A
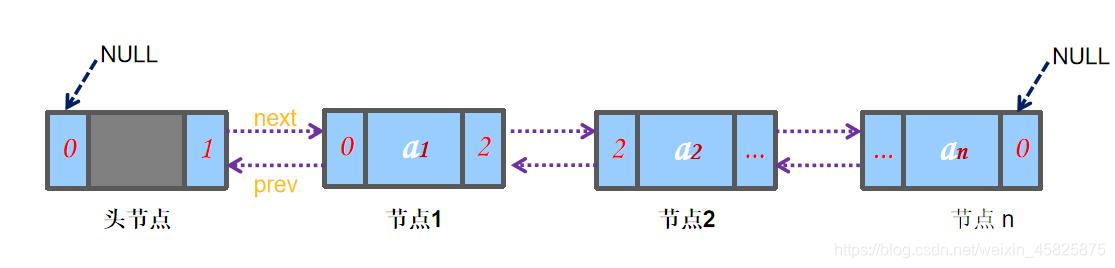
lista única vinculada duplamente vinculada em cada nó armazena seus próprios dados após a remoção, também o endereço armazenado do próximo nó, o próximo nó é, portanto, de fácil acesso e atrás do nó sucessor, mas se você quiser acessar o nó anterior Eu não posso voltar mais. Por exemplo, ao excluir um nó p, o nó anterior q deve ser encontrado primeiro e, em seguida, o nó p pode ser excluído.A lista vinculada individualmente só pode ir para trás, não para frente. E se você precisar seguir em frente?
Neste momento, precisamos que a lista duplamente vinculada apareça. A lista duplamente vinculada adiciona um ponteiro ao elemento anterior com base na
lista de colar único . Está na forma de typedef int Elemdata;
typedef struct _DoubleList { Elemdata data; // Aqui Elemdata é personalizado O tipo de elemento int _DoubleList * next; _DoubleList * prev;
} DoubleList, Node;
/ * Lista
duplamente vinculada
1, inicialização de lista duplamente vinculada
2, lista duplamente vinculada
antes do método de inserção 3, método de pós-inserção de
lista duplamente vinculada 4, inserção de lista duplamente vinculada em qualquer posição
5, duplamente vinculado list deletar elemento
6, lista duplamente vinculada obter o elemento
7, bidirecional A lista vinculada determina se o elemento existe
8. A travessia
da lista duplamente vinculada 9, a destruição da lista duplamente vinculada. A
chamada lista duplamente vinculada é sem dúvida, a adição de um ponteiro anterior com base em uma única lista de colar.
* /
No código
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<Windows.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int Elemdata;
typedef struct _DoubleList{
Elemdata data;
_DoubleList *next;
_DoubleList *prev;
}DoubleList,Node;
//1、双向链表初始化
bool initDoubleList(DoubleList *&L){
L= new DoubleList;
if(!L) return false;
L->next=NULL;
L->prev=NULL;
return true;
}
//2、双向链表的后插法
bool insert_end(DoubleList *&L,Node *node){
if(!L||!node) return false;
//查找最后一个结点
Node *p=L;
while(p->next){
p=p->next;
}
//找到最后一个结点后p
node->next = NULL;
node->prev = p;
p->next= node;
return true;
}
//3、双向链表的前面插入法则
bool insert_front(DoubleList *&L,Node *node){
if(!L||!node)return false;
//前插法则要判断前面的那个元素后面有没有元素
Node * p = L;
if(!L->next){
//如果仅有一个头节点,就先当与尾插法
node->next= p->next;//也可以写成node-next =NULL;
node->prev = p;
p->next = node;
}else{
//否则
node->next = p->next;
p->next->prev = node;
node->prev=p;
p->next=node;
}
return true;
}
//4、双向链表的任意位置插入
bool insertPos(DoubleList *&L,int i,Elemdata &e){
if(!L||i<1) return false;
//找到要插入的位置,必须是插入,尾部插入我们在这里不算必须要是在两个元素的中间插入
Node *p = L;
int j=0;
while(p&&j<i){
p=p->next;
j++;
}
//插入位置的next结点必须存在元素
if(!p||j!=i)return false;
Node *s = new Node;
s->data = e;
p->prev->next = s;
s->prev = p->prev;
s->next = p;
p->prev =s;
return true;
}
//5、双向链表删除指定位置的元素
bool deleteElem(DoubleList *&L,int i){
if(!L) return false;
int j=0;
Node *p,*d;
p = L;
//找到该位置的元素
while(j<i&&p){
p = p->next;
j++;
}
if(!p||j!=i) return false;
//判断该位置的下一个结点是否存在
if(p->next){
//下一个结点存在元素
d = p;
p->prev->next = p->next;
p->next->prev = p->prev;
}else{
//下一结点不存在
d = p;
p->prev->next = p->next;
delete d;
}
return true;
}
//获取元素
bool getElemdata(DoubleList *&L,int i,Elemdata &e){
//获取位置为i的元素
if(!L)return false;
DoubleList *p = L;
int j =0;
while(j<i&&p){
p=p->next;
j++;
}
if(!p||i!=j) return false;
e = p->data;
return true;
}
//判断元素是否存在
bool isExitElemdata(DoubleList *&L,Elemdata &e){
if(!L) return false;
Node *p=L->next;
while(p&&p->data!=e){
p = p->next;
}
if(!p)
return false; //如果是到p=NULL结束循环直接返回
else
return true;
//否则 得到元素
}
//双向链表的遍历
void printList(DoubleList *&L){
if(!L)return ;
DoubleList *p = L->next;
printf("顺序法遍历:");
while(p){
printf("%d\t",p->data);
p=p->next;
}
printf("\n");
DoubleList *last =L;
while(last->next){
last = last->next;
}
//找到最后一个节点后
printf("逆序遍历:");
while(last->prev){
printf("%d\t",last->data);
last=last->prev;
}
printf("\n");
}
void destoyed(DoubleList *&L){
if(!L) return ;
Node *p,*d;
p=L;
while(p){
d = p;
p=p->next;
delete d;
}
L = NULL;
}
//测试代码
int main(void){
DoubleList *L = NULL;
Node *s;
if(initDoubleList(L)){
printf("链表初始化成功!\n");
}else{
printf("链表初始化失败!\n");
}
cout<<"请输入5个元素:"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
s = new Node;
cin>>s->data;
insert_end(L,s);
}
printList(L);
int x=5;
if(insertPos(L,1,x)){
cout<<"元素"<<x<<"插入成功!"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"元素"<<x<<"插入失败!"<<endl;
}
printList(L);
int e=22;
if(isExitElemdata(L,e)){
cout<<"元素"<<e<<"存在"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"元素"<<e<<"不存在"<<endl;
}
//获取元素
if(getElemdata(L,1,e)){
cout<<"成功获取元素"<<e<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"失败获取元素"<<e<<endl;
}
//销毁链表
destoyed(L);
if(initDoubleList(L)){
printf("链表初始化成功!\n");
}else{
printf("链表初始化失败!\n");
}
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
s = new Node;
cin>>s->data;
insert_end(L,s);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
A dificuldade da cadeia dupla no algoritmo de estrutura de dados é considerada mais demorada para ser entendida.