Table of contents
6.2 Basic working principles of mobile IP
6.2.1 Agent discovery and registration
6.2.2 Fixed host sends IP datagram to mobile host
6.2.3 Mobile host sends IP datagram to fixed host
6.2.4 Co-located care-of address (simple understanding)
6.2.5 Triangular routing problem (simple understanding)
6.1 Concept of Mobile IP
A mobile station is a host that changes its point of attachment from one network or subnet to another.
Mobile IP technology means that mobile stations use fixed network IP addresses to implement roaming functions across different network segments, and ensure that network permissions based on network IP do not change in any way during the roaming process. The goal of Mobile IP is to automatically deliver packets to mobile stations.
If TCP transmission (reliable service with connection) is required during movement, the TCP connection should be maintained while the mobile station is roaming, otherwise the TCP connection of the mobile station will be intermittent. It can be seen that if the TCP connection of the mobile station is not interrupted during the move, the IP address of the notebook must remain unchanged during the move . This is the issue to be studied in mobile IP.
Mobile IP defines three functional entities :
- Move node . A mobile station with a permanent IP address.
- Local (home) agent . Typically this is the router connected to the home network (the network to which it was originally connected).
- Field Agent . This is usually the router connected to the visited network (the network you moved to another location).

6.2 Basic working principles of mobile IP
6.2.1 Agent discovery and registration
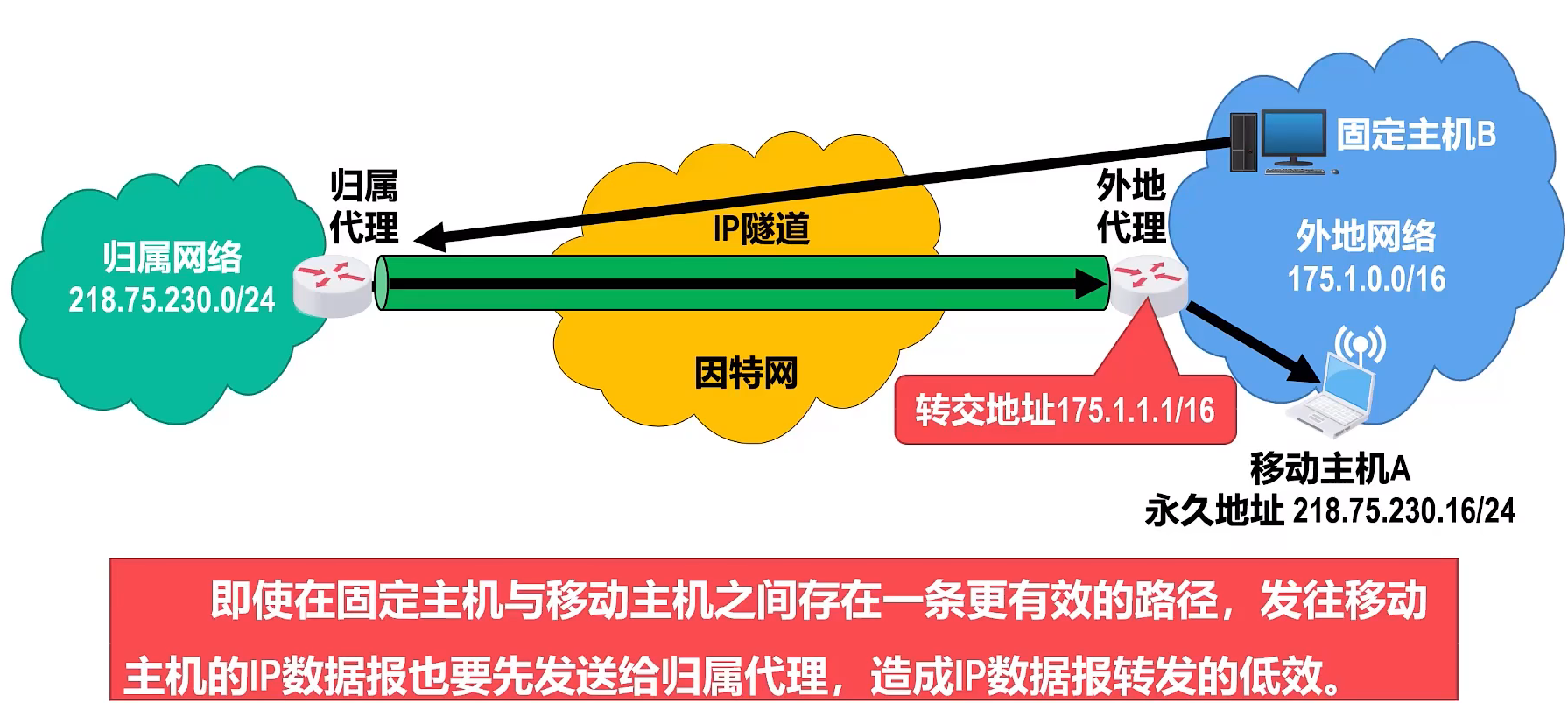
- ① Mobile host A establishes contact with the foreign agent through its own agent discovery protocol , and obtains a care-of address belonging to the foreign network from the foreign agent (for example, 175.1.1.1/16). At the same time , it registers its permanent address and home address with the foreign agent. proxy address.
- ③The home agent will record the care-of address of mobile host A. Afterwards, the home agent will receive all IP datagrams sent to the mobile host on behalf of the mobile host, and forward these datagrams to the mobile host in the foreign network using IP tunnel technology. .

6.2.2 Fixed host sends IP datagram to mobile host
- When the foreign agent and the mobile host are not the same device, the care-of address is actually the address of the foreign agent rather than the address of the mobile host. The care-of address will neither be used as the source address of the IP datagram sent by the mobile host nor as the mobile host. The destination address of the received IP datagram.
- The care-of address is simply the exit address of the IP tunnel from the home agent to the foreign agent.
- When the foreign agent receives and decapsulates the original IP datagram from the IP tunnel , it will search the MAC address corresponding to the permanent IP address of the mobile host in its own agent registry , and encapsulate the datagram to the destination address of The MAC address is sent to the mobile host in the frame. (This is different from the normal IP datagram forwarding process, otherwise the datagram will be sent back to the mobile host's home network)

6.2.3 Mobile host sends IP datagram to fixed host
- The IP datagram is sent by mobile host A according to the normal sending process. Since the IP router does not care about the source address of the IP datagram, the IP datagram is routed directly to fixed host B without forwarding it through the home agent.
- To this end, the mobile host can use the foreign agent as its default router , or it can obtain the addresses of other routers in the foreign network from the foreign agent through the agent discovery protocol and set them as its own default router .

6.2.4 Co-located care-of address (simple understanding)

6.2.5 Triangular routing problem (simple understanding)
Based on the above communication process, you still need to pay attention to the following points :
- The basic working process can be divided into four stages: agent discovery→registration→group routing→logout .
- Mobile IP packet routing can be divided into unicast, broadcast and multicast.
- When other networks communicate with the mobile station, the mobile station can neither receive packets directly nor send packets directly (although the transmission does not go through the home agent, it still needs to go through the external agent).
- The care-of address is used by mobile stations, home agents, and foreign agents and is not used by various applications.
- When the foreign agent wants to send a datagram to the mobile station connected to the visited network, it directly uses the MAC address of the mobile station (as mentioned above, if the IP address is used, it returns to the home network)