- After the rapid development of the Internet decades, to February 2011, IPV4's 32-bit address has been exhausted, and therefore proposes IPV6
solutions through the use of:
- Subnetting
- Classless Addressing CIDR
- ANT method using network address translation (192.168.1.1 for the host of this is legal, but in the Internet WAN is not legitimate, it will be converted)
根本措施:Creating IPV6
A major change
- Larger address space: 32 -> 128
- Extended address hierarchy (???)
- Improved options: option control information in the payload can be placed
- Flexible header format, byte-aligned header to 8: IPv6 defines a number of optional extension header
- Plug and Play (initial use and when not to assign IP addresses, IPv6 does not need to be DHCP)
- Basic header to cancel a lot of IPv4 fields in the field in the figure below circled in red in IPv6 all canceled (some fields on the extension field).
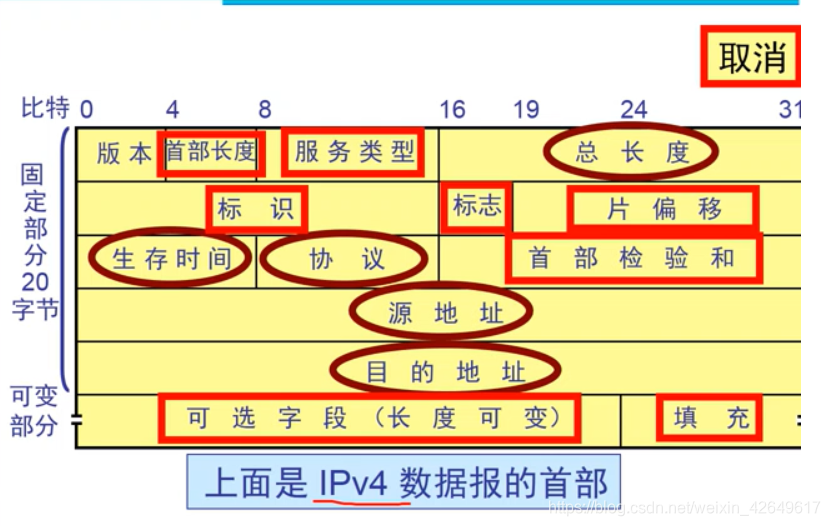
Second, the general form of IPv6 datagrams
基本首部有效载荷:All extension headers and payload or data together called the payload of the datagram. Data is part of TCP / UDP packets
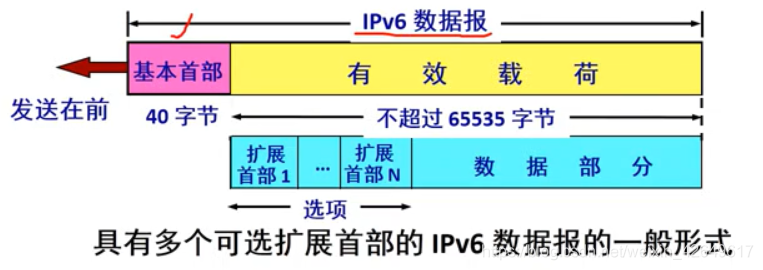
basic header:
- The header byte 40 becomes fixed, known as the basic header
- Abolition of unnecessary functions, reducing the number of field header to only eight. (Such as the abolition of inspection and functional header to speed up the processing speed of the router datagram)
- Allowing substantially behind the header and zero or more extension header.
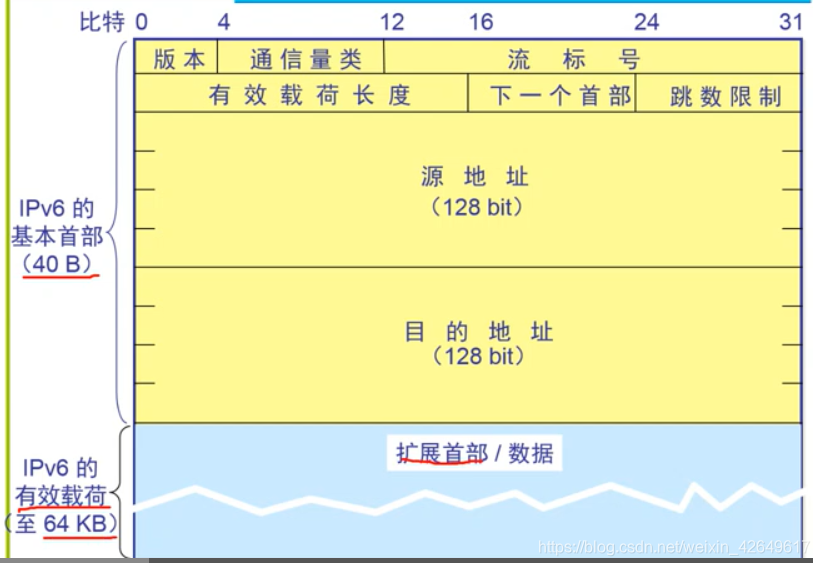
- It accounted for 16 payload 64kb. The basic header representing 40B, (2 320 bit is also is . 8 to 2 . 9 between. ???),
版本: Accounting for 4, 0-3. Value is 6通信量类:Accounting for 8, 4-11. For distinguishing between different classes or IPv6 packet priority.流标号:Accounting for 20, 12-31. "Stream" on the Internet from a particular source to a particular end point of a series of data packets. All packets belonging to the same class have the same flow label.有效载荷长度:16bit, 64KB maximum (in bytes B). It indicates the length of the payload.下一个首部:The next extension header (different values represent different functions of a header)
跳数限制:The equivalent of IPv4 TTL (Time) field
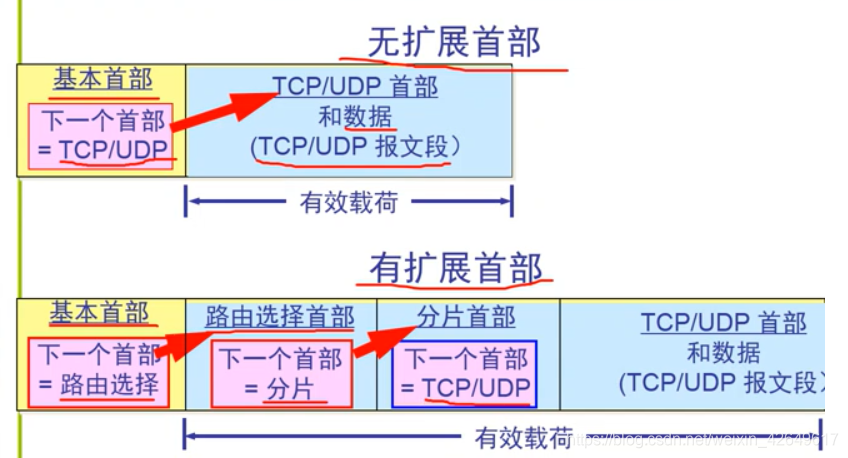
Extension headers
- IPv6 the original IPv4 header optional features are placed on the extension header, and the extension of the original and a destination host left both ends of the route header to process (since the extension header is not substantially header, a router handles only basic header,
除了逐跳选项this extension capital). This greatly improves the processing efficiency of the router

IPv6 address classification :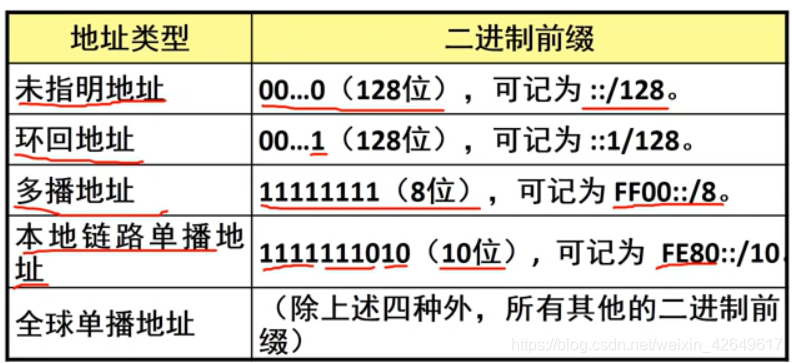 **
**
Three, IPv6 representation:
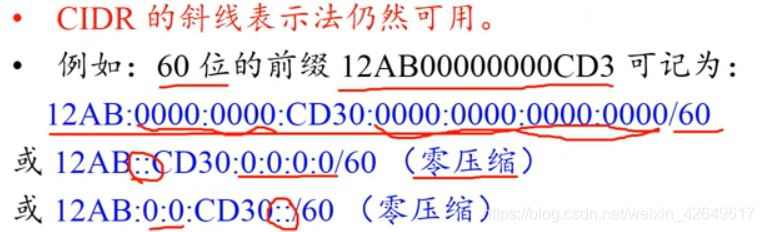
Colon hexadecimal notation
- Each 16 bit value represented in hexadecimal, colon split between values.
- Such as: 68E6: 8C64: FFFF: FFFF: 0: 1180: 960A: FFFF
- Allow zero compression, i.e., a string of consecutive zeros may be substituted with one pair of the colon (FF05: 0: 0: 0 : 0: 0: B3 can be written FF05 :: B3). In addition, not zero compression in the same address twice inside. Because if you can not know in the end the two compression compress several zero.
Suffix dotted decimal notation: - Common language IPv4 to IPv6
转换阶段. - For example: IPv4 to IPv6 127.10.2.1 can be converted into the 0: 0: 0: 0: 0: 0: 127.10.2.1.
IPv6 address classification
Global unicast address
- IPv6 is the most used global unicast address
- Partitioning method has the following forms:
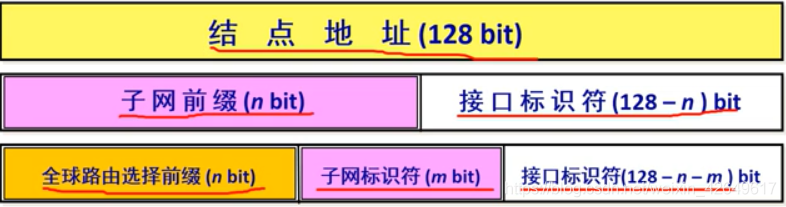
Five, IPv4 transition to IPv6
- Excessive only method of gradual evolution to IPv6, and IPv6 installation must also be compatible with IPv4, but also to accept and forward IPv4 packets.
- Two transition strategies :
使用双协议栈:- Part of the host (or router) is provided with two protocol stacks, one IPv4 a IPv6. Referred to as IPv6 / IPv4, indicating that it has both IP address: an IPv6 address and an IPv4 address. This host is also known as dual-protocol host.
- IPv6 dual protocol of the host and the IPv6 address on the use of communications, and data packets into IPv6 datagram header. IPv4 and IPv4 address to host communication, and uses substantially IPv4 header. (
一部分字段可能会丢失,比如流标号) - It may be determined using an IPv4 address type or IPv6 address according to the address returned by DNS
使用隧道技术:- When IPv6 datagram to enter the IPv4 network, the IPv6 packet
封装into an IPv4 datagram. (That is, become IPv6 IPv4 datagram data section)
- When IPv6 datagram to enter the IPv4 network, the IPv6 packet
