引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>dom4j</groupId>
<artifactId>dom4j</artifactId>
<version>1.5.2</version>
</dependency>
xml范本
book.xml文件
<books>
<book id="001">
<title>Harry Potter</title>
<author>J K. Rowling</author>
</book>
<book id="002">
<title>Learning XML</title>
<author>Erik T. Ray</author>
</book
</books>
解析xml文件
使用list方式
import java.io.File;
import java.util.List;
import org.dom4j.Attribute;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
File file = new File("books.xml");
Document document = reader.read(file);
Element root = document.getRootElement();
List<Element> childElements = root.elements();
for (Element child : childElements) {
//未知属性名情况下
/*List<Attribute> attributeList = child.attributes();
for (Attribute attr : attributeList) {
System.out.println(attr.getName() + ": " + attr.getValue());
}*/
//已知属性名情况下
System.out.println("id: " + child.attributeValue("id"));
//未知子元素名情况下
/*List<Element> elementList = child.elements();
for (Element ele : elementList) {
System.out.println(ele.getName() + ": " + ele.getText());
}
System.out.println();*/
、
//已知子元素名的情况下
System.out.println("title" + child.elementText("title"));
System.out.println("author" + child.elementText("author"));
}
}
}
使用Iterator迭代器的方式来解析xml
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.dom4j.Attribute;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document document = reader.read(new File("books.xml"));
Element root = document.getRootElement();
Iterator it = root.elementIterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Element element = (Element) it.next();
//未知属性名称情况下
/*Iterator attrIt = element.attributeIterator();
while (attrIt.hasNext()) {
Attribute a = (Attribute) attrIt.next();
System.out.println(a.getValue());
}*/
//已知属性名称情况下
System.out.println("id: " + element.attributeValue("id"));
//未知元素名情况下
/*Iterator eleIt = element.elementIterator();
while (eleIt.hasNext()) {
Element e = (Element) eleIt.next();
System.out.println(e.getName() + ": " + e.getText());
}
System.out.println();*/
//已知元素名情况下
System.out.println("title: " + element.elementText("title"));
System.out.println("author: " + element.elementText("author"));
System.out.println();
}
}
}
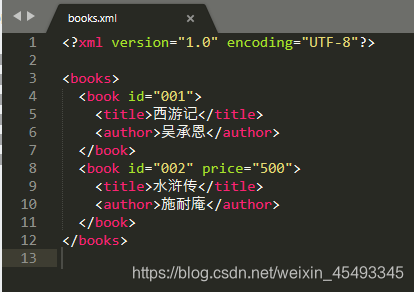
写入xml文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Document doc = DocumentHelper.createDocument();
//增加根节点
Element books = doc.addElement("books");
//增加子元素
Element book1 = books.addElement("book");
Element title1 = book1.addElement("title");
Element author1 = book1.addElement("author");
//为子节点添加属性
book1.addAttribute("id", "001");
//为元素添加内容
title1.setText("西游记");
author1.setText("吴承恩");
Element book2 = books.addElement("book");
Element title2 = book2.addElement("title");
Element author2 = book2.addElement("author");
book2.addAttribute("id", "002");
book2.addAttribute("price","500");
title2.setText("水浒传");
author2.setText("施耐庵");
//实例化输出格式对象
OutputFormat format = OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint();
//设置输出编码
format.setEncoding("UTF-8");
//创建需要写入的File对象
File file = new File("D:" + File.separator + "books.xml");
//生成XMLWriter对象,构造函数中的参数为需要输出的文件流和格式
XMLWriter writer = new XMLWriter(new FileOutputStream(file), format);
//开始写入,write方法中包含上面创建的Document对象
writer.write(doc);
System.out.println("生成成功");
}
查看效果