Source: Beast Finance Author: Beast Finance

Company Profile
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSM) is a semiconductor company established in Taiwan in 1987, and took the lead in implementing the "commercial fab" foundry model in the world. The company provides wafer foundry services to semiconductor producers who outsource some or all of their production. TSMC's products have been applied to various industries, such as high-performance computing (HPC), smartphones and automotive electronics.
TSMC dominated the global semiconductor foundry industry between Q1 2019 and Q4 2022, with revenues growing at the 3-10nm node, (52% of its total revenue in 2022) The share of the circular foundry market is 58.5%.
According to the "Global Semiconductor Equipment: Market, Market Share, and Market Forecast" research report, TSMC is a clear leader in terms of revenue from the 3-10nm technology node compared to competitors such as Samsung, as shown in the figure,
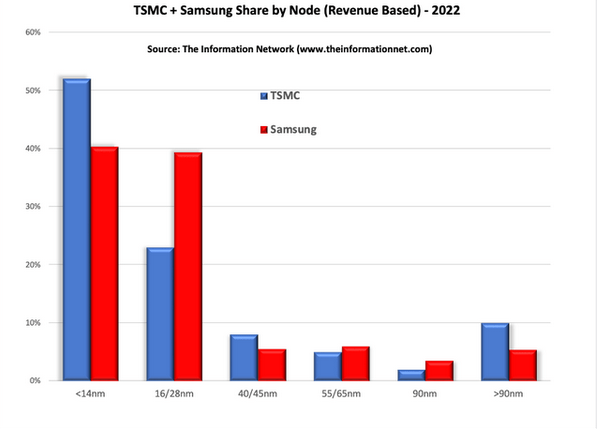
Compared with other foundries such as United Microelectronics (UMC), GlobalFoundries (GFS), SMIC, etc., TSMC also occupies a dominant position in the small node market.
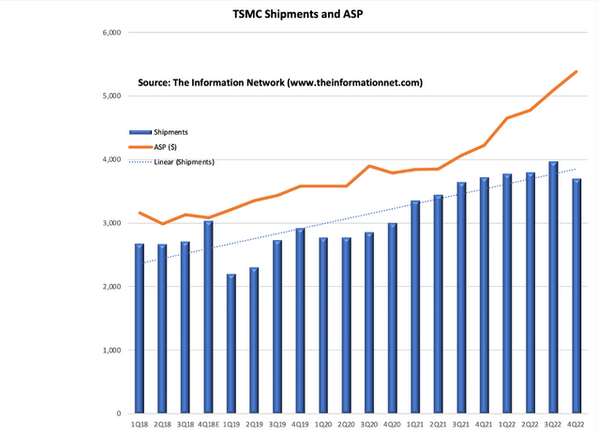
TSMC's shipments have also been growing strongly from the first quarter of 2018 to the fourth quarter of 2022 (the blue part in the figure). TSMC’s shipments fell slightly in the fourth quarter of 2022 due to a slowdown in the PC and smartphone industries. However, as the market demand for small-node chips continues to grow, especially 3nm chips, TSMC's ASP (average selling price) also increased in the fourth quarter of 2023.
In fiscal year 2021, TSMC accounts for 26% of the global semiconductor output value. As more companies turn to fabless factories, Boldbeast Finance believes that this proportion may increase in the future. In fiscal year 2021, TSMC produced 12,302 different semiconductor products for 535 customers. As demand increased, TSMC's margins also expanded, with operating margins rising 140 basis points to 52%, with plans to grow another 100 basis points in fiscal 2023.
Semiconductor foundry manufacturing is an industry with very high barriers to entry, requiring significant capital expenditures, connections, and technology. Even the well-funded and experienced Intel (INTC) is struggling below 7nm. As the market demand will double, TSMC will also participate in this growth trend with a dominant position.
TSMC has been called the most important company in the world and the linchpin of the global economy. Its financial situation is currently very good, and it is also very competitive in terms of competition. Beast Finance believes that TSMC is not only a great company, but also a great investment.
In this article, Boldbeast Finance will analyze TSMC’s fundamentals (including key indicators of TSMC’s stock, positive factors driving TSMC’s stock price rise, and unfavorable factors affecting TSMC’s stock price), financial performance, market analysis of the global semiconductor industry, market demand, future Conduct a comprehensive and in-depth analysis of TSMC in terms of forecast and risk.
Key Indicators for TSMC Stock
In the past five years, TSMC's stock price has more than doubled, and its total shareholder return has increased by nearly 138%. During that period, the S&P 500 returned just 50%.
The company's shares are part of a larger trend in which the semiconductor industry is outperforming global markets. Over the past five years, the MSCI World Semiconductor and Semiconductor Equipment Index has delivered a net annual return of 16.22%, compared with the MSCI World Index's net annual return of 6.88%. In fact, even on 10- and 20-year time horizons, the semiconductor industry has outperformed the broader market. In the 14 years since the financial crisis, the semiconductor industry has outperformed the overall market in nine of those years.
Positive Factors Driving TSMC's Stock Rise
1. The global demand for 3nm chips is strong.
Boldbeast Finance predicts that TSMC’s 3nm chips will start production in 2023 and will occupy 24% of the market below 7nm, while the market share of 7nm will drop to 28%. The market share of 5nm will drop to 48%. The main customers of TSMC's 3nm chips are Apple's (APPL) A17 (smartphone) and M3 (computer) processors. Moreover, TSMC's first-generation 3nm chips will mainly supply Apple. The second generation will use an improved process, resulting in faster production times, higher yields, higher performance, and lower power consumption. 3nm chips should start production in the second half of 2023.
2. The chip bill and new fabs
TSMC continues to expand production capacity by building fabs. The U.S. Chip Act will also provide $50 billion in subsidies to chip companies such as TSMC to pay for the construction costs of factories producing chips in the United States.
(1) TSMC is currently building a fab in Arizona, USA, and will use 4nm and 3nm processes to produce chips, and plans to start mass production in 2024 and 2026.
(2) TSMC has also built two fabs in Japan, using the company's 12nm, 16nm and 22nm processes and 28nm expertise, and is expected to start commercial production in 2024, and build a 5nm and 10nm fab in 2025. fab.
(3) TSMC has also built a fab in Dresden, Germany, and plans to start production in 2025.
3. Chat GTP and generative AI
The popularity of the generative artificial intelligence chatbot ChatGPT has been rising for some time. According to the co-founder of ChatGPT, Sam Altman, on Twitter on February 5th, within five days of ChatGPT’s release, there were more than 1 million chatbots. The user is registered.
The key catalyst for TSMC’s rise: ChatGPT runs on Nvidia’s (NVDA) A100 and H100 processors, which are manufactured on TSMC’s 7nm and 4nm processes.
Although ChatGPT is the leader in the generative artificial intelligence market, and its chip suppliers Nvidia and SK Hynix are the biggest beneficiaries, the development of some other companies in the field of artificial chatbots is also an opportunity for TSMC, because several other Companies are developing their own AI chatbot services. These include:
(1) In February 2023, Google begins rolling out an AI chatbot service called "Bard," based on its LaMDA AI initiative.
(2) Baidu also launched an artificial intelligence chat robot similar to ChatGPT, called "Wen Xin Yi Yan".
(3) Microsoft says it will "soon" integrate ChatGPT access through its Azure cloud.
(4) South Korean search engine company Naver also announced in February 2023 that it will launch an artificial intelligence chatbot service called "SearchGPT" in the first half of 2023.
(5) Russian search engine company Yandex also announced in February 2023 that they will launch a Russian-language artificial intelligence chatbot service called "YaLM 2.0" by the end of 2023.
At present, these companies have their own hardware suppliers, including Google's TPU, AMD's Instinct GPU, AWS's Graviton 4 chip; and artificial intelligence chips from startups such as Cerebras, Sambanova and Graphcore.
But so far, these new chips have rarely captured market share. Only Google is the exception though (whose TPUs are gaining traction in steady proliferation). However, in addition to this, the chips used by all the above companies are produced by TSMC, as shown in the figure.

Headwinds Affecting TSMC's Share Price
1. TSMC’s fabs in the United States are expensive
TSMC stated in a letter to the U.S. Department of Commerce in November 2022 that TSMC’s current difficulties include a shortage of skilled workers, high costs, and its No. Sudden construction problems at a factory, etc.
In the fourth quarter 2022 financial report meeting, TSMC Chief Financial Officer Wendell Huang said:
【"The main reason for the high cost is the construction cost of building facilities. The construction cost of the US fab may be four to five of that of the Taiwan fab. times. The high cost of construction includes labor costs, license costs, occupational safety and health regulations costs, inflation costs in recent years, and personnel and learning costs. Therefore, the initial cost of the US fab is higher than our fabs in Taiwan Round factory."]
2. Customer inventory backlog
Over the past year, Intel, Texas Instruments, Qualcomm, Nvidia, and AMD have all increased their inventory days as demand for chips weakened.
This compares to GlobalFoundries' inventory days of 83 days, TSMC's 81 days, and UMC's 65 days. But it must be remembered that wafer foundries produce chips for customers, so they are able to adjust production time according to customer contracts. On the other hand, these chip customers depend on the needs of downstream customers.
One risk factor for gains in chip stocks is that the semiconductor industry still has to adjust its pent-up inventory. Capex overruns, largely by memory companies, have led to a glut of chips, exacerbated by a disconnect in fiscal and monetary policy, with customers spending less on capital.
World-class financial performance
Although TSMC does not break down its revenue, in its latest financial report, we can still understand the revenue of TSMC's different businesses.
TSMC's net income has increased from 1,031.47 billion yuan in 2018 to 2,263.89 billion yuan in 2020, with a five-year compound annual growth rate of 17.03%. To get an idea of how good TSMC's financial performance is, we can refer to a research report published by Credit Suisse, which tells us that only 6% of companies have achieved similar growth rates over a 5-year period. TSMC's growth rate has exceeded 91.5% companies, the average five-year compound annual growth rate has reached 6.9%.
TSMC's revenue is so large that it dwarfs competitors such as Samsung, UMC, GLOBALFOUNDRIES, SMIC, TowerJazz, VIS, Hua Hong Semiconductor and DB HiTek.

TSMC's huge revenue also earns it more than half of the foundry's total revenue and gives it enough capital to expand its scale.

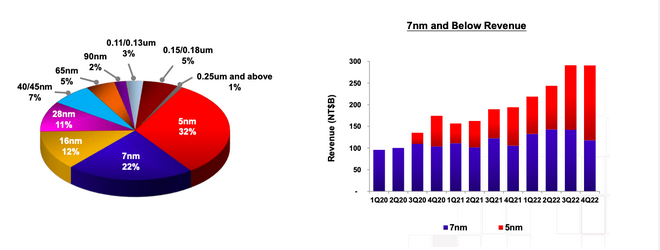
TSMC’s largest revenue source is 5nm chips, which accounted for 32% of its revenue in the fourth quarter of 2022, followed by 7nm chips at 22%, 16nm chips at 12%, and 28nm chips. Chips accounted for 11% of its total revenue. 5nm technology is becoming more important over time and will become TSMC's biggest revenue generator as its applications become more widespread.
In terms of segmented business, high-performance computing is the most important business of TSMC, accounting for 42% of revenue, followed by smartphone business, accounting for 38% of revenue.

Robert Novy-Marx's research shows that a company becomes attractive when its gross margin is 0.33 or higher, and TSMC's gross margin has risen to 0.27 from 0.23 in 2018.
TSMC's operating profit has also increased from 383.74 billion yuan in 2018 to 1,121.27 billion yuan in 2022, and the five-year compound annual growth rate of operating profit is 23.92%. Operating margin increased from 37.2% in 2018 to 49.53% in 2022. Globally, the average operating profit margin of semiconductor stocks is usually 8.1%, and the median operating profit margin is 8.5%. Currently, TSMC's operating profit margin ranks among the top five among semiconductor stocks. In the first quarter of 2023, management expects operating margins to be in the range of 41.5% to 43.5%.
TSMC's net income has also risen from 363 million yuan in 2018 to more than 1 billion yuan in 2022, with a five-year compound annual growth rate of 22.87%. Globally, only 8.8% of companies can achieve similar growth rates over a 5-year period.
TSMC's free cash flow has also increased from 3,039.4 billion yuan in 2018 to 527.93 billion yuan in 2022, and the five-year free cash flow compound annual growth rate is 15.16%. Return on invested capital has also risen from 32.9% in 2018 to 36.1% in 2022. Likewise, ROE has risen from 22% in 2018 to 39.8% in 2022.
Market structure of the global semiconductor industry
At present, the scale of the global semiconductor foundry market is growing rapidly. In fiscal year 2022, the global semiconductor market will grow by 8.2% to $573 billion, of which wafer foundries will increase by 27% to $77.8 billion. Fiscal 2023 is likely to decline by about 3-5% along with TSMC's revenue.
However, over the next ten years, a CAGR of 12.2% is projected to grow the market size to $1.38 trillion by 2030. For reference, even with conservative estimates, market demand for semiconductors has grown only in 10 years out of 50 years.
Semiconductor devices contain many complex components, each of which plays an important computational role. This drives up the capital cost of manufacturing as the required size of wafers shrinks. Wafers beyond 7nm are used in industrial applications such as automotive or machinery. Sub-7nm is used in more specialized industrial equipment and consumer electronics.
The days of companies designing in-house and then manufacturing end-to-end in their own foundries are becoming a thing of the past. In traditional computing, the number of transistors on a chip doubles every two years (known as Moore's Law), but this rate has begun to slow as the technology and money required to make chips with all but a few options has become unbearable. Although the market size of the overall semiconductor industry is expected to grow enormously over the next decade, it is unlikely that any new players will enter the stage.
For example, around 2005, the complexity of precision manufacturing and design almost brought AMD down. As the advantages of concentrated investment become more and more obvious, companies begin to turn to fabless foundry production. Because huge capital expenditures require high utilization rates to justify the investment. TSMC expects this effect to be more pronounced at the 5nm level. Even with the continued weakness in the supply chain during the 2019 pandemic, customer demand for chips below 7nm has been strong. At the same time, the input costs and capital expenditures required for 5nm chip design and manufacturing continue to increase.
Demand for cutting-edge chips remains strong.
Often analysts tend to abandon old technologies too quickly, forgetting that the road to new technologies can be long, but in the meantime, old technologies can still generate revenue and find new ones. Applications.
With the widespread adoption of microprocessors, the demand for chips has grown. When it comes to chips, most devices aren't made up of purely cutting-edge chips, a large percentage of those chips are laggard chips. For example, if you look at the chip shortage in the automotive space, it's mostly due to a shortage of laggard chips.
Most chipmakers for 90nm and above processes are located in China. Margins on these chips are razor-thin and simply don't justify the massive investment given that building a new fab at 90nm and beyond would be a loss-making exercise in the current economy. That's why TSMC, Intel and Samsung are building new fabs to produce cutting-edge chips.
TSMC's legacy fabs have become more important to the U.S. and its allies as global demand for cutting-edge chips has grown stronger. Cutting-edge chips underpin the global economy. Cutting-edge chips are also the future, but there is still a long way to go.
Future forecast
In fiscal year 2022, TSMC's revenue has shifted to chips below 7nm. This trend is being driven by the massive increase in demand for high-performance computing and smartphones. High-performance computing is projected to grow at an annual rate of 59 percent, and smartphones at 28 percent. These demand trends are expected to weaken over five years, especially as inventories normalize.
For chips over 7nm, Boldbeast Finance predicts that TSMC’s IoT and automotive business will continue to lead the market demand. Automotive demand will increase by 74% per year, and IoT demand will increase by 47% per year. Competition is also fierce beyond 7nm, as these are mainly used in non-specialized industrial applications and automotive. In addition, in the market beyond 7nm, the start-up cost is also very low.
Beast Finance expects TSMC's capital expenditure in fiscal year 2023 to be the same as fiscal year 2022. TSMC has invested $40 billion in two new fabs in Arizona, which are expected to start production in fiscal 2024. It is also investing $60 billion in new fabs in Taiwan and $20 billion in Japan. We also expect TSMC's capex to increase significantly over the next few years as TSMC continues to expand its lead as the fab of choice for major global companies for sub-7nm chips and attempts to distance itself from Chinese fabs .
In fiscal year 2022, TSMC's R&D expenses accounted for 7.2% of net income. By fiscal year 2023, TSMC expects R&D expenses to increase by 20%. In addition, TSMC is targeting the release of 3nm chips, which will lead to another increase in its capital expenditures.
TSMC generated $17.4 billion in free cash flow in fiscal 2022, double that in fiscal 2021. Due to the normalization of the semiconductor market, Beast Finance expects TSMC's revenue and EPS to decline slightly in FY2023. However, as TSMC expands its products and manufacturing base, we expect a steady recovery and return to long-term growth. Even at this level of spending, TSMC's yield is expected to be 2.0%.
Risks
Although TSMC is a leader in the global semiconductor industry, there are still some investment risks.
First, demand for semiconductors can fluctuate wildly depending on the health of the overall macro environment. Fluctuations in demand could affect TSMC's stock price, as TSMC's revenue and profitability are closely tied to the global market's demand for semiconductors. A drop in demand for semiconductors would also pose a significant risk to TSMC's financial performance.
Second, the semiconductor industry is very competitive: TSMC's competitors include companies with huge resources, such as Samsung and Intel, and the technologies of these companies are developing rapidly. If TSMC cannot keep up with the pace of innovation in the semiconductor industry, it may lose a lot market share.
in conclusion
After decades of development, TSMC has become the most important company in the world. The barriers to entry in this industry are also very high, and the lead over competitors is widening. TSMC's position will only grow stronger as demand for leading and lagging chips rises. TSMC's financial performance and valuation are also very attractive. Beast Finance believes that TSMC is a rare high-quality company in investors' portfolios, and it is a great company and a great investment.