试类:
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestCycle {
@Test
public void demo02() {
//spring工厂
String xmlPath = "com/spring/e_lifecycle/beans.xml";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath);
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("UserServiceId",UserService.class);
userService.addUser();
//要求:1.容器必须close,销毁方法执行
// 2.必须是单例的
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) applicationContext). close();
}
}
实现结果:

下一节:【Spring框架】Spring入门(四)——五种属性注入方式(详细代码)
