Article directory
The concept of the bus
A bus is a set of common information transfer lines that can be time- shared by multiple components .
shared
Sharing means that multiple devices share the same bus, that is, multiple components can be hung on the bus.
time-sharing
It means that only one component is allowed to send information to the bus at the same time. If there are multiple components that want to transmit information to the bus, they must come one by one, that is, time-sharing transmission.
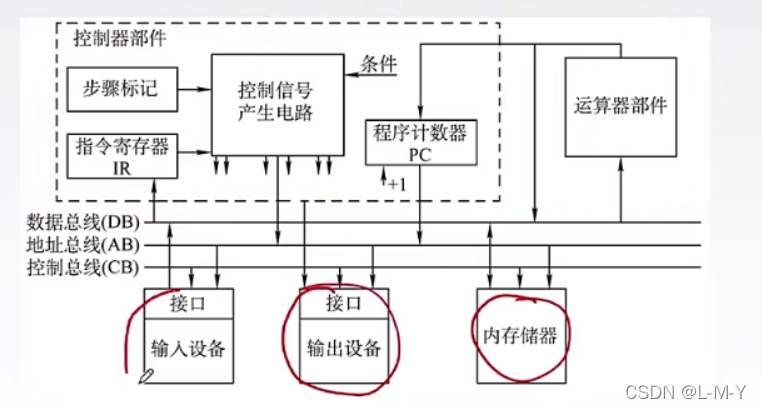
The emergence of the bus is to increase the flexibility of the connection between the external device and the host computer . Early computers used decentralized connections, which made it difficult to increase or decrease external devices at any time. Therefore, modern computers use bus connections instead.
Characteristics of the bus
- Mechanical characteristics: size, shape, number of pins, arrangement order
- Electrical characteristics: transmission direction and effective level range
- Functional characteristics: the function of each transmission line (address, data, control)
- Temporal characteristics: the timing relationship of signals
Classification of the bus
By data transmission format
-
The serial bus
can transmit one bit of data at a time (typical chestnut: USB), and only needs one transmission line. The cost is low, and it is widely used in long-distance transmission. When it is used in a computer, it can save wiring space. -
The parallel bus
can transmit multiple bits of data at a time
. The logic sequence is simple and the circuit is easy to realize, but there are many signal lines, the space is large, and there will be interference between parallel signal lines.
By bus function
on-chip bus
The bus inside the chip is the public connection line between the internal registers of the CPU chip and between the registers and the ALU.
system bus
The bus that interconnects the various functional components of a computer system.
- The data bus
is used to transmit data information between various functional components. It is a bidirectional transmission bus , and its number of bits is related to the machine word length and storage word length.
Machine word length : the number of bits that the CPU can process data at one time, usually related to the number of register bits of the CPU
Storage word length : the number of bits of binary code stored in a storage unit (storage address) in the memory, that is, the bit of the MDR in the memory number
-
The address bus
is used to point out the address of the main memory unit or I/O port where the source data on the data bus is located. It is a one-way transmission bus, and the number of bits of the address bus is related to the size of the main memory address space. -
The control bus
transmits control information, including control commands sent by the CPU and feedback signals returned from the main memory to the CPU.
communication bus
A bus for transferring information between computer systems or between a computer system and other systems.
Structure of the system bus
single bus structure
Hang the CPU, main memory, and I/O devices on a set of buses , allowing direct exchange of information between I/O devices, and between I/O devices and main memory without the intervention of intermediate devices.
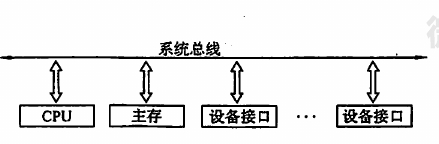
The structure is simple, the cost is low, and it is easy to connect new devices, but the bandwidth is low and the load is heavy. Multiple components can only compete for the only bus and do not support concurrent transmission operations.
dual bus structure
It is divided into two buses:
the main memory bus , which is used to transfer data between the CPU, main memory and channels, and
the I/O bus , which is used to transfer data between multiple external devices and channels
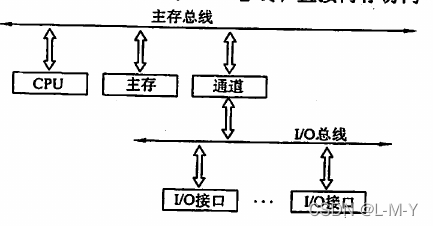
Separate the low-speed I/O device from the single bus to realize the separation of the memory bus and the I/O bus, but it is necessary to add hardware devices such as channels
Three bus structure
Main memory bus (CPU and memory transfer address, data, control information)
I/O bus (communication between CPU and various peripherals)
Direct memory access bus (DMA) (for direct transmission between memory and high-speed peripherals data)
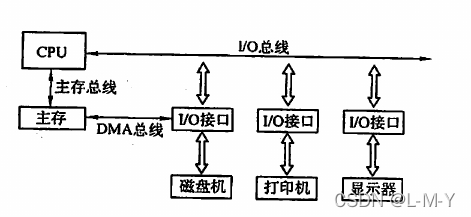
Improves the performance of I/O devices and improves system throughput, but the system work efficiency is relatively low
Performance indicators of the bus
1) Transmission cycle : the time required for a bus operation (application, addressing, transmission, end), referred to as the bus cycle.
2) Bus clock cycle : the clock cycle of the machine, the computer has a unified clock to control the various components of the entire computer.
3) Working frequency : the frequency of various operations, that is, how many times data is transmitted within 1 second
4) Bus width : the number of data bits that can be transmitted on the bus at the same time is equal to the number of the bus.
5) Bus bandwidth : the data transmission rate of the bus, that is, the number of bits that can transmit data on the bus per unit time, and the unit is byte/second.
Bus bandwidth = bus operating frequency (bus width/8) *
6) bus multiplexing
7) number of signal lines