Table of contents
- Improving Usability, Efficiency, and Safety of UA V Path Planning through a Virtual Reality Interface
- AirSim simulators for drones, cars and more
- Design of multi-mode UAV human-computer interaction system
- Multi-Robot Interfaces and Operator Situational Awareness: Study of the Impact of Immersion and Prediction
- Hololens-based airport command and control
- Research on Virtual Reality Interaction of Unmanned Vehicle for Attitude Estimation at Any Position
- ABB AR control in hololens2 (digital twin control of robotic arm)
Improving Usability, Efficiency, and Safety of UA V Path Planning through a Virtual Reality Interface
| * | # |
|---|---|
| Link | https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/6392969. |
| Key words | VR , path planning , VR usability experiment |
Summary
As the capabilities and complexity of UA Vs continue to increase, the complexity required to specify instructions3D flight paths get more complex. Immersive interfaces such as those provided by virtual reality (VR) have several unique features that canImprove user perceptionandAbility to specify 3D information. These features include stereoscopic depth cues that induce a sense of physical space, and natural head pose and gesture interactions in six degrees of freedom (DoF).
This paper presents a method for virtual realityAn open source platform for 3D route planning, and compared it with existing UA V navigation interfaces. The final results show significant improvements in safety and efficiency compared to manual control interfaces. The immersive interface offers a viable alternative to touchscreen interfaces for UAV path planning.
introduce
Piloting UAVs (UA Vs) controlled with manual joysticks requiresHigh level of training and experienceto managecollision risk. These systems use automation to translate user-defined paths into low-level controls (i.e., roll, pitch, yaw, and thrust). However, 2D interfaces and 2D input schemes pose usability challenges when tasks require precise 3D perception and manipulation.
We envision that potential UAV applications that would benefit from the adoption of VR interfaces are those involving remote UAV path planning scenarios such asLarge-Scale 3D Modeling, Urban Surveillance, and Disaster Search and Rescue. These types of applications require the UA to cover a large area, making it difficult to monitor with line-of-sight manual control. We chose a VR interface instead of an Augmented Reality (AR) interface becauseLimited line-of-sight and potential with AR。
experiment
Design experiment: Observe human users completing a series of hoop navigation tasks (a series of hoop navigation tasks), and evaluate the performance of three interfaces.Efficiency, Safety and Availability- VR interface, 2D touch interface and hover-assisted manual controls.
12 participants, reporting on their experiences with VR and autonomous driving.
Mission: Pilot a UAV through a circular sequence without crashing.
Oral tutorial -> 3 minute familiarization phase -> three experiment runs until the UAV crashes or is successfully traversed -> end of experiment,7-point Likert scaleRatings consist of five statements assessing usability
Results and discussion
The VR interface saved more than a minute (48% of the total time) in planning time compared to the flat interface mirroring the consumer drone standard.
Both VR and 2D interfaces improve system safety over manual control methods. This suggests that the increased security is due toHierarchical Space Planning, combining the security control with the two abstract control schemesDecoupling of user path planning。
对比无人机,无人船没有上下这个DoF,还需要考虑分层空间规划吗?那将VR界面用于无人船的控制意义是什么?
We hypothesize that our VR interface enables faster, more robust, and more precise risk assessment and risk correction. It outperforms manual interfaces in terms of usability and safety, while significantly reducing path planning time compared to 2D touchscreen interfaces
AirSim simulators for drones, cars and more
https://microsoft.github.io/AirSim/
Design of multi-mode UAV human-computer interaction system
| * | # |
|---|---|
| Link | Design of multi-mode UAV human-computer interaction system. |
| Key words | Based on the system and functional modules, the UAV human-computer interaction system is designed |
introduce
The US "Blue Shark Laboratory" under the US Office of Naval Research (US ONR) combines display technologies (such as virtual and augmented reality technology, 3D visualization systems) and input devices (including mobile phones to tablets, head-mounted Systems, etc.), proposed "Enhanced Environment Communication and Collaboration (E2C2)" technology, and used it for UAV control [4], as shown in Figure 1. China is also actively exploring multi-mode UAV interactive control technology. The WJ-600 UAV operating system equipped with a VR helmet was exhibited at the 2016 Zhuhai Aircraft Exhibition, as shown in Figure 2.

Multi-Robot Interfaces and Operator Situational Awareness: Study of the Impact of Immersion and Prediction
| * | # |
|---|---|
| Link | Multi-Robot Interfaces and Operator Situational Awareness: Study of the Impact of Immersion and Prediction. |
| Key words | Definition of multi-robot control , situational awareness , workload |
Summary
too much workandlack of awarenessConsequences may range fromlow efficiencyranging from accidents. This work takes into account related issues such as multimodal interaction, immersive devices, predictive capabilities, and adaptive displays. Specifically, four interfaces are designed and developed: regular interface, predictive regular interface, virtual reality interface, and predictive virtual reality interface.24 operatorssupervised8 multibotsFire surveillance and fire fighting tasks. Load test and situational awareness test results show that VR improves situational awareness without increasing operator workload, while the effect of predictive components is insignificant and depends on their implementation.
introduce
In the scenario of multiple robots and a single operator, the most relevant problem ispeak workloadandlack of situational awareness。
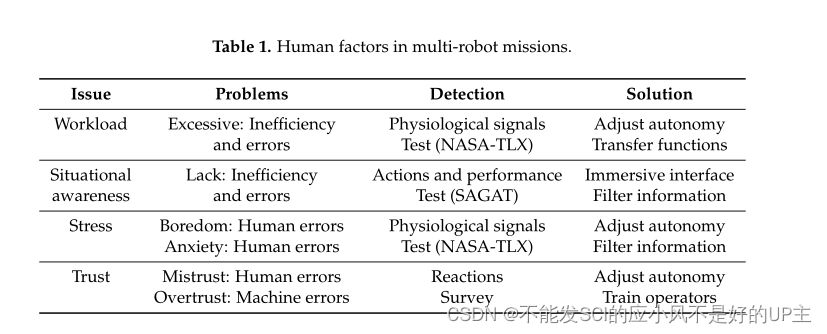
Workload can be defined as the sum of the operator's workload, working time and subjective experience [3]. However, workload studies usually consider multiple attributes == (input load, operator effort, and job performance) [4] and dimensions (physical and mental demands) ==.
Operators of multi-robot missions must sense information, understand the situation, make decisions and generate commands. In this case, excessive workload leads to increased latency, wrong decisions, and therefore, reduced task performance [6].
Hololens-based airport command and control
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t5L-jBLD04I

Research on Virtual Reality Interaction of Unmanned Vehicle for Attitude Estimation at Any Position
| * | # |
|---|---|
| Link | Research on virtual-real interaction of unmanned vehicle for arbitrary position and attitude estimation . |
| Key words | digital twin , unmanned boat , unity3d |
introduction
As an offshore mobile platform, the unmanned boatAffected by wind, waves, currents, etc., it will produce six degrees of freedom motion, including translation in 3 directions and rotation in 3 directions. For rotary motion at sea, the distances between different positions of the hull and the center of rotation are not equal,Rotational motion produces different linear velocities, while the hullThe resultant velocity at any point is the vector sum of the translational and rotational velocities, so the hull of the actual sea-going unmanned boatThe resultant velocity vectors at each point are not equal. Many operating scenarios of UAVs rely on observing the UAV itselfPose information of a local position, for example, the deployment and recovery of unmanned boats, the docking of multiple unmanned boats, the docking and departure of unmanned boats, the position and attitude compensation of boat-borne sensors (such as cameras, scanning sonar, obstacle avoidance sonar, bottom sonar, laser radar, etc. )wait. to this end,How to obtain the real-time pose status of any position on the hullIt has become one of the important challenges for the key technology of information perception in the intelligent development of unmanned boats.
The real-time position and attitude acquisition of any position of the hull usually requires the fusion processing of several inertial navigation sensor data. some oh
The research focuses on the data fusion of multiple physical sensors to calculate the real-time pose of the local position of the sensor. Although the accuracy is high, it cannot meet the real-time observation requirements of any number of measuring points. With the increase of unmanned boats, the expansion of the limited number of inertial navigation sensors significantly increases the complexity and investment cost of the sensing system.