Article directory
1 RF
RF, is the abbreviation of Radio Frequency,
Radio, n. radio; radio communication; v. use radio communication (or send messages)
Frequency, n. frequency
RF Chinese is usually translated as radio frequency .
For people without a professional background, it may be difficult to understand the meaning just by looking at these two words.
To explain it using the word splitting method,
"shoot" means emission and transmission, and this kind of signal is transmitted through the air or other media.
"Frequency" comes from frequency, which refers to the number of vibrations of a signal per unit time.
In radio frequency, frequency is an important parameter to measure the characteristics of radio waves.
therefore,The meaning of radio frequency is: the transmission of radio signals with a specific frequency range through the air or other media.
So radio frequency transmits radio wave signal. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves that can travel in free space, including air and vacuum. Radio frequency transmitters convert various data into radio wave signals, and then transmit these signals into the air through antennas. Receivers (such as mobile phones, radios, etc.) will receive these radio wave signals and decode them to restore the original data information.
2 RFID
ID is the abbreviation of identification, n. identification; identity;
our ID card is the identification card (ID card).
The combination of RFID refers to "the technology of identification through the frequency of radio waves". The full name is Radio frequency identification technology, which is translated into radio frequency identification in Chinese .
2.1 Application scenarios of RFID
It may not be easy to understand just explaining what RFID is, and it is quite abstract.
The common application scenarios of RFID are listed below:
- Transportation: For example, the electronic toll collection system (ETC) uses RFID technology to track vehicles and automatically deduct fees.
- Security checks: such as passports and employee certificates, RFID technology is used for rapid verification and identification.
- Retail industry: Used for product anti-theft, inventory management and self-checkout, improving store operation efficiency.
- Medical industry: management of patient identity information, drug tracking, medical device management, etc.
- Warehousing and logistics: Real-time tracking and management of goods through RFID tags, improving inventory accuracy and operational efficiency.
- Manufacturing: Real-time tracking of parts, tools and equipment in the production process to improve production efficiency.
- Animal management: RFID tags are implanted in animals for information management such as animal identification and vaccination.
- UAV: Use RFID technology for air cargo transportation to achieve unmanned delivery.
The current technology can make the RFID electronic tag to the millimeter level.
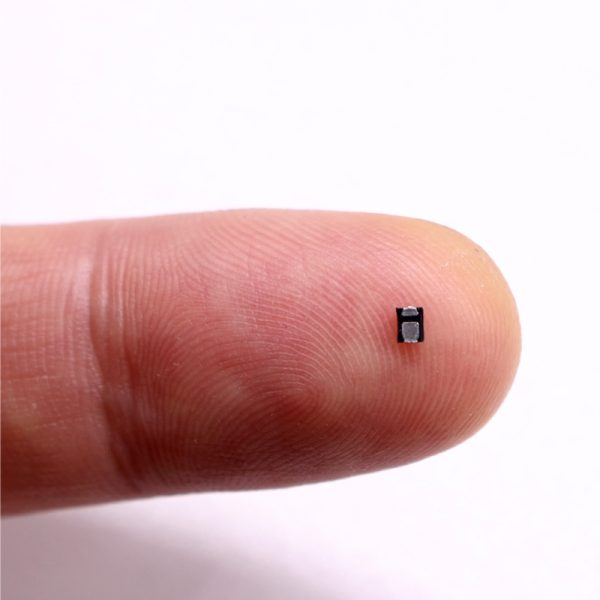
2.2 Working principle of RFID
Let me explain how RFID works.
The working principle of RFID is based on radio wave communication, which can also be known from the above RF introduction.
The whole system is mainly composed of RFID tags (also known as electronic tags) , RFID readers and antennas .
- RFID tag : Contains a microchip and antenna to store specific information (such as product identification, serial number, etc.). Electronic tags can be active (Active Tag, built-in battery provides energy, also known as active tags) or passive (Passive Tag, also known as passive electronic tags, obtain energy from readers).

- RFID reader : responsible for transmitting radio frequency signals and receiving responses from tags. Readers can read and write tag information.

- RFID antenna : connected to the RFID reader, responsible for sending signals to tags and receiving response signals from tags.

Take the operation of the bus card system as an example.
When you get on a bus, there is a card reader on the bus. The card reader is both a "transmitter" and a "receiver". The credit card machine on the bus is emitting radio waves all the time.
After disassembling the bus card, it is found that it has a coil and a chip inside (network diagram),

The card itself has no power. When the coil senses the electromagnetic wave, it gets energy and the circuit starts to work. The chip in the bus card reads the deduction information sent by the card reader, finds the balance in the card, and executes the deduction logic.