Network layer: (3 messages) Computer network network layer_Put on straw sandals to travel blog-CSDN blog
Table of contents
1. Virtual interconnection network
3.IP address and hardware address
Internet Protocol IP
The IP here is the fourth version of the IP protocol, actually called IPv4. Newer is IPv6.
There are three protocols supporting the IP protocol:
- Address Resolution Protocol ARP
- Internet Control Message Protocol ICMP
- Internet Group Management Protocol IGMP
1. Virtual interconnection network
Networks vary greatly because no single network can suit the needs of all users. Therefore, the network needs to be connected through some intermediate devices.
According to the level at which it is located, intermediate devices can be divided into the following four types:
1. What is used in the physical layer is called a transponder.
2. What is used in the data link layer is called a bridge or bridge.
3. What is used in the network layer is called a router.
4. What is used above the network layer is called a gateway.
Using repeaters at the physical layer or bridges at the data link layer only enlarges a network. From a network layer perspective, this is still a network, not a network interconnection. Network interconnection is achieved through routers at the network layer.
Network interconnections that all use the IP protocol are called virtual interconnection networks, which means that these networks that are different at the physical level appear to be a unified network at the network layer, also called an IP network. The current Internet uses the IP protocol and TCP protocol.
2. Classified IP addresses
IP address and its representation: IP addresses are 32-bit binary codes. In order to improve readability, we often insert a space into every 8 bits of the 32- bit IP address (but there is no such space on the machine ). In order to make it easier for people to write and remember, it is often expressed in its equivalent decimal number, and a decimal point is added between each number. This is called dotted decimal notation.
The entire Internet is a single, abstract network. An IP address is a globally unique 32-bit identifier assigned to each interface of every host or router on the Internet.
The addressing method of IP address has gone through three stages:
1. Classified IP addresses.
2. Division of subnets.
3. Form a supernet.
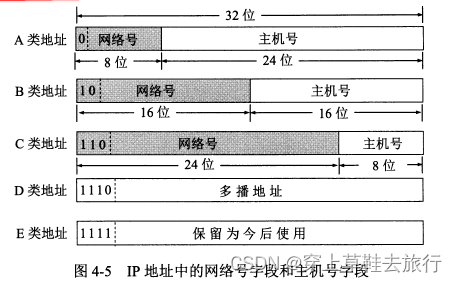
Classified IP addresses mean that IP addresses are divided into multiple fixed classes, and each class of addresses consists of two fixed-length fields.
1. The first field is the network number, which identifies the network to which the host is connected. A network number is unique within the entire Internet.
2. The second field is the host number, which identifies the host (or router). A host number is unique within the network range indicated by the network number.

IP address = {,}, which specifies both the host interface and the network.
Classified IP addresses are divided into the following 5 categories:
1. Class A, Class B, and Class C are all unicast addresses and are the most commonly used.
2. Class is used for multicast (one-to-many communication).
3. Class E addresses are reserved for future use.
The classification takes into account the differences between different networks. Some networks have many hosts, while others have few.
Unclassified IP addresses are now widely used for routing, and classified addresses are a thing of the past.
The IP address is 4 bytes with a total of 32 characters. Usually, what is displayed on the computer is the result of converting each byte into decimal, which is called dotted decimal method.

IP addresses have the following characteristics:
- Each IP address consists of two parts, the network number and the host number, and is a hierarchical address structure. This structure has several advantages
- The IP address management agency only allocates the network number when allocating the IP address, and the host number is allocated internally by the unit that obtains the network number.
- The router only forwards the packet based on the network number to which the destination host is connected, regardless of the host number. This greatly reduces the number of items in the routing table, reducing the storage space and search time of the routing table.
- An IP address identifies a host (or router) and an interface on a link. If a host is connected to two networks at the same time, it has two IP addresses.
- Every router is connected to at least two networks, so a router has at least two different IP addresses.
- In the Internet, a network refers to a collection of hosts with the same network number. Therefore, several LANs connected by repeaters or bridges are still one network.
- Within an IP address, all networks assigned a network number are equal, no matter how large or small the range.
3.IP address and hardware address
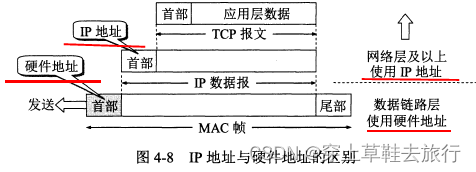
Hardware address (also known as physical address, MAC address) is the address used by the data link layer and physical layer. The source address and destination address used when transmitting MAC frames are hardware addresses and are placed in the header of the MAC frame.
The IP address is an address used by the network layer and the layers above and is a logical address. Placed in the header of the IP datagram.
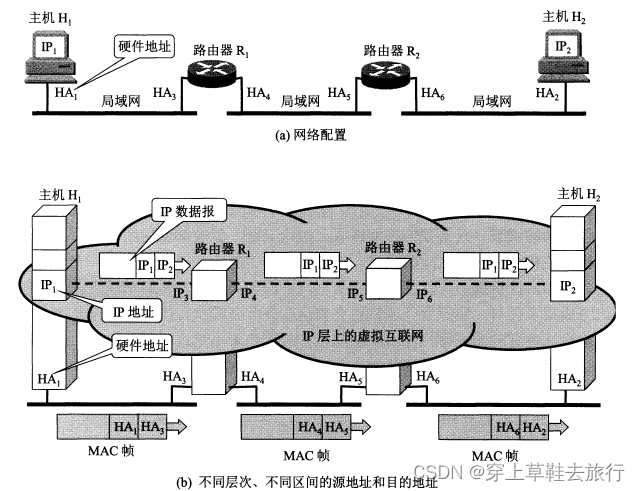
Below are three LANs connected together through two routers, and host H1 wants to communicate with host H2.
Because the router is connected to two LANs at the same time, it has two hardware addresses.
Notice:
- Only IP datagrams are visible on the Internet at the IP layer abstraction. Although the information has to be forwarded by routers R1 and R2, the source address and destination address in the IP header are always IP1 and IP2.
- Although the IP datagram header has a source address, the router only makes a selection based on the network number of the destination station's IP address.
- At the link layer of the LAN, only MAC frames are visible. When MAC frames are transmitted on different networks, the source address and destination address in the MAC frame header will change.
- The IP layer abstracts the Internet from the complex details of the underlying layers. As long as you are at the network layer, you can use unified, abstract IP addresses to study host-to-host communication.