文章目录
〇、前言
这两周开始跟着【MOOC-浙江大学-陈越、何钦铭-数据结构】进行数据结构与算法的学习,特此记录复习一下,虽然记不住,但是一直记一直记一直记,成为复读机就好了。

一、线性表
线性表(Linear List):由同类型数据元素构成有序序列的线性结构
- 表中元素个数称为 线性表的长度
- 线性表没有元素时,称为 空表
- 表起始位置称 表头,表结束位置称 表尾
1、List MakeEmpty():初始化一个空线性表L;
2、ElementType FindKth( int K, List L ):根据位序K,返回相应元素 ;
3、int Find( ElementType X, List L ):在线性表L中查找X的第一次出现位置;
4、void Insert( ElementType X, int i, List L):在位序i前插入一个新元素X;
5、void Delete( int i, List L ):删除指定位序i的元素;
6、int Length( List L ):返回线性表L的长度n。
1、线性表的顺序存储实现
利用数组的连续存储空间顺序存放线性表的各元素。
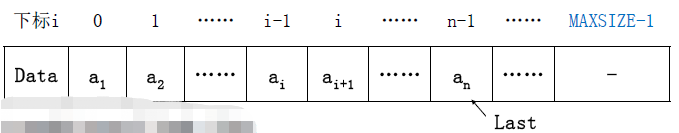
typedef int Position;
typedef struct LNode *List;
struct LNode {
ElementType Data[MAXSIZE];
Position Last;
};
/* 初始化 */
List MakeEmpty()
{
List L;
L = (List)malloc(sizeof(struct LNode));
L->Last = -1;
return L;
}
/* 查找 */
#define ERROR -1
Position Find( List L, ElementType X )
{
Position i = 0;
while( i <= L->Last && L->Data[i]!= X )
i++;
if ( i > L->Last ) return ERROR; /* 如果没找到,返回错误信息 */
else return i; /* 找到后返回的是存储位置 */
}
/* 插入 */
/*注意:在插入位置参数P上与课程视频有所不同,
课程视频中i是序列位序(从1开始),这里P是存储下标位置(从0开始),两者差1*/
bool Insert( List L, ElementType X, Position P )
{ /* 在L的指定位置P前插入一个新元素X */
Position i;
if ( L->Last == MAXSIZE-1) {
/* 表空间已满,不能插入 */
printf("表满");
return false;
}
if ( P<0 || P>L->Last+1 ) { /* 检查插入位置的合法性 */
printf("位置不合法");
return false;
}
for( i=L->Last; i>=P; i-- )
L->Data[i+1] = L->Data[i]; /* 将位置P及以后的元素顺序向后移动 */
L->Data[P] = X; /* 新元素插入 */
L->Last++; /* Last仍指向最后元素 */
return true;
}
/* 删除 */
/*注意:在删除位置参数P上与课程视频有所不同,
课程视频中i是序列位序(从1开始),这里P是存储下标位置(从0开始),两者差1*/
bool Delete( List L, Position P )
{ /* 从L中删除指定位置P的元素 */
Position i;
if( P<0 || P>L->Last ) { /* 检查空表及删除位置的合法性 */
printf("位置%d不存在元素", P );
return false;
}
for( i=P+1; i<=L->Last; i++ )
L->Data[i-1] = L->Data[i]; /* 将位置P+1及以后的元素顺序向前移动 */
L->Last--; /* Last仍指向最后元素 */
return true;
}
2、线性表的链式存储实现
不要求逻辑上相邻的两个元素物理上也相邻;通过“链”建立起数据元素之间的逻辑关系。

typedef struct LNode *PtrToLNode;
struct LNode {
ElementType Data;
PtrToLNode Next;
};
typedef PtrToLNode Position;
typedef PtrToLNode List;
/* 查找 */
#define ERROR NULL
Position Find( List L, ElementType X )
{
Position p = L; /* p指向L的第1个结点 */
while ( p && p->Data!=X )
p = p->Next;
/* 下列语句可以用 return p; 替换 */
if ( p )
return p;
else
return ERROR;
}
/* 带头结点的插入 */
/*注意:在插入位置参数P上与课程视频有所不同,
课程视频中i是序列位序(从1开始),这里P是链表结点指针,在P之前插入新结点 */
bool Insert( List L, ElementType X, Position P )
{ /* 这里默认L有头结点 */
Position tmp, pre;
/* 查找P的前一个结点 */
for ( pre=L; pre&&pre->Next!=P; pre=pre->Next ) ;
if ( pre==NULL ) { /* P所指的结点不在L中 */
printf("插入位置参数错误\n");
return false;
}
else { /* 找到了P的前一个结点pre */
/* 在P前插入新结点 */
tmp = (Position)malloc(sizeof(struct LNode)); /* 申请、填装结点 */
tmp->Data = X;
tmp->Next = P;
pre->Next = tmp;
return true;
}
}
/* 带头结点的删除 */
/*注意:在删除位置参数P上与课程视频有所不同,
课程视频中i是序列位序(从1开始),这里P是拟删除结点指针 */
bool Delete( List L, Position P )
{ /* 这里默认L有头结点 */
Position tmp, pre;
/* 查找P的前一个结点 */
for ( pre=L; pre&&pre->Next!=P; pre=pre->Next ) ;
if ( pre==NULL || P==NULL) { /* P所指的结点不在L中 */
printf("删除位置参数错误\n");
return false;
}
else { /* 找到了P的前一个结点pre */
/* 将P位置的结点删除 */
pre->Next = P->Next;
free(P);
return true;
}
}
二、堆栈
后入先出:Last In First Out(LIFO)
1、Stack CreateStack( int MaxSize ): 生成空堆栈,其最大长度为MaxSize;
2、int IsFull( Stack S, int MaxSize ):判断堆栈S是否已满;
3、void Push( Stack S, ElementType item ):将元素item压入堆栈;
4、int IsEmpty ( Stack S ):判断堆栈S是否为空;
5、ElementType Pop( Stack S ):删除并返回栈顶元素;
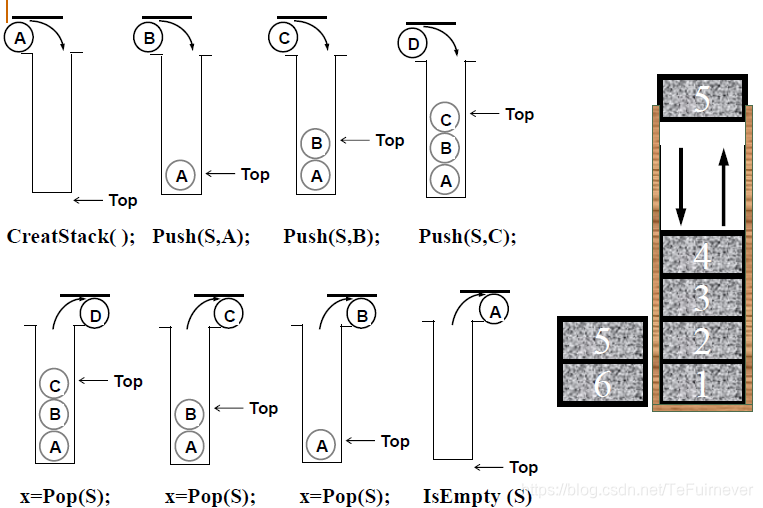
1、堆栈的定义与操作,顺序存储实现
typedef int Position;
struct SNode {
ElementType *Data; /* 存储元素的数组 */
Position Top; /* 栈顶指针 */
int MaxSize; /* 堆栈最大容量 */
};
typedef struct SNode *Stack;
Stack CreateStack( int MaxSize )
{
Stack S = (Stack)malloc(sizeof(struct SNode));
S->Data = (ElementType *)malloc(MaxSize * sizeof(ElementType));
S->Top = -1;
S->MaxSize = MaxSize;
return S;
}
bool IsFull( Stack S )
{
return (S->Top == S->MaxSize-1);
}
bool Push( Stack S, ElementType X )
{
if ( IsFull(S) ) {
printf("堆栈满");
return false;
}
else {
S->Data[++(S->Top)] = X;
return true;
}
}
bool IsEmpty( Stack S )
{
return (S->Top == -1);
}
ElementType Pop( Stack S )
{
if ( IsEmpty(S) ) {
printf("堆栈空");
return ERROR; /* ERROR是ElementType的特殊值,标志错误 */
}
else
return ( S->Data[(S->Top)--] );
}
2、堆栈的定义与操作,链式存储实现
typedef struct SNode *PtrToSNode;
struct SNode {
ElementType Data;
PtrToSNode Next;
};
typedef PtrToSNode Stack;
Stack CreateStack( )
{ /* 构建一个堆栈的头结点,返回该结点指针 */
Stack S;
S = (Stack)malloc(sizeof(struct SNode));
S->Next = NULL;
return S;
}
bool IsEmpty ( Stack S )
{ /* 判断堆栈S是否为空,若是返回true;否则返回false */
return ( S->Next == NULL );
}
bool Push( Stack S, ElementType X )
{ /* 将元素X压入堆栈S */
PtrToSNode TmpCell;
TmpCell = (PtrToSNode)malloc(sizeof(struct SNode));
TmpCell->Data = X;
TmpCell->Next = S->Next;
S->Next = TmpCell;
return true;
}
ElementType Pop( Stack S )
{ /* 删除并返回堆栈S的栈顶元素 */
PtrToSNode FirstCell;
ElementType TopElem;
if( IsEmpty(S) ) {
printf("堆栈空");
return ERROR;
}
else {
FirstCell = S->Next;
TopElem = FirstCell->Data;
S->Next = FirstCell->Next;
free(FirstCell);
return TopElem;
}
}
三、队列
先来先服务,先进先出:FIFO
1、Queue CreatQueue( int MaxSize ):生成长度为MaxSize的空队列;
2、int IsFullQ( Queue Q, int MaxSize ):判断队列Q是否已满;
3、void AddQ( Queue Q, ElementType item ): 将数据元素item插入队列Q中;
4、int IsEmptyQ( Queue Q ): 判断队列Q是否为空;
5、ElementType DeleteQ( Queue Q ):将队头数据元素从队列中删除并返回。
1、队列的定义与操作,顺序存储实现
typedef int Position;
struct QNode {
ElementType *Data; /* 存储元素的数组 */
Position Front, Rear; /* 队列的头、尾指针 */
int MaxSize; /* 队列最大容量 */
};
typedef struct QNode *Queue;
Queue CreateQueue( int MaxSize )
{
Queue Q = (Queue)malloc(sizeof(struct QNode));
Q->Data = (ElementType *)malloc(MaxSize * sizeof(ElementType));
Q->Front = Q->Rear = 0;
Q->MaxSize = MaxSize;
return Q;
}
bool IsFull( Queue Q )
{
return ((Q->Rear+1)%Q->MaxSize == Q->Front);
}
bool AddQ( Queue Q, ElementType X )
{
if ( IsFull(Q) ) {
printf("队列满");
return false;
}
else {
Q->Rear = (Q->Rear+1)%Q->MaxSize;
Q->Data[Q->Rear] = X;
return true;
}
}
bool IsEmpty( Queue Q )
{
return (Q->Front == Q->Rear);
}
ElementType DeleteQ( Queue Q )
{
if ( IsEmpty(Q) ) {
printf("队列空");
return ERROR;
}
else {
Q->Front =(Q->Front+1)%Q->MaxSize;
return Q->Data[Q->Front];
}
}
2、队列的定义与操作,链式存储实现
typedef struct Node *PtrToNode;
struct Node { /* 队列中的结点 */
ElementType Data;
PtrToNode Next;
};
typedef PtrToNode Position;
struct QNode {
Position Front, Rear; /* 队列的头、尾指针 */
int MaxSize; /* 队列最大容量 */
};
typedef struct QNode *Queue;
bool IsEmpty( Queue Q )
{
return ( Q->Front == NULL);
}
ElementType DeleteQ( Queue Q )
{
Position FrontCell;
ElementType FrontElem;
if ( IsEmpty(Q) ) {
printf("队列空");
return ERROR;
}
else {
FrontCell = Q->Front;
if ( Q->Front == Q->Rear ) /* 若队列只有一个元素 */
Q->Front = Q->Rear = NULL; /* 删除后队列置为空 */
else
Q->Front = Q->Front->Next;
FrontElem = FrontCell->Data;
free( FrontCell ); /* 释放被删除结点空间 */
return FrontElem;
}
}
四、一元多项式的 加法与乘法运算

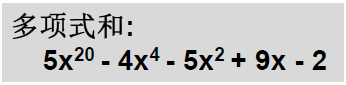
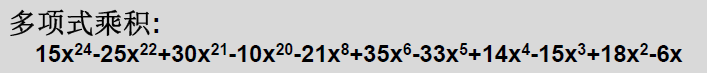
题意理解:

实现在后面的第二题!
五、课后题

1、02-线性结构1 两个有序链表序列的合并 (15分)

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int ElementType;
typedef struct Node *PtrToNode;
struct Node {
ElementType Data;
PtrToNode Next;
};
typedef PtrToNode List;
List Read(); /* 细节在此不表 */
void Print( List L ); /* 细节在此不表;空链表将输出NULL */
List Merge( List L1, List L2 );
int main()
{
List L1, L2, L;
L1 = Read();
L2 = Read();
L = Merge(L1, L2);
Print(L);
Print(L1);
Print(L2);
return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
输入样例:
3
1 3 5
5
2 4 6 8 10
输出样例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 8 10
NULL
NULL
List Merge( List L1, List L2 ){
List L,p1,p2,p3;
L=(List)malloc(sizeof(PtrToNode));
p1=L1->Next;
p2=L2->Next;
p3=L;
while(p1&&p2){
if(p1->Data<p2->Data){
p3->Next=p1;
p3=p3->Next;
p1=p1->Next;
}
else{
p3->Next=p2;
p3=p3->Next;
p2=p2->Next;
}
}
if(p1==NULL){
p3->Next=p2;
}
else if(p2==NULL){
p3->Next=p1;
}
L1->Next=NULL;
L2->Next=NULL;
return L;
}
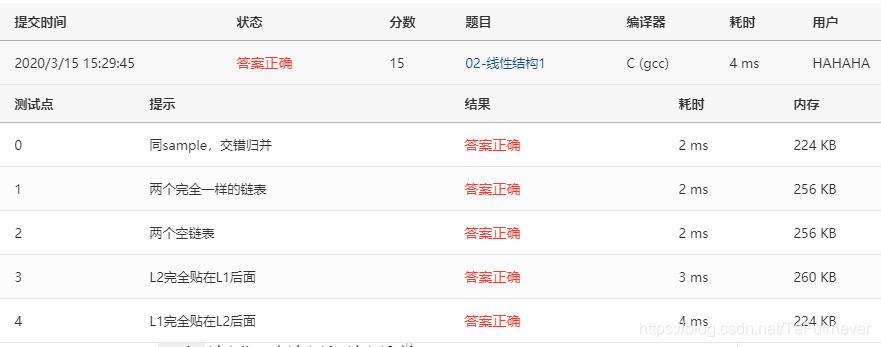
2、02-线性结构2 一元多项式的乘法与加法运算 (20分)
对应上面的求解。
输入样例:
4 3 4 -5 2 6 1 -2 0
3 5 20 -7 4 3 1
输出样例:
15 24 -25 22 30 21 -10 20 -21 8 35 6 -33 5 14 4 -15 3 18 2 -6 1
5 20 -4 4 -5 2 9 1 -2 0
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct PolyNode *Polynomial;
struct PolyNode{
int coef;
int expon;
Polynomial link;
};
void Attach(int c,int e,Polynomial *pRear){
Polynomial P;
P=(Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
P->coef=c;
P->expon=e;
P->link=NULL;
(*pRear)->link=P;
*pRear=P;
}
Polynomial ReadPoly(){
Polynomial P,Rear,t;
int c,e,N;
scanf("%d",&N);
P=(Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
P->link=NULL;
Rear=P;
while(N--){
scanf("%d %d",&c,&e);
Attach(c,e,&Rear);
}
t=P; P=P->link; free(t);
return P;
}
Polynomial Mult(Polynomial P1, Polynomial P2){
Polynomial t1,t2,P,Rear,t;
int e,c;
if(!P1||!P2) return NULL;
t1 = P1; t2 = P2;
P = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
P->link = NULL;
Rear=P;
while(t2){
Attach(t1->coef*t2->coef,t1->expon+t2->expon,&Rear);
t2 = t2->link;
}
t1 = t1->link;
while(t1){
Rear = P;
t2 = P2;
while(t2){
c = t1->coef*t2->coef;
e = t1->expon+t2->expon;
while(Rear->link&&Rear->link->expon>e)
Rear=Rear->link;
if(Rear->link &&Rear->link->expon==e){
if(Rear->link->coef+c)
Rear->link->coef+=c;
else{
t = Rear->link;
Rear->link = t->link;
free(t);
}
}
else{
t = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
t->coef = c;
t->expon=e;
t->link = Rear->link;
Rear->link =t;
Rear = Rear->link;
}
t2 = t2->link;
}
t1 = t1->link;
}
t = P; P = P->link; free(t);
return P;
}
Polynomial Add(Polynomial P1, Polynomial P2){
Polynomial t1,t2,P,Rear,t;
int e,c;
if(!P1&&!P2) return NULL;
t1 = P1;
t2 = P2;
P=(Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
Rear = P;
while(t1&&t2){
if(t1->expon==t2->expon){
if(t1->coef!=-(t2->coef))
Attach(t1->coef+t2->coef, t1->expon, &Rear);
t1 = t1->link;
t2 = t2->link;
}
else if(t1->expon>t2->expon){
Attach(t1->coef, t1->expon, &Rear);
t1 = t1->link;
}
else {
Attach(t2->coef, t2->expon, &Rear);
t2 = t2->link;
}
}
Rear->link = t1 ? t1 : t2;
t = P; P = P->link; free(t);
return P;
}
void PrintPoly(Polynomial P){
int flag=0;
if(!P){
printf("0 0\n");
return;
}
while(P){
if(!flag)
flag=1;
else
printf(" ");
printf("%d %d",P->coef,P->expon);
P=P->link;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main(){
Polynomial P1,P2,PP,PS;
P1=ReadPoly();
P2=ReadPoly();
PP=Mult(P1,P2);
PrintPoly(PP);
PS=Add(P1,P2);
PrintPoly(PS);
return 0;
}
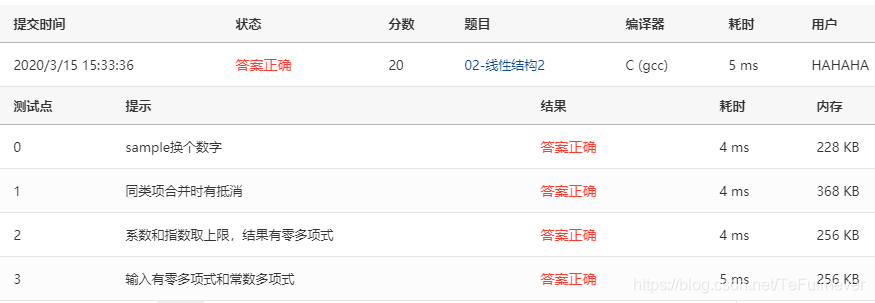
3、02-线性结构3 Reversing Linked List (25分)
Sample Input:
00100 6 4
00000 4 99999
00100 1 12309
68237 6 -1
33218 3 00000
99999 5 68237
12309 2 33218
Sample Output:
00000 4 33218
33218 3 12309
12309 2 00100
00100 1 99999
99999 5 68237
68237 6 -1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MaxSize 100005
int main(){
int Data[MaxSize];
int Next[MaxSize];
int List[MaxSize];
int FirstAdd,N,K;
scanf("%d %d %d",&FirstAdd,&N,&K);
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<N;i++){
int tAdd,tData,tNext;
scanf("%d %d %d",&tAdd,&tData,&tNext);
Data[tAdd]=tData;
Next[tAdd]=tNext;
}
int sum=0;
while(FirstAdd!=-1){
List[sum++]=FirstAdd;
FirstAdd=Next[FirstAdd];
}
for(i=0;i<sum-sum%K;i+=K){
for(j=0;j<K/2;j++){
int t=List[i+j];
List[i+j]=List[i+K-j-1];
List[i+K-j-1]=t;
}
}
for(i=0;i<sum-1;i++){
printf("%05d %d %05d\n",List[i],Data[List[i]],List[i+1]);
}
printf("%05d %d -1\n",List[i],Data[List[sum-1]]);
return 0;
}

4、02-线性结构3 Reversing Linked List (25分)

Sample Input:
5 7 5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
3 2 1 7 5 6 4
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
5 6 4 3 7 2 1
1 7 6 5 4 3 2
Sample Output:
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct SNode *Stack;
struct SNode{
int data[1010];
int top;
};
void push(Stack ptrl,int a);
void pop(Stack ptrl);
int main(){
Stack ptrl;
ptrl=(Stack)malloc(sizeof(struct SNode));
// ptrl->top=-1;
int m,n,k,i,j;
scanf("%d %d %d",&m,&n,&k);
int b[1010];
while(k--){
ptrl->top=-1;
j=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&b[i]);
}
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
push(ptrl,i);
if(ptrl->top >= m){
break;
}
while(ptrl->top!=-1&&ptrl->data[ptrl->top]==b[j]){
j++;
pop(ptrl);
}
}
if (ptrl->top == -1) {
printf("YES\n");
}
else {
printf("NO\n");
}
}
}
void push(Stack ptrl,int a){
ptrl->data[++(ptrl->top)]=a;
}
void pop(Stack ptrl){
ptrl->top--;
}
总结
简单总结下这周的学习内容,正式开始接触了数据结构与算法,线性表,堆栈,队列等等,感觉自己真的是太菜,好多题都不会,只能参考别人的,,,还是得手撕代码!!!都背一背!!!
