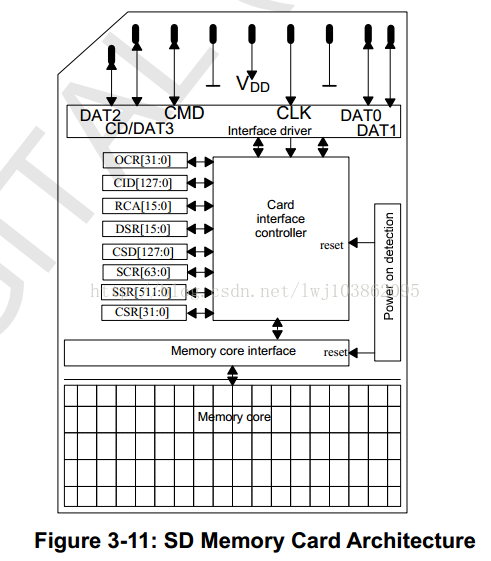
1. SD card internal structure
Before getting familiar with SD/MMC related registers, let's take a look at the internal architecture of the SD card, as shown in the following figure:
2. Introduction of SD/MMC related registers
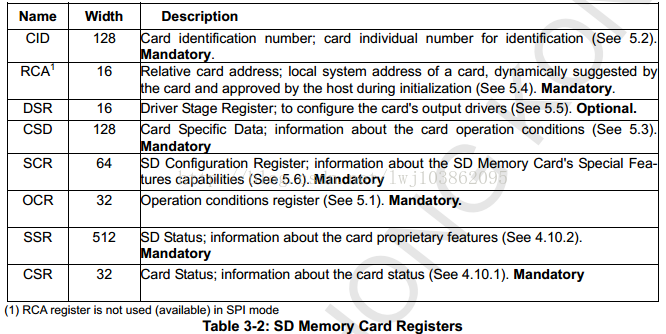
Summarized from the above figure: There are 7 registers inside the SD card.
1. The OCR, CID, CSD and SCR registers save the configuration information of the card;
2. The RCA register saves the address temporarily allocated by the card during the communication process (only suitable for SD mode);
3. The CSR register card status (Card Status) and the SSR register SD status (SD Status) registers save the card status (for example, whether the writing is successful, whether the CRC check of the communication is correct, etc.), the contents of these two registers are related to the communication mode (SD mode or SPI mode) dependent.
Fourth, the MMC card does not have SCR and SSR registers.
The following is a detailed explanation of the more important registers among the 7 registers, which are the 5 registers of CID, CSD, SCR, OCR, and RCA.
2.1. Card Identification Register(CID)
This CID register is 16 bytes long, as shown in the table below, it contains the unique identification code (ID number) of the card. These messages are programmed (burned) during the production of the card and their contents cannot be modified by the host controller. Note: The CID register of SD card and the CID register of MMC card are different in record structure.
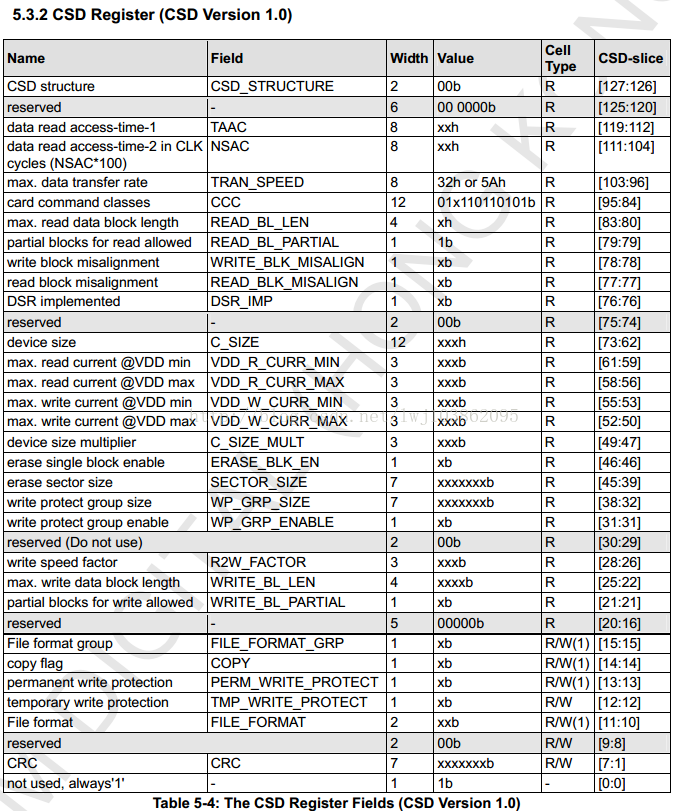
2.2.Card Specific Data Register(CSD)
The Description Data Register (CSD) is 128 bytes long, as shown in the table below, and contains the necessary configuration information for accessing the card's data. The "cell type" column defines whether the area of the CSD is read-only (R), programmable once (R/W) or erasable (R/W/E) ["R/W" means that it can be erased and written multiple times , "R/W(1)" means write-once only, not erasable]. The values shown in this table all correspond to the respective regions and codes in the real CSD structure. The style of the CSD area follows the style of the column mark (and a check mark √). Note that the CSD register in the SD card and the CSD register in the MultiMedia card have different structures.
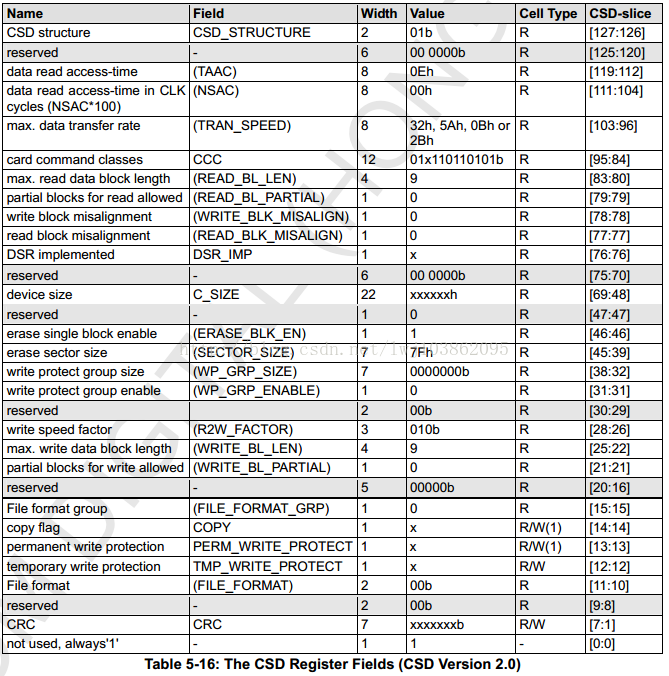
In the SD3.0 protocol, CSD is divided into version 1.0 and version 2.0. Version 1.0 corresponds to standard-capacity SD cards, and version 2.0 corresponds to high-capacity and ultra-high-capacity SD cards.
The CSD Version 2.0 is as follows:
2.3.SD card Configuration Register (SCR)
In addition to the CSD register, there is another configuration register named: SD Card Configuration Register (SCR). SCR provides some special features of SD card in this card. Its size is 64 bits. The content of this register is set by the manufacturer in the factory, MMC cards do not have SCR.
SCR_STRUCTURE The version number of the SCR structure in the physical level description on the SD card.
SD_SPEC describes the specification version supported by this SD card at the physical level.
DATA_STAT_AFTER_ERASE defines the state of the data after erasing. is either "0" or "1" (depending on the card provider).
SD_SECURITY describes the security algorithms supported by this card. 0: None 1: Security Protocol 1.0 Security Specification Version 0.96 2: Security Protocol 2.0 Security Specification Version 1.0 - 1.01. other reservations
SD_BUS_WIDTHS describes all data bus widths supported by the card. Any SD card will have at least two bits 0 and 2 set (ie SD_BUS_WIDTH = 0101) since SD cards support at least 1-bit or 4-bit wide bus modes, 1.4 bits are reserved.
2.4.Operating Conditions Register (OCR)
This 32-bit operating condition register stores the VDD voltage profile of the card. Any standard SD card host controller can use a 2V to 3.6V operating voltage for the SD card to perform this voltage recognition operation (CMD1). Array operations that access memory require a 2.7V to 3.6V operating voltage anyway. The OCR register shows the voltage range required to access the card's data. Structure description of the OCR register:
2.5.RCA register
This 16-bit card address register holds the device address issued by the card during the card identification process. This address is used by the host to communicate with the card after card identification. This register is only valid in SD bus mode.