1. The basic concept of the bus
Bus concept: It is an information transmission line connecting various components and a transmission medium shared by each component;
1.1 Why do you need a bus
The bus structure facilitates the addition and removal of peripherals, while reducing the number of information transmission lines.
A bus is a common transmission line for signals,
1.2 Transmission of information on the bus
Serial------------
Parallel: Multiple data lines are transmitted at the same time. Since the lines are parallel to each other, if the transmission distance is relatively long, interference will occur and the transmission signal will be deformed.
1.3 Bus structure
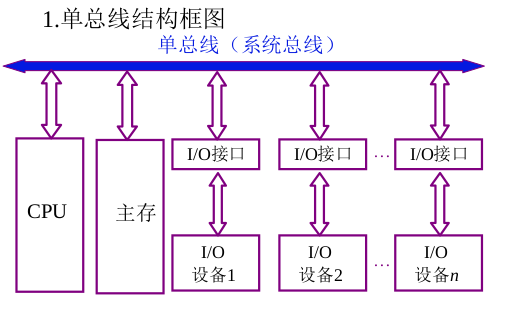
Single-bus structure
The bus is a common transmission line for signals, and only one pair of components can use this bus at any one time.
If data transmission is performed between an I/O device and the main storage through the I/O interface,
Then this bus cannot be used between the main memory and the CPU for data transmission;
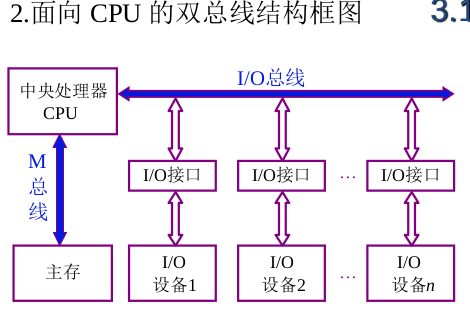
CPU-oriented dual-bus architecture
The central processing unit is the core,
Both instructions and data come from the main memory, and the information exchange between the CPU and the main memory is very busy.
Disadvantages:
- The device exchange between the external device and the main memory requires the central processing unit as the medium for information transmission;
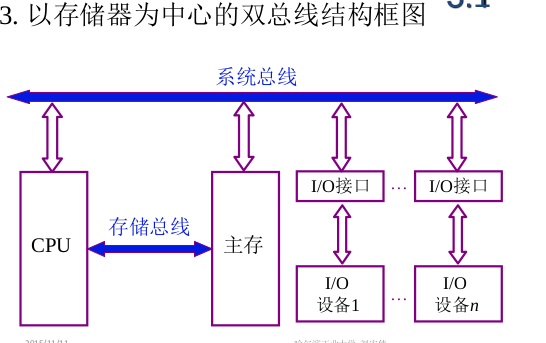
Dual-bus structure with memory as the core
2. Classification of buses
On-chip bus The bus inside the chip
The system bus is the information transmission line between the various components of the computer
Data bus: Bidirectional is related to machine word length and storage word length
Address bus: unidirectional related to memory addresses, I/O addresses
Control bus: output, memory read, memory write;
bus enable, interrupt request;
There are: interrupt request, bus request;
Communication bus
is used for communication between computer systems or between computer systems and other systems, such as control instruments, mobile communications, etc.;
transfer method:
- traverse the communication bus;
- Parallel communication bus;
3. Bus performance and performance indicators
3.1 Physical implementation of the bus
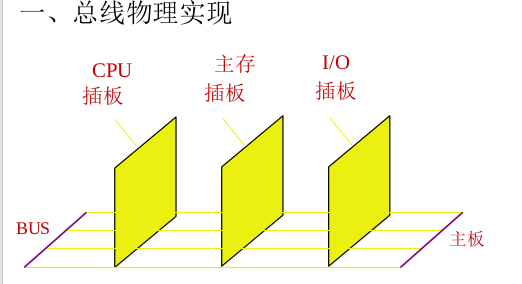
3.2 Bus characteristics
-
Mechanical characteristics:
size, shape, number of pins, and arrangement order; -
Electrical characteristics
Transmission direction and effective level range -
Functional characteristics
Each transmission first functional signal,
address signal, data signal, control signal, status feedback signal;
- time characteristics
Signal Timing Relationship
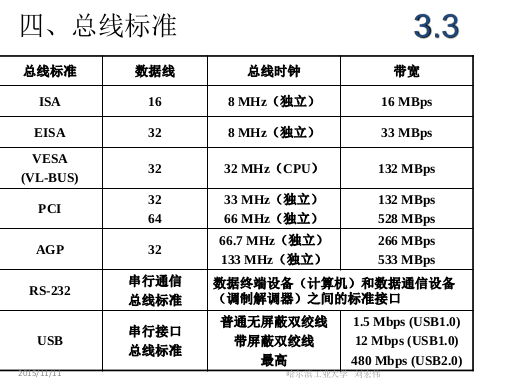
3.3 Performance indicators of the bus
-
Bus width: the number of data lines
-
Standard Transfer Rate: The maximum number of bytes transferred per second (MBps)
-
Clock synchronous, asynchronous: synchronous, and not synchronous
-
Bus multiplexing address line and data line multiplexing
-
Number of signal lines: sum of address lines, data lines and control lines
-
Bus control mode: burst, automatic, arbitration, logic, counting
-
Other indicators load capacity
3.4 Bus Standards
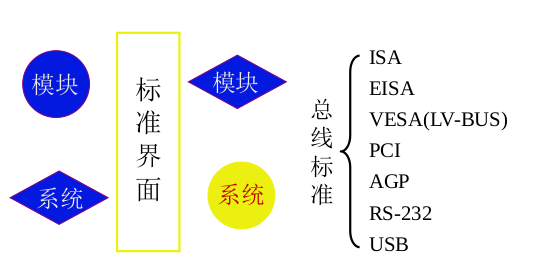
When different manufacturers produce different computer components,
for example
- Some manufacturers are responsible for the production of CPU,
- Different manufacturers are responsible for memory;
In order to enable the components produced by different manufacturers to coordinate and operate in the end, each manufacturer needs to abide by the same agreement when producing equipment;