Article Directory
Foreword
Mainly on the content:
- How to calculate the OSPF routing domain
- Two kinds of domain routing LSA
- SPF algorithm
Preliminaries
LSA :Link-State Advertisement
LSA (Link State Advertisement) packet is a link-state protocol, which includes information about the neighbor channels and cost. Receiving router LSA is used to maintain their routing tables.
LSA head

LSA classification
Only records the more common LSA
| Type | description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Router LSA (Router LSA) |
| 2 | 网络 LSA (Network LSA) |
| 3 | Network Summary LSA (Network-summary-LSA) |
| 4 | ASBR Summary LSA (ABSR-summary-LSA) |
| 5 | AS外部LSA(AS-external-LSA) |
| 7 | NSSA external LSA (NSSA-LSA) |
Router LSA (Router LSA)
Each router will generate a router LSA notice. The basic list of advertised router LSA all links or interfaces, and indicate their status and the outbound direction along each link overhead, and all known OSPF neighbors over the link. These notices will only LSA flooding diffused inside their region of origin. Huawei Device command display ospf lsdb router self-originatecan view the LSA generated by the router itself
Router LSA describes P2P networks
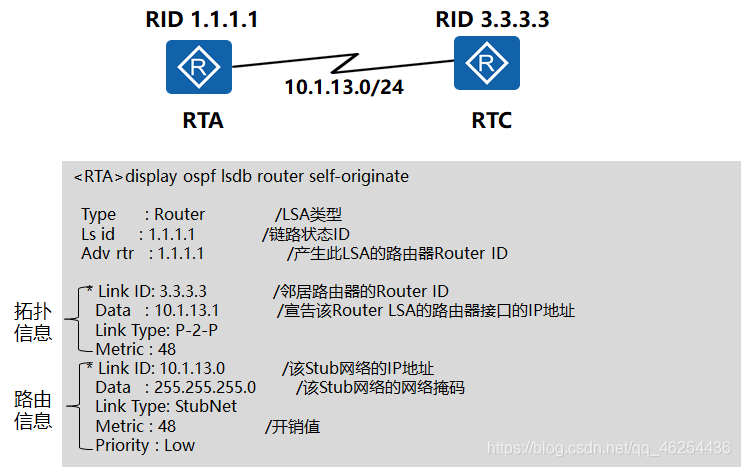
Each OSPF router Router-LSA describes the use of a link state information of the region.
Router-LSA can describe a plurality of links, each link information is described by a Link ID, Data, Link Type Metric and composition,
<RTA>display ospf lsdb router self-originate
Type : Router //LSA类型
Ls id : 1.1.1.1 //链路状态ID
Adv rtr : 1.1.1.1 //产生此LSA的路由器Router ID
//拓扑信息
* Link ID: 3.3.3.3 //邻居路由器的Router ID
Data : 10.1.13.1 //宣告该Router LSA的路由器接口的IP地址
Link Type: P-2-P
Metric : 48
//路由信息
* Link ID: 10.1.13.0 //该Stub网络的IP地址
Data : 255.255.255.0 //该Stub网络的网络掩码
Link Type: StubNet
Metric : 48 //开销值
Priority : Low
Router LSA NBMA network or a network described MA

In the description of MA or NBMA network in Router-LSA type, Link ID is the interface IP address of the DR, Data IP address of the local interface.
as the picture shows:
Between RTB, RTC, RTE interconnected by Ethernet link, for example to produce LSA RTC, Link ID is the interface IP address of the DR (10.1.235.2), Data router connected to this local network interface IP address MA (10.1 .235.3), Link Type of TransNet, Metric represents the cost to reach the value of DR.
TransNet link includes only the described connection relationship of DR and overhead information is not any network number / masks and other routers on the shared link.
<RTC>display ospf lsdb router self-originate
Type : Router //LSA类型
Ls id : 3.3.3.3 //链路状态ID
Adv rtr : 3.3.3.3 //产生此LSA的路由器的Router ID
//拓扑信息
* Link ID: 10.1.235.2 //DR的接口IP地址
Data : 10.1.235.3 //宣告该Router LSA的路由器接口的IP地址
Link Type: TransNet
Metric : 1
Tips
If the Data Link ID is the same, the router as the DR network segment
Why, Multiple Access Router LSA network topology information only, no routing information? Multiaccess network routing information advertised by generating a second type of LSA in the network DR.
Network LSA (网络 LSA)
Each multiaccess network is designated router (DR) will produce a network LSA advertised . As previously discussed, the DR router as a "dummy" node, or a virtual router, used to describe a multi-access network and all routers connected thereto. From this perspective, a network announcement may also depicts LSA "false" a logical node, like a router LSA advertisement depicts a single router on the same physical. LSA lists all network router advertisement associated therewith, including DR router itself. Just as a router LSA, network LSA is only produced in the interior region of this network LSA flooding spread.
Network LSA describes MA, NBMA network
Network Number MA, NBMA shared network segment / mask and links between routers, are presented by Network LSA.
<RTB>display ospf lsdb network self-originate
OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 2.2.2.2
Area: 0.0.0.0
Link State Database
//拓扑信息、路由信息
Type : Network //LSA类型
Ls id : 10.1.235.2 //DR接口的IP地址
Adv rtr : 2.2.2.2 //产生此Network LSA的路由器Router ID及DR的Router ID
Net mask : 255.255.255.0 //网络掩码
Priority : Low
Attached Router 2.2.2.2 //连接到该网段的路由器列表,呈现了此网段的拓扑信息
Attached Router 3.3.3.3
Attached Router 5.5.5.5
//基于上述字段表达的信息,LS ID和Net mask做与运算,即可得出该网段的IP网络号,另外,从DR路由器到其所连接的路由器的开销为0
//从Attached Router部分可以看出,2.2.2.2、3.3.3.3、5.5.5.5共同连接到该共享MA网段中,DR路由器为2.2.2.2,网络号10.1.235.0,掩码255.255.255.0。
OSPF LSDB in the region
LSDB
Link state database. LSA is the smallest constituent units LSDB, that there is a section of the LSA LSDB composition.
By display ospf lsdbLSDB to view information on the router
As shown, five interconnected and running OSPF routers. In the RTA LSDB an example, which includes five routers Router-LSA generated, and Network-LSA two broadcast networks generated
- note
- DR election
-
- Election between each segment
-
- P2P networks are not elections DR, BDR
Therefore, only the topology between the RTA and RTB; DR between two elected RTB and RTC, RTE
<RTA>display ospf lsdb
OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 1.1.1.1
Link State Database
Area: 0.0.0.0
Type LinkState ID AdvRouter Age Len Sequence Metric
Router 4.4.4.4 4.4.4.4 1436 72 80000007 48
Router 2.2.2.2 2.2.2.2 1305 72 80000019 1
Router 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1 1304 60 80000007 1
Router 5.5.5.5 5.5.5.5 1326 60 80000017 1
Router 3.3.3.3 3.3.3.3 1325 60 8000000F 1
Network 10.1.235.2 2.2.2.2 1326 36 80000004 0
Network 10.1.12.2 2.2.2.2 1305 32 80000001 0
SPF algorithm
SPF algorithm (Shortest Path First) is also known as Dijkstra's algorithm, it is put forward in 1959 by the Dutch computer scientist Dick Stella.
SPF algorithm each router as a root (ROOT) to calculate its distance to each destination router, the routing topology of the domain router is calculated based on each of a unified database of accounting, which is similar to a tree structure of FIG., In SPF algorithm, known as the shortest path tree. In the OSPF routing protocol, the length of the shortest path tree trunk, i.e. from the OSPF router to each destination router, the OSPF called Cost. Use SPF overhead (cost) as a measure.
- SPF algorithm basic steps
-
- SPF tree constructed
according to the topology information in the Network LSA Router LSA and to construct trunk SPF
- SPF tree constructed
-
- Calculate the optimal route
based on the routing information SPF trunk and Router LSA, Network LSA is, to calculate the optimal route
- Calculate the optimal route
Detailed steps
The following topology diagram as an example to explain the specific steps SPF algorithm

step 1
- OSPF router as the root node itself, respectively, to calculate the shortest path tree. In RTA, for example, calculated as follows
-
RTA add themselves to the position of the shortest path tree root, and then check their generation Router-LSA, the LSA described for each connection, if it is not connected to a Stub, put the connection is added to the candidate list, divided candidate list for the node Link ID, Metric values and parent LSA described and reaches the root node of the cost corresponding to the present candidate overhead.
Router-LSA RTA root of the present TransNet Link ID is 10.1.12.2 Metric = 1 and P-2-P in the Link ID of the two connecting 3.3.3.3 Metric = 48 is added to the candidate list.
RTA candidate list candidate minimum total cost of the shortest path tree node 10.1.12.2 move, and delete from the candidate list.

Step 2
DR is added to the SPF, is next examined Ls id 10.1.12.2 the Network-LSA. If the division node LSA described shortest path tree already exists, the sub-node is ignored.
- As shown in FIG Attached Router Part:
-
1.1.1.1 nodes are ignored, because the shortest path tree has been 1.1.1.1.
The node 2.2.2.2, Metric = 0, the parent node to the root cost is 1, the total cost of the candidate 1, candidate list is added.
Two candidate node candidate node list, the node selects the smallest candidate overhead 2.2.2.2 Add the shortest path tree and removed from the candidate list.

Step 3
- 2.2.2.2 new node added to the shortest path tree, continue to check the case of Ls id is 2.2.2.2 Router-LSA:
-
TransNet first connection, Link ID is 10.1.12.2, this node has the shortest path tree, is ignored.
TransNet second connection, Link ID is 10.1.235.2, Metric = 1, the parent node to the root node is a cost, the total cost of the candidate 2, the candidate list is added.
The third P-2-P connection, Link ID is 4.4.4.4, Metric = 48, the parent node to the root node is a cost, the total cost of 49 candidates, the candidate list is added.
There are three candidate node candidate node list, the node selects the smallest candidate overhead 10.1.235.2 added shortest path tree and removed from the candidate list.

Step 4
lDR is added to the SPF, is next examined Ls id 10.1.235.2 the Network-LSA.
- As shown in FIG Attached Router Part:
-
2.2.2.2 nodes are ignored, because the shortest path tree has been 2.2.2.2.
The node 3.3.3.3, Metric = 0, the parent node to the root node cost of 2, the overhead of the candidate 2, the candidate list is added. (If two node ID in the candidate list appear the same but the cost to the root node is not the same, then the large overhead of the root node to delete, so delete nodes 3.3.3.3 cumulative cost for the candidate 48).
The node 5.5.5.5, Metric = 0, the parent node to the root node cost of 2, the overhead of the candidate 2, the candidate list is added.
There are three candidate node candidate node list, select a candidate node with the lowest total cost 3.3.3.3 and 5.5.5.5 added shortest path tree and removed from the candidate list.

Step 5
3.3.3.3 and 5.5.5.5 new node added to the shortest path tree, then continue to check Ls id 3.3.3.3 and 5.5.5.5 respectively of Router-LSA.
- Ls id and 3.3.3.3 of the LSA:
-
Link ID to 10.1.235.2 nodes already on the shortest path tree is ignored.
pLink ID of 1.1.1.1 nodes in the shortest path tree has been ignored.

Step 6
- Ls id for the LSA 5.5.5.5 of:
-
Link ID to 10.1.235.2 nodes already on the shortest path tree is ignored.
4.4.4.4 Link ID of the P-2-P connection, Metric = 48, the parent node to the root node cost of 2, 50 of a candidate overhead. 4.4.4.4 has occurred since the node in the candidate list, and the total cost of the candidate 49.49 <50, the child's parent node selection 4.4.4.4 2.2.2.2.
So far, through the command display ospf lsdb router 4.4.4.4 find adjacent nodes are connected as described in the LSA have been added to the SPF tree.
At this time, the candidate list is empty, the SPF calculation is completed, which is 10.1.12.2 and 10.1.235.2 dummy node (DR).

Step 7: Calculate the optimal path
The second phase of the routing information in the Router LSA Stub, Network LSA in calculating the optimal route is completed.
- Starting from the root, sequentially adding the routing information (order of add was added for each node of the tree SPF) of the LSA:
-
p1.1.1.1 (RTA) in the Router LSA, a total Stub connection, network number / mask 10.1.13.0/24,Metric=48;
p10.1.12.2 (the DR) of Network LSA, the network number / mask 10.1.12.0/24,Metric=1+0=1;
p2.2.2.2 (RTB-) in the Router LSA, a total Stub connection, network number / mask 10.1.24.0/24,Metric=1+ 49 + 48 = 0;
p10.1.235.2 (the DR) of network LSA, the network number / mask 10.1.235.0/24,Metric=1+0+1=2;
p3.3.3.3 (the RTC) of Router LSA, the total of a Stub connection, network number / mask 10.1.13.0/24, already on the RTA, ignored;
p5.5.5.5 (RTE) in the Router LSA, a total Stub connection, network number / mask code 10.1.45.0/24,Metric=1+0+0+1+48=50;
p4.4.4.4 (the RTD) in the Router LSA, a total of 2 Stub connection, network number / mask 10.1.24.0/24 , has been on the RTB, ignored; network number / mask 10.1.45.0/24, already on RTE, ignored.

View the OSPF routing table
<RTA>display ospf routing
OSPF Process 1 with Router ID 1.1.1.1
Routing Tables
Routing for Network
Destination Cost Type NextHop AdvRoute Area
10.1.12.0/24 1 Transit 10.1.12.1 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
10.1.13.0/24 48 Stub 10.1.13.1 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0
10.1.24.0/24 49 Stub 10.1.12.2 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
10.1.45.0/24 50 Stub 10.1.12.2 5.5.5.5 0.0.0.0
10.1.235.0/24 2 Transit 10.1.12.2 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0
Total Nets: 5
Intra Area: 5 Inter Area: 0 ASE: 0 NSSA: 0
Single Area OSPF configuration
Single area router configuration
ospf router-id 1.1.1.1
area 0
network [相邻网段] [反子网掩码]
network 10.1.12.0 0.0.0.255 //举例
