linux link is an important knowledge point a linux file, read a lot of information, summarize convenient for you to remember.
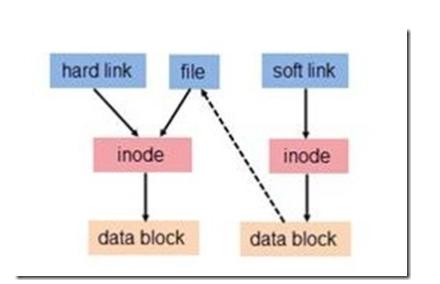
First, let's review what inode: linux system inside each file has an inode number, the inode which kept some what of it? Information saved the file attributes, such as file permissions, number of links, the most important thing is to keep the block address of the data block is really stored data. But does not include the file name
1. Classification and create links
Links are divided into soft links and hard links.
Create a soft link: ln -s source target
Create a hard link: ln source target
2. Hard Links
The characteristics of hard links
1. Hard links: source and target hard links hard links to each other, with the same inode number, to delete one of them, does not affect the other, between the two data are synchronized.
2. Hard links can only be applied to the file, not a directory, the file system can not span
3. Hard links typically used to back up important files, only Dangdang an inode number of links becomes zero, the system will reclaim the inode
3. soft links
Soft link characteristics
1. soft links: soft links similar to shortcut windows, is a link to the target
2. Soft links have their own separate inode number, inode pointed to block the block is stored in the target object file.
3. When the soft link after the target file is deleted, it will display the soft link is unavailable
4. Soft links can be applied to different file systems can also be applied to the directory
A map is well represented this relationship