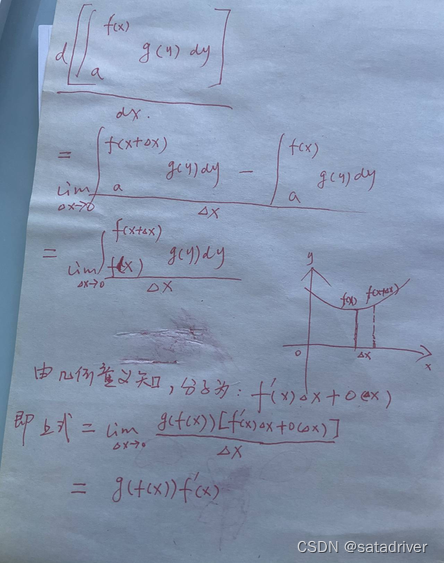
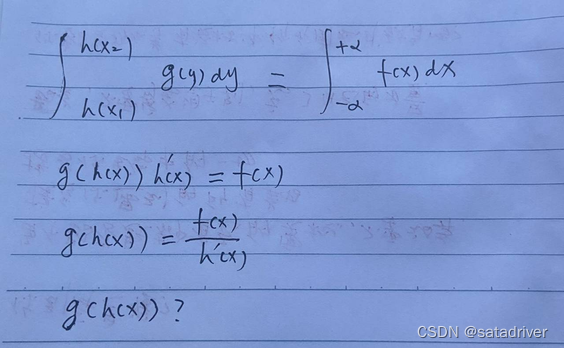Derivation book derivation of variable upper limit integral
The derivation process is based on the definition of the derivative and the geometric meaning of the integral, see the picture:
Derivation of Probability Density of Random Variables
If the random variable x obeys the probability density of f(x) in the interval (negative infinity, positive infinity), set y = g(x), x = h(y), and find the probability density of y.
Because the monotonicity of x = h(y) is unknown, there are two possibilities: monotonically increasing and monotonically decreasing, so its probability density also has two possibilities:

And the following approach cannot get the probability density about y: