Table of contents
Chapter 1 Getting Started GIS Theory and ArcGIS Pro Basics
Chapter 2 Basic ArcGIS Data Management and Transformation
Chapter 3 Data Editing and Query, Topology Check
Chapter 4 Mapping Map Symbols and Layout Design
Chapter 5 Spatial Analysis ArcGIS Vector Spatial Analysis and Application
Chapter 6 ArcGIS Grid Spatial Analysis and Application
Chapter 7 Image Remote Sensing Image Processing
Chapter 8 Three-Dimensional Part Three-Dimensional Analysis
Chapter 9 Advanced Spatial Statistical Analysis and Spatial Relationship Modeling Analysis
Chapter 10 GIS-based Geospatial Modeling
Chapter 11 Introduction to Python Scripting in ArcGIS Pro
GIS is the use of electronic computers and their external equipment to collect, store, analyze and describe the entire or part of the earth's surface and spatial information systems. Simply put, it combines geospatial information and some attribute information related to the geographic information in a certain region to achieve comprehensive management of geographic and attribute information. The research object of GIS is the whole geographic space, and geographic information is related to geographic location, so the development of GIS has been paid attention to worldwide. In recent years, GIS has also received much attention in our country, and has been used in urban and rural planning, disaster monitoring, resource inventory, land survey, environmental management, urban pipe network, combat command, macro decision-making, urban public services, transportation, navigation, e-government and other fields. been widely applied. So how to deeply understand the principles of GIS? How to efficiently process multi-source spatial data? How to establish practical GIS technology application solutions for specific fields? This course will provide a set of methods and cases based on ArcGIS Pro spatial data processing.
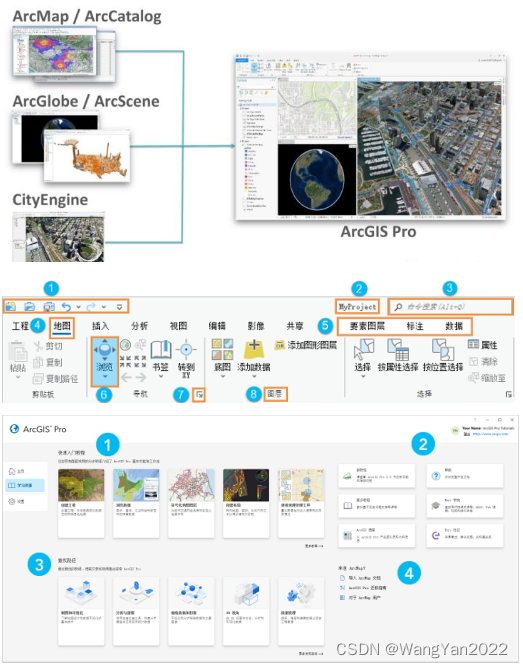
Compared with ArcGIS, ArcGIS Pro, as ESRI's GIS product for the new era, inherits the powerful data management, mapping, and spatial analysis capabilities of traditional desktop software (ArcMap) on the original ArcGIS platform, and also has its unique Some special functions, such as 2D and 3D fusion, big data, vector slice production and release, task workflow, super-forced map, space-time cube, etc. At the same time, it integrates ArcMap, ArcSence, and ArcGlobe to realize 3D integration and synchronization.
This tutorial will organize your GIS work into projects using ArcGIS Pro, which you can use to map 2D and 3D data. With ArcGIS Pro, you can create and edit a variety of features, while also integrating data from multiple sources such as text, vector, raster, lidar, multidimensional data into your project. This course will teach you to use ArcGIS Pro to analyze data, manage GIS data, and build tools for automating work or solving complex problems. You can use analysis and geoprocessing features in ArcGIS Pro to answer many spatial questions and perform spatial analysis. With spatial analysis tools such as vector data analysis, raster data analysis, 3D analysis, hydrological analysis, etc., you can solve complex location-oriented problems, explore and understand your data from a geographic perspective, identify relationships, detect and quantify patterns, evaluate trends, and make predictions and decisions. Python can be used to automate geoprocessing tools and provides the ability to create your own geoprocessing tools, either as script tools or as Python toolbox tools. This course will teach you to save time on repetitive tasks, minimize errors, and efficiently iterate on analyzes by creating models or scripts to transform into custom tools.
You will learn to use the above principles and technical methods in specific practical cases to improve the application ability and efficiency of GIS technology.
Chapter 1 Getting Started GIS Theory and ArcGIS Pro Basics
1. Introduction to basic principles of GIS and commonly used software
2. Installation and configuration of ArcGIS Pro
3. Introduction to new features of ArcGIS Pro 3.0
4. The main components of the ArcGIS Pro user interface (functional areas, views, and panes) and their interactions.
5. ArcGIS Pro project creation: including maps, scenes, layouts and other items
6. Browsing and viewing of spatial information
7. Query and output of spatial information
8. Document saving method
Chapter 2 Basic ArcGIS Data Management and Transformation
1. ArcGIS data management
2. Data type and conversion
3. Data structure and conversion
4. Data format and conversion 5.
ArcGIS and external data conversion
6. The theory, method and steps of geospatial data database construction
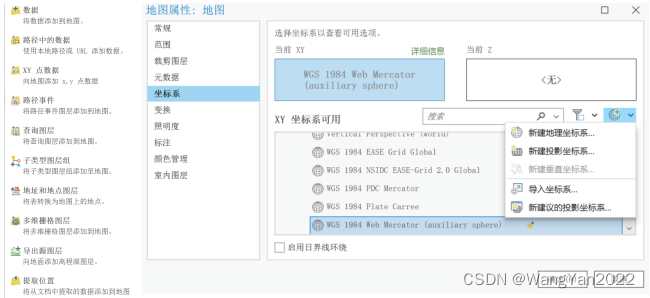
7. Map projection basis
8 .Common map projection and projection transformation operations in China
9. Transformation of Beijing54, Xian80, WGS84, CGCS2000 different geographic coordinate systems

Chapter 3 Data Editing and Query, Topology Check
1. Introduction to common data sources
2. Spatial data collection methods
3. Introduction to multiple georeferencing methods
4. Spatial data geometric collection
5. Spatial data attribute collection
6. Data inspection and topology processing
7. Data processing: data cutting, data splicing, data extraction

Chapter 4 Mapping Map Symbols and Layout Design
1. Introduction to GIS mapping
2. Symbol setting for spatial data display
3. Making professional map symbols
4. Labeling and annotation
5. Thematic map layout design and finishing
6. Thematic map drawing skills and map output
7. Research area map production

Chapter 5 Spatial Analysis ArcGIS Vector Spatial Analysis and Application
1. Introduction to ArcGIS Pro geoprocessing tools
Running tools in the "Geoprocessing" pane
Running tools in the model builder
Running tools in the Python window
2. GIS spatial analysis and functions
3. Vector processing tools and cases
4. Basic processing of vector data (stitching, cropping, fusion, etc.) and cases
5. Vector space overlay analysis and application
6. Proximity analysis and application


Chapter 6 ArcGIS Grid Spatial Analysis and Application
1. Introduction to spatial analysis of raster data
2. Geoprocessing environment settings; environment settings for applications, tools, models, and model processes
3. Basic processing of raster data (stitching, clipping, resampling, NoData processing, data conversion, etc.) and Case
4. Distance mapping
5. Density mapping
6. Raster interpolation
7. Statistical analysis
8. Reclassification
9. Raster calculation
10. Raster data model calculation and application

Chapter 7 Image Remote Sensing Image Processing
1. UAV data processing
Data loading Prick point Correction Accuracy evaluation Product generation
2. Mosaic dataset
Create mosaic dataset
Add raster to mosaic dataset
Remove black edges
Image uniform color
Synchronous mosaic Dataset
Mosaic dataset repair
NDVI calculation
3. Remote sensing image preprocessing and information extraction
Image viewing Image enhancement Band combination Orthorectification Image fusion Vegetation index extraction Using raster function chain
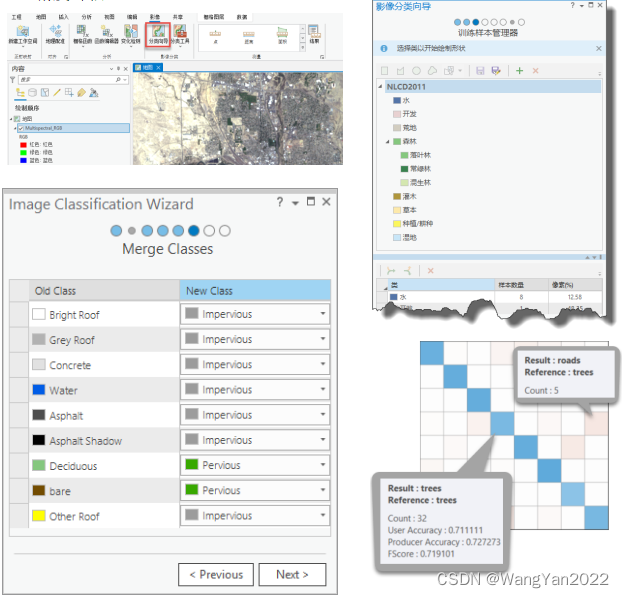
4. Remote sensing image classification
Create classification samples
Image segmentation
Training sample management
Select classifier
Output classification results
Merge classes
Reclassify
Accuracy evaluation
Chapter 8 Three-Dimensional Part Three-Dimensional Analysis
1. 3D production and animation demonstration
2. 3D data sources
2D and 3D data BIM data tilted photogrammetry data
3. 3D data analysis
DEM 3D production 3D format conversion 3D symbol design
Rapid creation of 3D models Polyhedron editing Visual analysis
4. Digital surface model and its application
Create grid surface
Basic analysis method based on grid DEM
Calculation of slope and aspect
Create curvature surface
Hydrological analysis
Visibility calculation
Hillshade calculation
5. Use of Lidar data
Create LAS dataset
Generate DEM, DSM
Extract trees
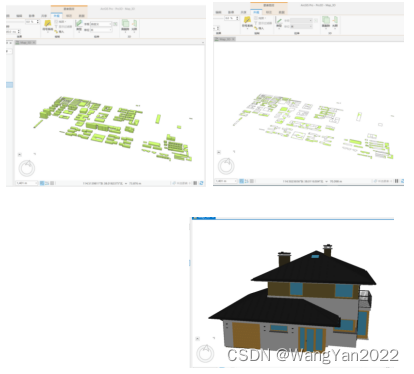
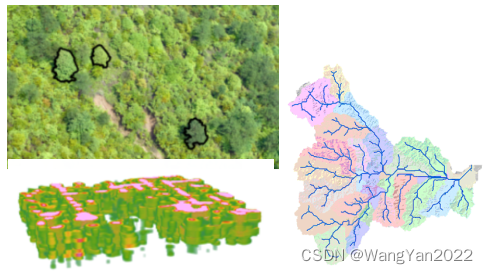
Chapter 9 Advanced Spatial Statistical Analysis and Spatial Relationship Modeling Analysis
1. Fishnet analysis
Method of setting spatial extent
Setting number of rows and columns
Rotation angle
Output feature class

2. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis "Analyze Mode" tool
Average Nearest Neighbor
High/Low Clustering: Getis-Ord General G statistic measures the degree of clustering of high or low values
Global Moran's I statistic measures spatial autocorrelation

Hot spot analysis
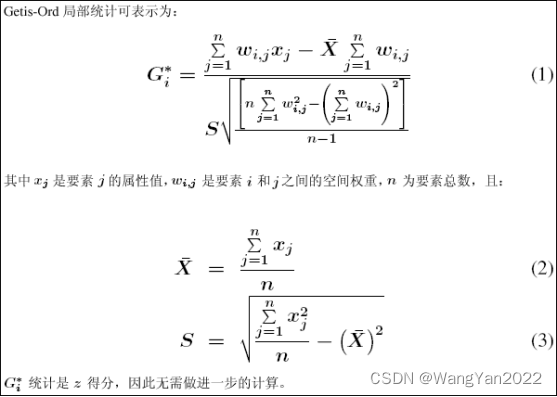

Optimized Hotspot Analysis
Initial Data Evaluation
Event Aggregation
Counting Events within Aggregate Surfaces Capture
Nearby Events to Create Weighted Points Test and spatial dependencies are automatically corrected. Output result: The output features will reflect the aggregated weighted features (fishnet polygon or hexagonal polygon cells or the aggregated polygons or weighted points provided for the Incident Point Aggregate Polygon parameter). Each feature has a z-score, p-value, and Gi Bin result, as well as the number of neighbors each feature included in the calculation.
3. Spatial relationship modeling
Ordinary least squares (OLS)

Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR)
Complete datasets using the Fill Missing Values tool
Three types of regression models: Continuous (Gaussian), Binary (Logistic) and Count (Poisson)
Select Neighborhood (Bandwidth)
Local weighting schemes
Forecasting
Raster of coefficients
Interpreting messages and diagnostics
Output graphs
Multi-scale geographically weighted regression (MGWR)

Chapter 10 GIS-based Geospatial Modeling
1. Geospatial modeling ideas
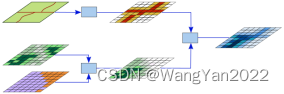
2. GIS-based geospatial modeling
Model connotation analysis
GIS-based model realization
Using Modelbuilder to construct calculation models
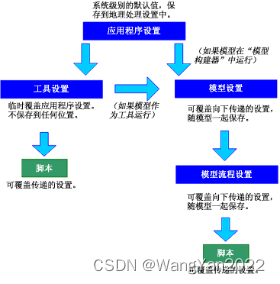
3. Modelbuilder modeling environment introduction
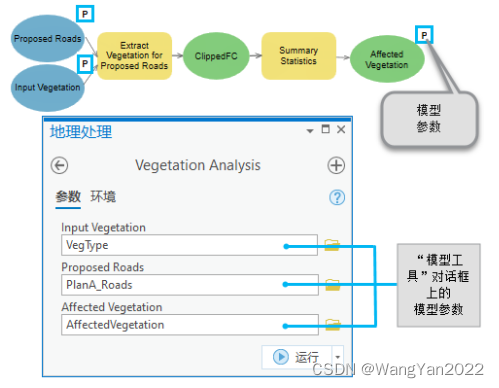
Build and save the model in Model Builder
Set model parameters
Set model tool properties
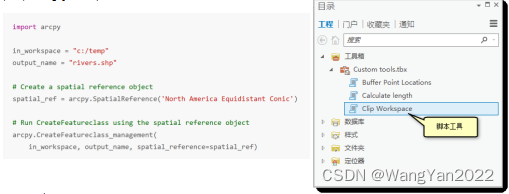
Document tools
4. NC data batch modeling training
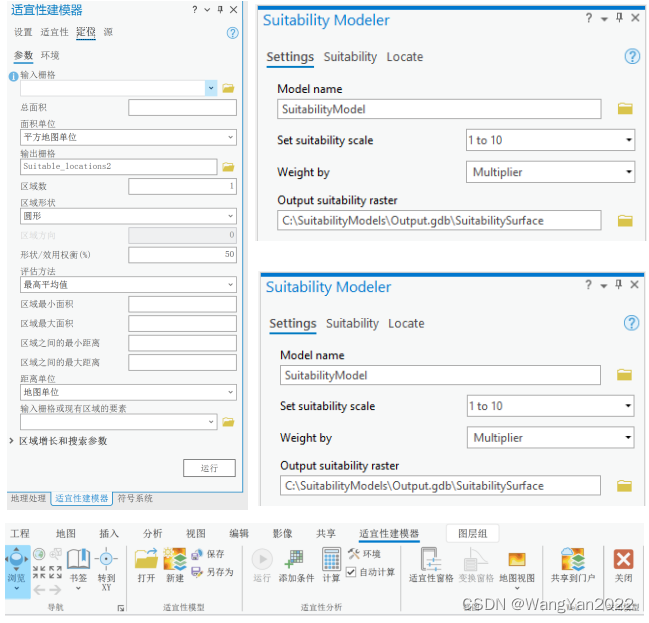
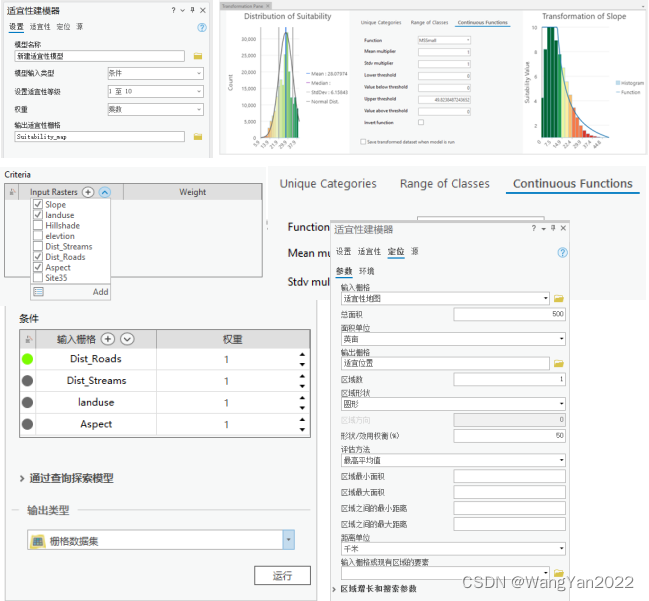
5. Implement suitability modeling workflow
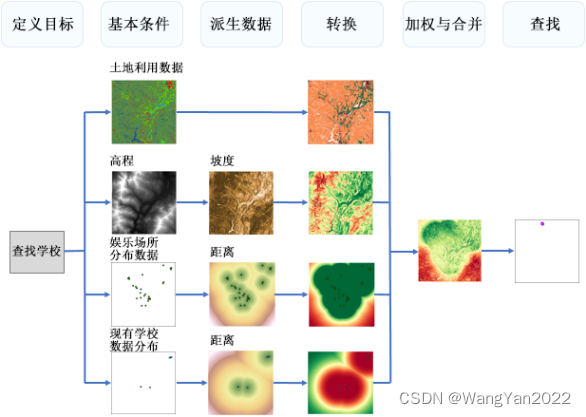
6. Create a suitability model
Identify and prepare condition data
Convert the value of each condition into a general suitability scale
Weight conditions relative to each other and combine them to create a suitability map
Find siting areas or protected areas
Share and run in server
Chapter 11 Introduction to Python Scripting in ArcGIS Pro
1.Python introduction and environment configuration and installation;
2.Python basics
3.ArcPy import and function introduction
Chart module (arcpy.charts)
Data access module (arcpy.da)
Geocoding module (arcpy.geocoding)
Image analysis Modules (arcpy.ia)
Cartography module (arcpy.mp)
Metadata module (arcpy.metadata)
Network Analyst module (arcpy.nax and arcpy.na)
Sharing module (arcpy.sharing)
Spatial Analyst module (arcpy .sa)
Workflow Manager (Classic) module (arcpy.wmx)
4. Access and manage spatial data
5. Feature geometry object manipulation
6. Raster data manipulation
7. Cartography
8. Tool creation in the Python toolbox
Special Application Analysis
Hydrological analysis

suitability evaluation
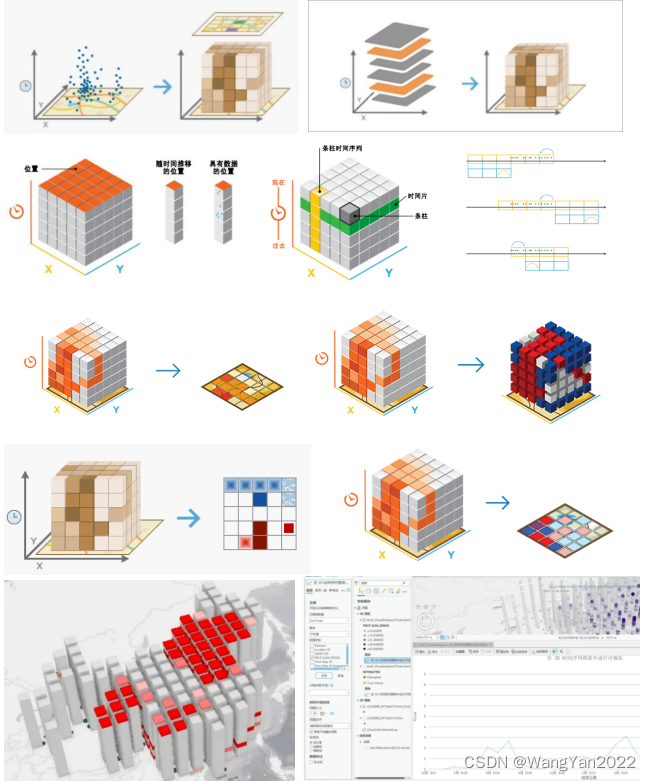
spatio-temporal analysis
more recommendations
R-Meta analysis and [bibliometric analysis, Bayesian, machine learning, etc.] multi-technology integration practice and advanced development_WangYan2022's blog-CSDN blog focuses on Meta analysis principles, formulas, operation steps and result analysis, and advanced applications Detailed analysis, combined with multiple examples, proficiency in the whole process of Meta analysis and uncertainty analysis, and combined with machine learning and other methods to explain the extended application of Meta analysis in literature big data. https://blog.csdn.net/WangYan2022/article/details/130924289?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502Based on the integration of ArcGIS Pro, R, INVEST and other technologies, the trade-off and collaborative dynamic analysis of ecosystem services_WangYan2022's Blog-CSDN Blog Systematically and comprehensively grasp the knowledge and technical content of spatial data processing, quantitatively explore the relationship between ecosystem service tradeoffs and synergies and social and ecological factors, and serve the coordinated and sustainable development of regional ecosystem protection and social economy.
https://blog.csdn.net/WangYan2022/article/details/130405562?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502 Constructing an ecological security pattern based on multi-technology integration ecosystem services such as ArcGIS Pro, Python, USLE, and INVEST models_WangYan2022's blog- The CSDN blog understands the use of geographic data, uses Python-related modules and libraries, and masters the spatial analysis and mapping skills of ArcGIS Pro; it teaches you from special topics: master the construction and calculation of the safety evaluation index system; master the use of catastrophic models in index integration function; master the methods of spatio-temporal process analysis and trend early warning of ecological security assessment. Based on the understanding of the trend and internal relationship of regional ecological changes, this course combines ecological problem diagnosis, ecological function demand assessment and landscape pattern planning to help ensure the functionality and service of the ecosystem.
https://blog.csdn.net/WangYan2022/article/details/130361525?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502 ★Follow the [Science Research and Charge Bar] public account to get massive tutorials and resources★