Memory access violation summarized as follows:
Memory access violation occurs when the following conditions are met accessed in two:
a. at least one write operation
b. they access the same piece of memory
c. They overlap an access time (for example, in the same function)
Example 1:
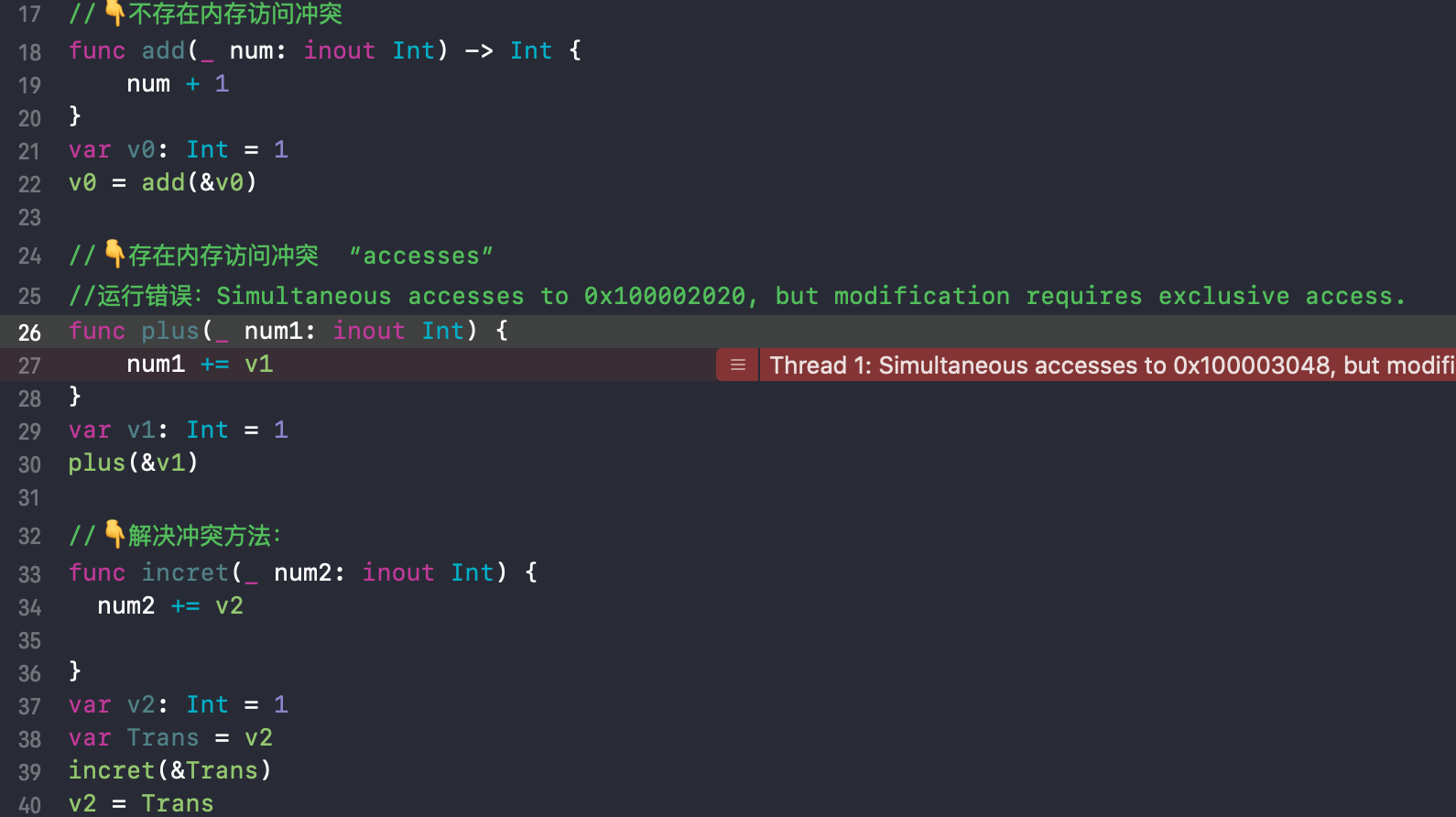
. 2-3-4 Example:


The focus is error to find the problem not to tangle! ! !
If the following condition is satisfied , it means access to the overlapping property of the structure is safe :
/*
1. Only access memory attributes instance, instead of computing the attribute or attribute class (as in the global area equivalent)
2. The structure of a local variable is not the global variable
3. The structure is either not or only the closure by a non-captured escape capture closure
*/
Example a: (tuple structure) as a local variable in a function which is the
