指针
指针的基本概念
指针的作用: 可以通过指针间接访问内存
-
内存编号是从0开始记录的,一般用十六进制数字表示
-
可以利用指针变量保存地址
指针变量的定义和使用
指针变量定义语法: 数据类型 * 变量名;
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//1、指针的定义
int a = 10; //定义整型变量a
//指针定义语法: 数据类型 * 变量名 ;
int * p;
//指针变量赋值
p = &a; //指针指向变量a的地址
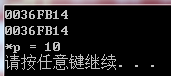
cout << &a << endl; //打印数据a的地址
cout << p << endl; //打印指针变量p
//2、指针的使用
//通过*操作指针变量指向的内存
cout << "*p = " << *p << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
指针变量和普通变量的区别
-
普通变量存放的是数据,指针变量存放的是地址
-
指针变量可以通过" * "操作符,操作指针变量指向的内存空间,这个过程称为解引用

指针所占内存空间
提问:指针也是种数据类型,那么这种数据类型占用多少内存空间?
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 10;
int * p;
p = &a; //指针指向数据a的地址
cout << *p << endl; //* 解引用
cout << sizeof(p) << endl;
cout << sizeof(char *) << endl;
cout << sizeof(float *) << endl;
cout << sizeof(double *) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
![]()
空指针和野指针
空指针:指针变量指向内存中编号为0的空间
用途:初始化指针变量
注意:空指针指向的内存是不可以访问的

野指针:指针变量指向非法的内存空间

![]()
const修饰指针
const修饰指针有三种情况
-
const修饰指针 --- 常量指针
-
const修饰常量 --- 指针常量
-
const即修饰指针,又修饰常量
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
//const修饰的是指针,指针指向可以改,指针指向的值不可以更改
const int * p1 = &a;
p1 = &b; //正确
//*p1 = 100; 报错
//const修饰的是常量,指针指向不可以改,指针指向的值可以更改
int * const p2 = &a;
//p2 = &b; //错误
*p2 = 100; //正确
//const既修饰指针又修饰常量
const int * const p3 = &a;
//p3 = &b; //错误
//*p3 = 100; //错误
system("pause");
return 0;
}![]()
指针和数组
作用:利用指针访问数组中元素
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
int * p = arr; //指向数组的指针
cout << "第一个元素: " << arr[0] << endl;
cout << "指针访问第一个元素: " << *p << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
//利用指针遍历数组
cout << *p << " ";
p++;
}
cout<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
指针和函数
作用:利用指针作函数参数,可以修改实参的值
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//值传递
void swap1(int a ,int b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
//地址传递
void swap2(int * p1, int *p2)
{
int temp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = temp;
}
int main() {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
swap1(a, b); // 值传递不会改变实参
swap2(&a, &b); //地址传递会改变实参
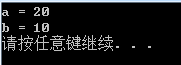
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
指针、数组、函数
案例描述:封装一个函数,利用冒泡排序,实现对整型数组的升序排序
例如数组:int arr[10] = { 4,3,6,9,1,2,10,8,7,5 };
int * arr 也可以写为 int arr[]
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//冒泡排序函数
void bubbleSort(int * arr, int len) //int * arr 也可以写为int arr[]
{
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++)
{
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
{
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
//打印数组函数
void printArray(int arr[], int len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main() {
int arr[10] = { 4,3,6,9,1,2,10,8,7,5 };
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int);
bubbleSort(arr, len);
printArray(arr, len);
system("pause");
return 0;
}![]()
![]()
