Scalability: refers to the need to change hardware and software design of the site, simply by changing the number of servers deployed can be enlarged or reduced service processing capabilities of the site.
First, the design flexibility

1, to achieve physical separation of different functions telescopic
(1) a longitudinal separation (stratification after separation): partial separation of different business processes deployed on, for system scalability.
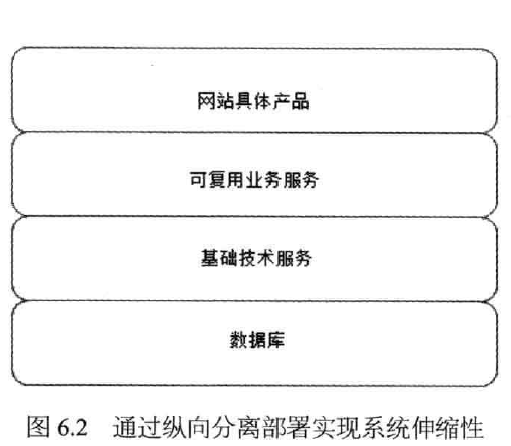
(2) laterally separated (after separation operations segmented): separation of different service modules deployed, for system scalability.
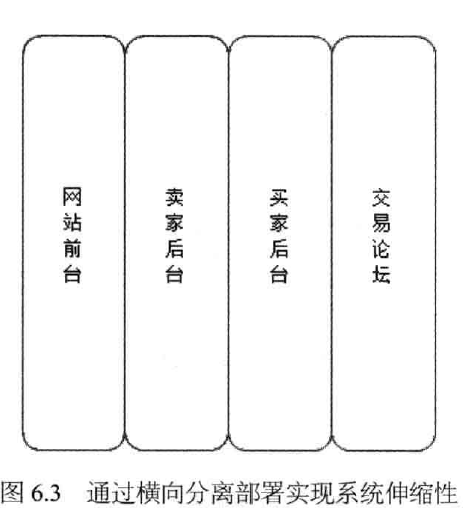
2, single function achieved by stretching cluster size
Design flexibility Second, the application server cluster

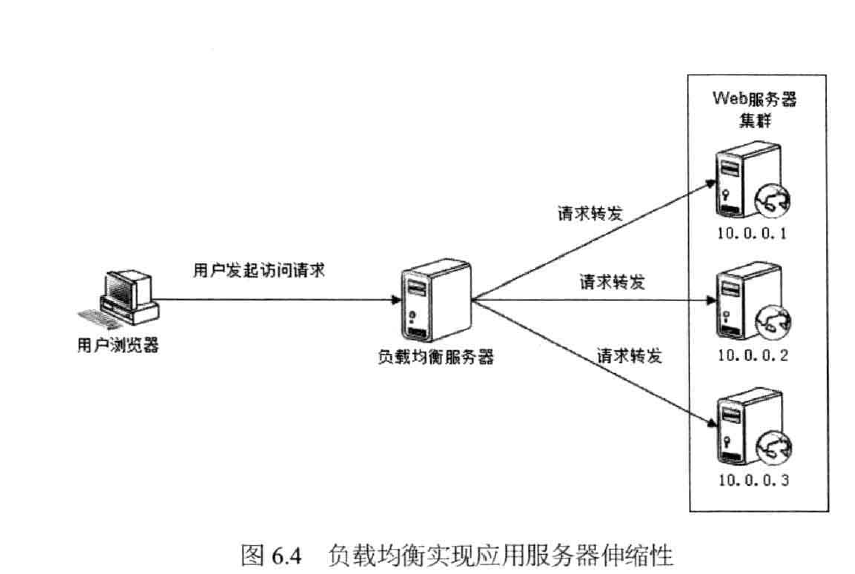
1, HTTP redirect load balancing

Advantages: relatively simple
Cons: browser needs two requests to complete a server access, poor performance
2, DNS DNS load balancing


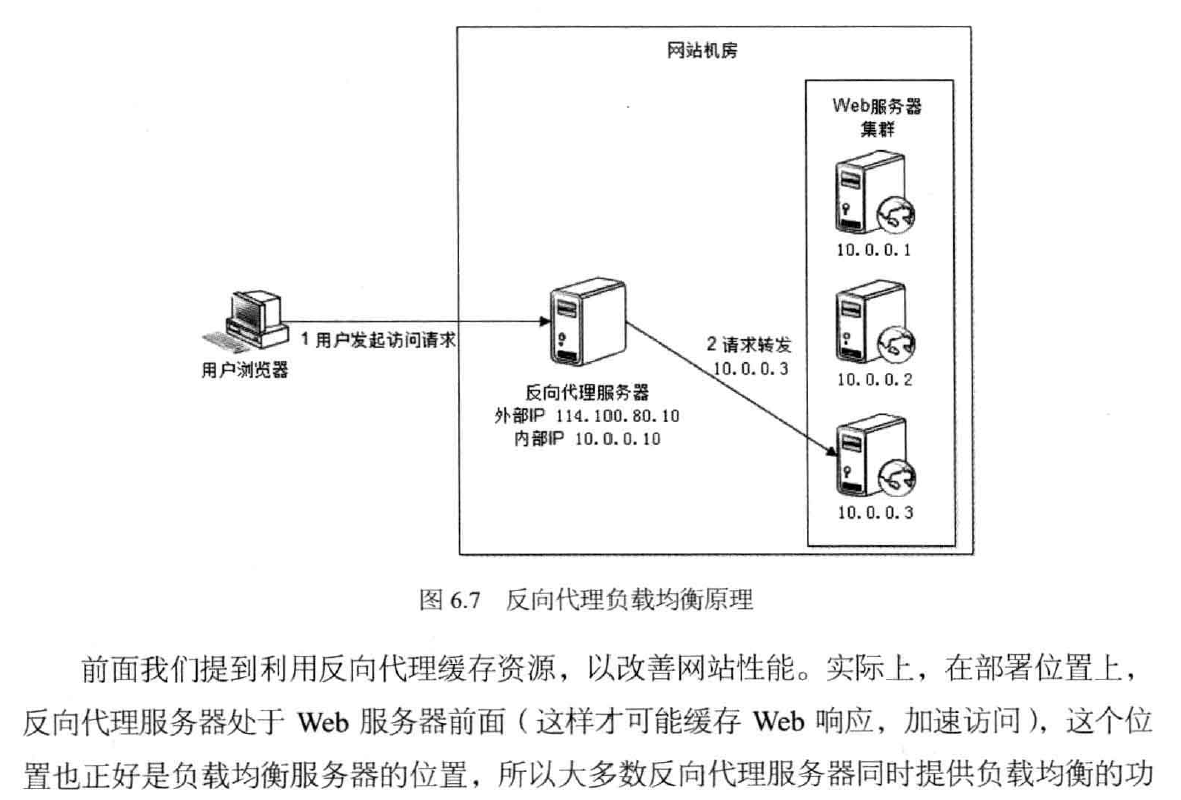
3, the reverse proxy load balancing (load balancing application layer) protocol layer -HTTP

4, IP Load Balancing
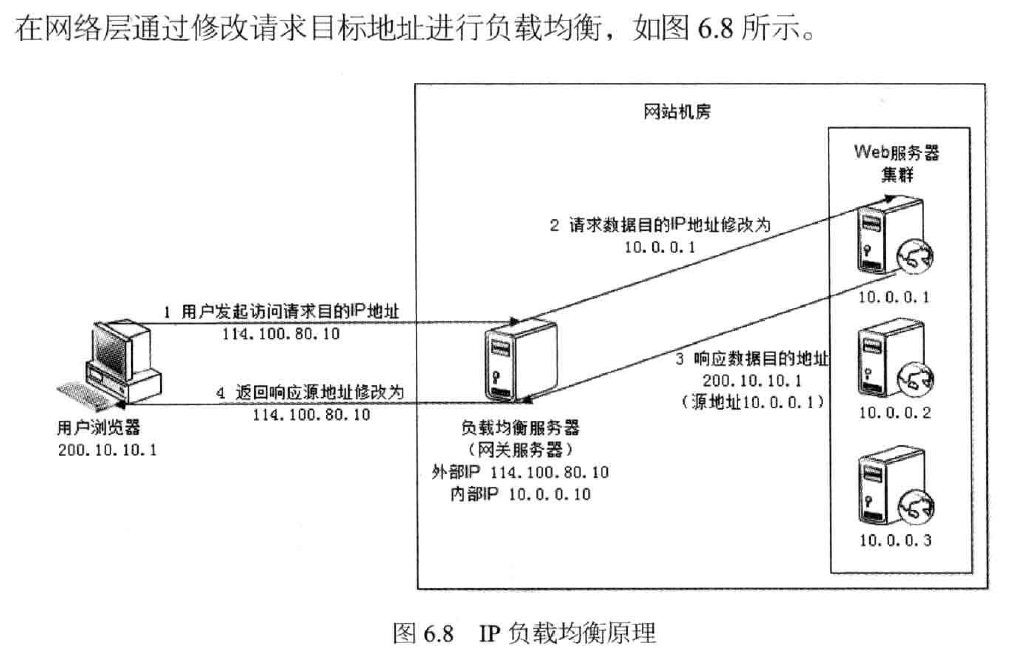
5, the data link layer load balancing


6, the load balancing algorithm
(1) Polling (Round Robin, RR)

(2) weighted round robin (Weighed Round Robin, WRR)
The case where the application server hardware performance, on the basis of the polling, in accordance with the configuration of the right weight distribute requests to each server, the server can allocate more high performance requests.
(3) random (the Random)

(4) Least Connection (Least Connections)

(5) the source address hash (Source Hashing)

Third, the design of scalable distributed cache cluster
Access model 1, Memcached distributed caching cluster

2, scalability challenge Memcached distributed caching cluster

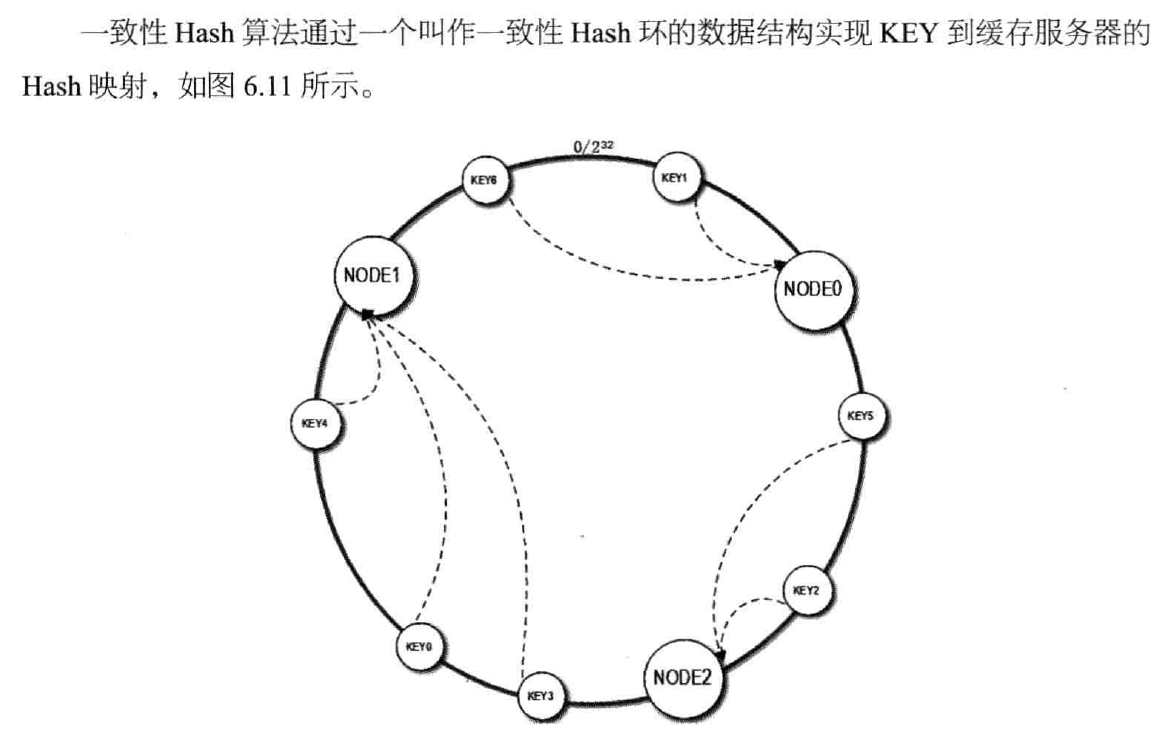
3, distributed cache coherence hashing algorithm (): a physical server virtual node reference 150

Fourth, the design of scalable data storage server clusters
1, the relationship between data clusters stretchable design: the master copy, the data sub-libraries, sub-libraries sub-table

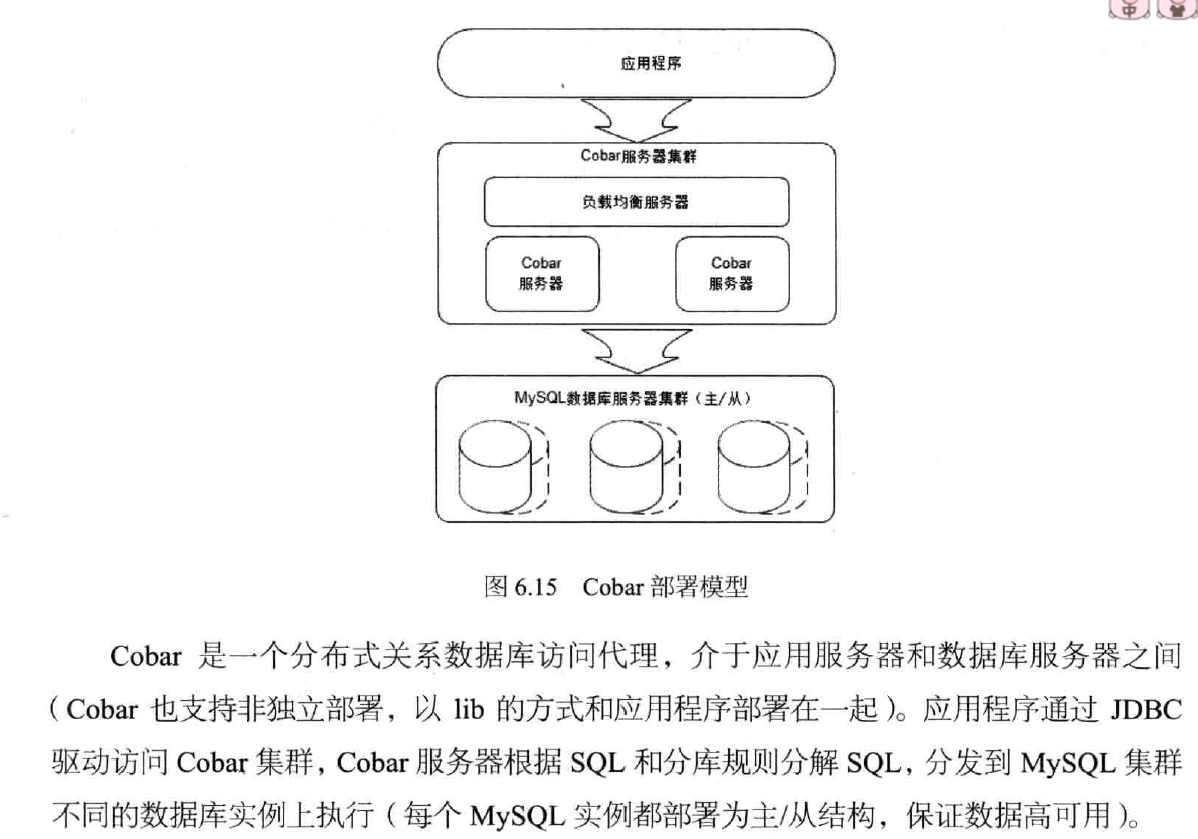
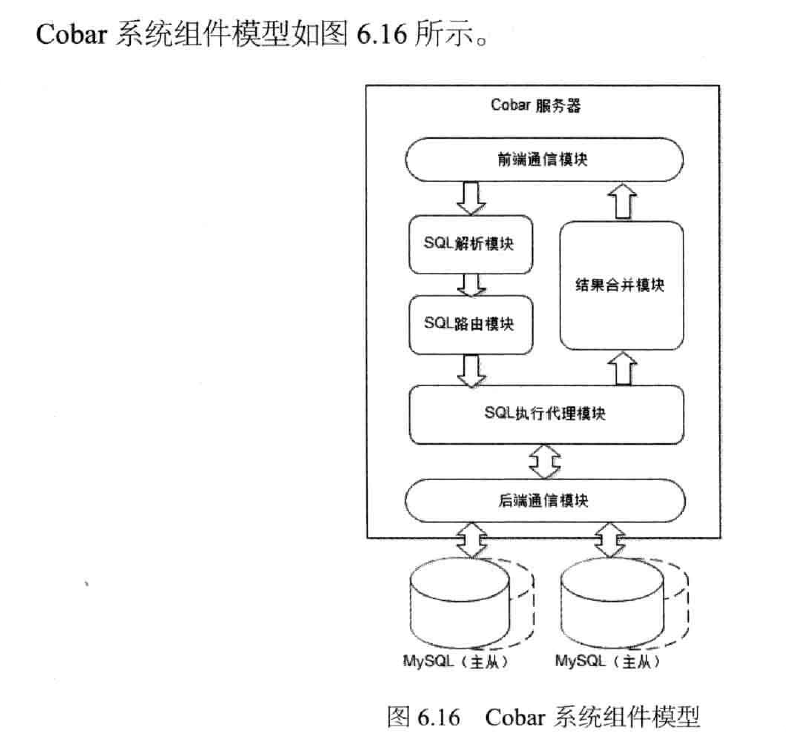
2, scalable database design Nosql
