Foreword
RabbitMQ six kinds queue mode - Simple Queue
RabbitMQ six kinds queue mode - work queue
RabbitMQ six kinds queue mode - Publish Subscribe
RabbitMQ six kinds queue mode - routing mode
RabbitMQ six kinds queue mode - Themes [paper]
We turn from the front of several experienced exchange mode from the fanout> direct the transformation process, when fanout, we can only perform simple broadcast, the corresponding type is relatively simple, the use of direct, consumers can choose to some extent, However, direct or limitations, it does not support multiple routing conditions.
How about it?
direct support does not match routingKey, but a bound is binding, while the topic theme support matching rules, provided that they meet routingKey can be sent to the binding queue.
Article Directory
1. What is the theme 2. Code section 2.1 Producer 2.2 * Consumers 2.3 Consumer # 2.4 run shot 3. Summary
1. What is the theme
Official Links: http://www.rabbitmq.com/tutorials/tutorial-five-java.html
topics themes with routing routing mode similar, but fixed routing mode is specified route key routingKey, and themes can be fuzzy matching routing key routingKey, their relationships and the like are similar to SQL.
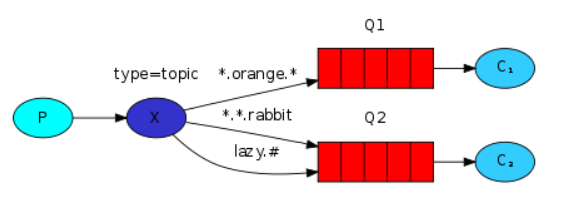
P represents for producers, X represents a switch, it indicates that the queue C1C2 represented consumers, red.
topics 模式与 routing 模式比较相近,topics 模式不能具有任意的 routingKey,必须由
一个英文句点号“.”分隔的字符串(我们将被句点号“.”分隔开的每一段独立的字符串称为一个单词),比如 "lazy.orange.fox"。topics routingKey 中可以存在两种特殊字符“”与“#”,用于做模糊匹配,其中“”用于匹配一个单词,“#”用于匹配多个单词(可以是零个)。
"*" 表示任何一个词
"#" 表示0或1个词
以上图中的配置为例:
如果一个消息的 routingKey 设置为 “xxx.orange.rabbit”,那么该消息会同时路由到 Q1 与 Q2,routingKey="lazy.orange.fox”的消息会路由到Q1与Q2;
routingKey="lazy.brown.fox”的消息会路由到 Q2;
routingKey="lazy.pink.rabbit”的消息会路由到 Q2(只会投递给Q2一次,虽然这个routingKey 与 Q2 的两个 bindingKey 都匹配);
routingKey="quick.brown.fox”、routingKey="orange”、routingKey="quick.orange.male.rabbit”的消息将会被丢弃,因为它们没有匹配任何bindingKey。
接下来代码为例:
2. 代码部分
2.1 生产者
public class ProducerTopic {
private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "my_topic_exchange";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
/** 1.创建新的连接 */
Connection connection = MQConnectionUtils.newConnection();
/** 2.创建通道 */
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
/** 3.绑定的交换机 参数1交互机名称 参数2 exchange类型 */
channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic");
/** 4.发送消息 */
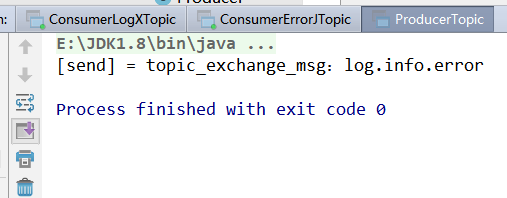
String routingKey = "log.info.error";
String msg = "topic_exchange_msg:" + routingKey;
System.out.println("[send] = " + msg);
channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, routingKey, null, msg.getBytes());
/** 5.关闭通道、连接 */
channel.close();
connection.close();
/** 注意:如果消费没有绑定交换机和队列,则消息会丢失 */
}
}
2.2 *消费者
public class ConsumerLogXTopic {
private static final String QUEUE_NAME = "topic_consumer_info";
private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "my_topic_exchange";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
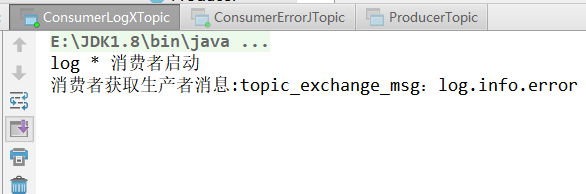
System.out.println("log * 消费者启动");
/* 1.创建新的连接 */
Connection connection = MQConnectionUtils.newConnection();
/* 2.创建通道 */
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
/* 3.消费者关联队列 */
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
/* 4.消费者绑定交换机 参数1 队列 参数2交换机 参数3 routingKey */
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "log.*");
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body)
throws IOException {
String msg = new String(body, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("消费者获取生产者消息:" + msg);
}
};
/* 5.消费者监听队列消息 */
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, true, consumer);
}
}
2.3 #消费者
public class ConsumerLogJTopic {
private static final String QUEUE_NAME = "topic_consumer_info";
private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "my_topic_exchange";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
System.out.println("log # 消费者启动");
/* 1.创建新的连接 */
Connection connection = MQConnectionUtils.newConnection();
/* 2.创建通道 */
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
/* 3.消费者关联队列 */
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
/* 4.消费者绑定交换机 参数1 队列 参数2交换机 参数3 routingKey */
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "log.#");
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body)
throws IOException {
String msg = new String(body, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("消费者获取生产者消息:" + msg);
}
};
/* 5.消费者监听队列消息 */
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, true, consumer);
}
}
2.4 运行截图
生产者
星花*消费者
#消费者

3. 总结
1、topic 相对于之前几种算是比较复杂了,简单来说,就是每个队列都有其关心的主题,所有的消息都带有一个“标题”(RouteKey),exchange 会将消息转发到所有关注主题能与 routeKey 模糊匹配的队列。
2、在进行绑定时,要提供一个该队列关心的主题,如“#.sscai.#”表示该队列关心所有涉及 sscai 的消息(一个 routeKey 为 "club.sscai.tmax”的消息会被转发到该队列)。
3、"#”表示0个或若干个关键字,“”表示一个关键字。如“club.”能与“club.sscai”匹配,无法与“club.sscai.xxx”匹配;但是“club.#”能与上述两者匹配。
4、同样,如果 exchange 没有发现能够与 routeKey 匹配的 Queue,则会抛弃此消息。
案例代码:https://www.lanzous.com/i5ydu6d
我创建了一个java相关的公众号,用来记录自己的学习之路,感兴趣的小伙伴可以关注一下微信公众号哈:niceyoo
